Astronomers have used a telescope in Chile to capture an incredible image that showcases a debris trail caused by NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART).

A team of astronomers used the Southern Astrophysical Research (SOAR) Telescope in Chile to observe the asteroid Dimorphos and the impact debris caused by the DART spacecraft, which collided with the asteroid's surface at the end of September. From millions of miles away, astronomers were able to observe a debris trail partly caused by DART, which is stretching 6,000 miles and is expected to continue growing.
According to researchers, NASA's kamikazeing spacecraft caused the initial debris, and pressure from solar radiation is causing it to accelerate away from the asteroid, resulting in the long debris trail seen above. As previously mentioned, astronomers expect the trail to continue stretching and disperse even more, eventually becoming so thin that it won't be detectable as the dust will be like any other dust floating around the solar system.
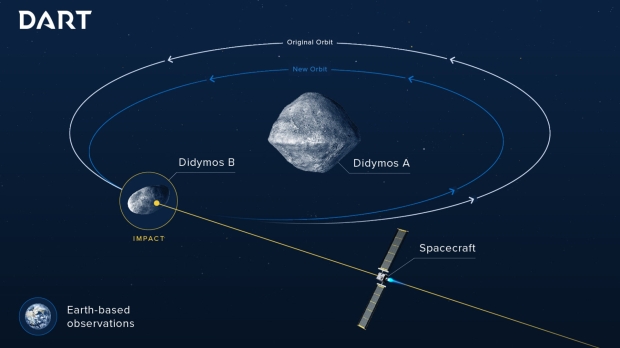
For those that don't know, NASA deliberately collided the DART spacecraft into the 525-foot-wide asteroid Dimorphos to conduct the very first planetary defense test where a high-speed spacecraft collision attempts to modify the orbit of an asteroid. The technique, called a kinetic impact, will be used in the future if proven effective in deflecting asteroids that pose a threat to Earth.
In addition to capturing a spectacular photograph of the asteroid debris trail, these recent observations of the aftermath of the collision will be used by researchers to gain more knowledge about the surface of Dimorphos, how much material was ejected by the collision, the speed the material was ejected and the distribution of particle sizes throughout the expanding debris plume. An example of this gained knowledge would be if DART's collision caused large chunks of debris to be launched from the surface or very fine dust-like particles.
In other DART news, astronomers were shocked to see that DART's impact caused the asteroid Dimorphos to brighten significantly. Additionally, NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, along with the famous Hubble Space Telescope, have observed DART's impact and snapped unique observations of their own. Lastly, NASA's Webb has caught a cosmic spider.



