Runway busted stealing 100,000+ YouTube videos for AI training
Artificial intelligence-powered tools and applications are certainly impressive in what they can generate, but where these AI companies get the data to train these impressive models remains ambiguous or completely closed off from public knowledge.
A new report revealed only last week that Apple, NVIDIA, Anthropic, and others used a public dataset containing hundreds of thousands of YouTube video transcripts to train their AI models. While Apple, NVIDIA, and others weren't the ones to download the transcripts, the data was still used to train AI models, which strictly violates YouTube's Terms of Service (ToS). Earlier in the year, YouTube's CEO stated that any data downloaded from its platform is a violation of its ToS.
Now, a new report from 404 Media states that the popular AI video generator company Runway trained its Gen-3 Alpha model on thousands of YouTube videos without obtaining permission from the creator or YouTube. The report also states the company used pirated content for AI model training. 404 Media was sent a spreadsheet that lists how many videos were taken from a specific source, and judging from the list, the sources are extensive and cover a large variety of channels.
Continue reading: Runway busted stealing 100,000+ YouTube videos for AI training (full post)
AMD Ryzen 9000 reviews, here's when you can read all about the new Ryzen 9 9950X and Zen 5 CPUs
Yesterday, we learned that AMD was delaying the launch of its new Zen 5-powered Ryzen 9000 Series CPUs from July to August due to an unspecified quality issue with the initial production run. "Out of an abundance of caution and to maintain the highest quality experiences for every Ryzen user, we are working with our channel partners to replace the initial production units with fresh units," AMD said.
With that, we've got new release and launch dates for the Ryzen 9000 Series, with the launch now spread out over two weeks. The Ryzen 7 9700X and Ryzen 5 9600X will launch on August 8. The flagship Ryzen 9 9950X and Ryzen 9 9900X will follow on August 15.
In the lead-up to the new Ryzen CPU generation launch, we've seen several leaked benchmark results, alongside the Ryzen 9 9950X pushed to 6.6 GHz with LN2 cooling - the anticipation is real. And now, thanks to Hardware Unboxed, we know when we can expect official reviews to appear online.
Global Windows outage estimated to cost Earth multiple billions
A week ago, CrowdStrike rolled out an update that caused approximately 8.5 million Windows machines worldwide to enter infinite boot loops.
The global IT outage has been described as the largest in history and is being directly compared to the historic Y2K scare. The CrowdStrike outage was a result of a faulty kernel driver update being rolled out CrowdStrike's Falcon Sensor security software, and, unfortunately, the faulty update caused a kernel-level malfunction that required physical intervention for remediation.
The outage affected numerous industries around the globe, such as airlines, supermarkets, telecommunications systems, point-of-sale systems, emergency services, and various other businesses. Now, we are starting to hear the first estimations of the amount of money lost due to Windows machines being down, with cloud monitoring and insurance company Parametrix estimating a fourth of the Fortune 500 companies were affected by the outage.
Continue reading: Global Windows outage estimated to cost Earth multiple billions (full post)
NVIDIA has a new GeForce RTX 3050, and it's built on Ada Lovelace
Yes, there is another. According to sources, NVIDIA isn't entirely done with the GeForce RTX 30 Series, and the company plans to release a new version of the GeForce RTX 3050 Laptop GPU. What makes this interesting is that this will be an Ampere 8nm generation GPU built with current-gen Ada Lovelace architecture and advanced node technology.
There is a GeForce RTX 4050 in the laptop space (we've yet to see one for the desktop graphics card market), so there's a valid reason for NVIDIA to revamp the GeForce RTX 3050 Laptop GPU with Ada tech - as it would lead to a more efficient and compact GPU.
The news of this new GeForce RTX 3050 arrives via The PC ID Repository, which lists a new entry in the form of the AD106M[GeForce RTX 3050 A Laptop GPU]. Per NVIDIA's GPU naming, AD refers to Ada Lovelace architecture. The existing GeForce RTX 3050 uses the Ampere-based GA107 chip.
Continue reading: NVIDIA has a new GeForce RTX 3050, and it's built on Ada Lovelace (full post)
Half-Life: Alyx on PlayStation VR2 arrives August 6 via the PS VR2 App on Steam
Although sales for Sony's next-gen PlayStation VR2 headset for PlayStation 5 haven't set the virtual world on fire, and reports indicating that Sony is pulling the plug on VR game development, there is some good news.
Yes, you'll be able to play Valve's killer VR app Half-Life: Alyx on PlayStation VR2, thanks to the arrival of full PC support and the PS VR2 App. Although Sony hasn't formally announced the launch, the Steam page for the PS VR2 App is now live with a release date of August 6 listed. We've also got screenshots of the PS VR2 App's interface, which looks similar to how it's set up on the PS5.
The listing states, "Play VR games and apps on Steam using your PlayStation VR2 headset and PlayStation VR2 Sense controllers." This confirms that the motion controllers will work (via Bluetooth) and that the headset will be integrated into SteamVR. However, there is one catch.
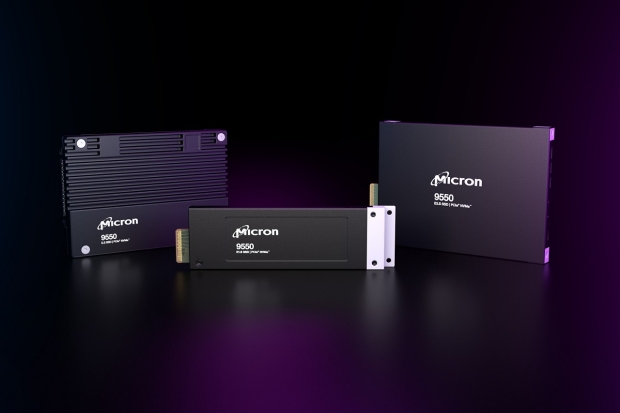
Micron intros 9550 Gen5 SSD: the world's fastest data center SSD, 14GB/sec for AI workloads
Micron has just announced its new Micron 9550 PCIe Gen5 SSD which is the world's fastest data center SSD and industry leader in AI workload performance and power efficiency.
The company has combined its in-house Gen5 SSD controller, NAND, DRAM and firmware into "one world-class product" with the new Micron 9550 Gen5 SSD. This new integrated solution provides class-leading performance, power efficiency, and security features for data center operators.
Micron's new 9550 SSD offers 14GB/sec sequential reads and 10GB/sec sequential writes, which the company says provides up to 67% better performance over similar competitive SSDs, and enables industry-leading performance for demanding workloads like AI.
Bethesda's Skyrim is now available on GeForce NOW, making sure you can play it on anything
Another place to play Bethesda's The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim? Skyrim has made its way to another platform with The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim (and the Special Edition of the game), now playable on NVIDIA's cloud gaming GeForce NOW service. It joins the PC, Xbox 360, PlayStation 3, Xbox One, PlayStation 4, Xbox Series X|S, PlayStation 5, Nintendo Switch, and Alexa as the latest digital location where you can fire up the iconic RPG.
NVIDIA notes that GeForce NOW Ultimate members can stream and experience Skyrim at up to 4K and 120 frames per second, running on a GeForce RTX 4080-powered rig in the cloud. For those looking toward cloud gaming who haven't signed up for GeForce NOW, you can save 50% off Ultimate and Priority subscriptions as part of the GeForce NOW Summer Sale.
Seven more games, including a few notable new releases, have been added to GeForce NOW this week, including The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim. Interestingly, GeForce NOW subscribers can stream Skyrim via Steam and Xbox (PC Game Pass).
AMD Zen 5 HX 'Fire Range' APUs use FL1 package, RTX 50 GPU laptops with Ryzen chips coming
AMD's next-generation Zen 5-based "HX" laptop "Fire Range" CPUs will arrive on the same FL1 package, meaning that laptop makers won't have to redesign motherboards from current "Dragon Range" systems.
We first learned about AMD's new Zen 5-based "Fire Range" CPU in leaks from Moore's Law is Dead back in October 2023. But In a new post by hardware reviewer and leaker "Golden Pig Upgrade" we're hearing that next-gen Ryzen HX mobile processors based on the Zen 5 architecture codenamed "Fire Range" will use the same FP1 socket as the Zen 4-based "Dragon Range" CPUs we have now. This includes up to the flagship Ryzen 9 7945HX3D processor with the Zen 4 architecture and X3D V-Cache technology.
AMD using the same FL1 package with its new Fire Range processors as its Dragon Range processors is a great thing for laptop manufacturers, as they won't need to redesign the motherboard. However, CPU competitor Intel is changing things up from its 14th Gen Core CPUs and its new Core Ultra 200 CPUs which forces laptop manufacturers to redesign their laptop motherboards.
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5090 rumor: 48% faster than RTX 4090, TITAN AI is 63% faster than RTX 4090
NVIDIA's next-generation GeForce RTX 50 series "Blackwell" gaming GPUs are not too far away now, with the flagship GeForce RTX 5090 being reportedly up to 48% faster than the current-gen gaming GPU champ, the RTX 4090.
We knew that NVIDIA would be shooting high with performance with the new GeForce RTX 5090, with its new process node, upgraded Blackwell architecture, next-gen GDDR7 memory, when compared to the RTX 4090. NVIDIA would've been fine launching the RTX 4080 on its own at the time, which kept up and beat AMD's flagship RDNA 3-based Radeon RX 7900 XTX.
But they didn't, NVIDIA instead unleashed the beefier GeForce RTX 4090 with more VRAM (24GB versus 16GB) and even more gaming performance. The same goes with the RTX 5090, which is reportedly a monstrous 48% faster than the RTX 4090 according to 'RTX 50 performance targets' from NVIDIA in leaks by RedTechGaming.
NVIDIA AI Foundry helps companies train and develop custom AI 'supermodels'
NVIDIA AI Foundry is a new enterprise service where NVIDIA will help companies build AI 'Supermodels' - custom Llama 3.1 generative AI models built with NVIDIA software and expertise. These AI 'Supermodels' are custom-trained for specific industry use cases using proprietary and synthetic data from Llama 3.1 405B and the NVIDIA Nemotron Reward model.
Hardware-wise, it's powered by the NVIDIA DGX Cloud AI platform, which allows it to access the most advanced AI hardware, architecture, and technologies. It's an NVIDIA AI Foundry, so that's to be expected. Meta's open-source Llama 3.1 405B model was announced earlier this week, offering capabilities and power previously limited to closed-source models. This new partnership between NVIDIA and Meta is a big deal for companies everywhere.
"Meta's openly available Llama 3.1 models mark a pivotal moment for the adoption of generative AI within the world's enterprises," said Jensen Huang, founder and CEO of NVIDIA.