
The Bottom Line
Introduction, Specifications, and Pricing
The 883 DCT is Samsung's flagship enterprise SATA SSD sold through the channel. The series ships in five capacities ranging from 240GB to a massive 3.84TB and targets moderate workloads that require higher performance consistency for critical data applications.

Despite the rise in popularity of NVMe, SATA SSDs are still the workhorse of the industry. Samsung's advanced V-NAND technology allows the 883 DCT SATA SSDs to deliver high quality of service (QoS). The series providers higher endurance (0.8 DWPD) than the 860 DCT (0.2 DWPD).
Specifications
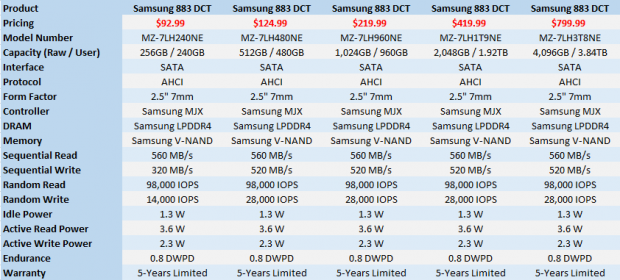
The Samsung 883 DCT ships in five capacities but the performance is similar for all but one model. The series shares the same 560 MB/s sequential write rating for all capacities. The 240GB model rates at 320 MB/s sequential write while the others increase the rating to 520 MB/s. Random read performance is 98,000 IOPS across the board. Random write performance reaches as high as 14,000 IOPS for the 240GB and 28,000 IOPS for the four larger capacities. The ratings come from steady-state performance and not fresh out of box numbers like consumer-focused SSDs.
Pricing, Warranty, and Endurance
We found the entire 883 DCT series on Amazon as well as other popular online outlets. The pricing is attractive for a critical application SSD with host-power failure protection. The series starts at just $92.99 on Amazon for the 240GB 883 DCT.
Samsung backs this series with a 5-year warranty that includes a 0.8 drive write per day endurance rating.
Accessories and Software
The 883 DCT works with Samsung's enterprise version of Magician called Data Center Magician SSD management utility. The software works for both Windows and Linux.
A Closer Look




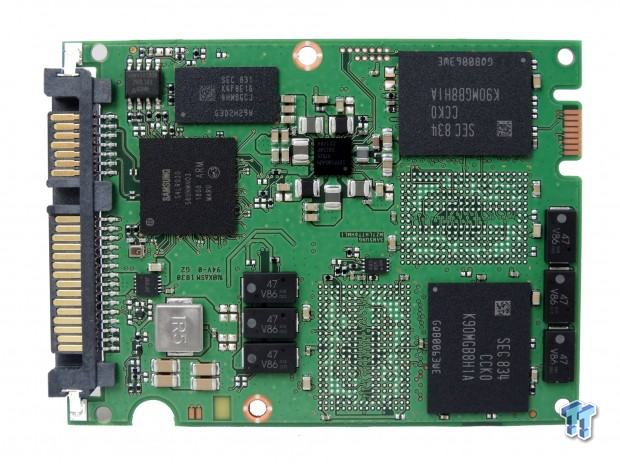
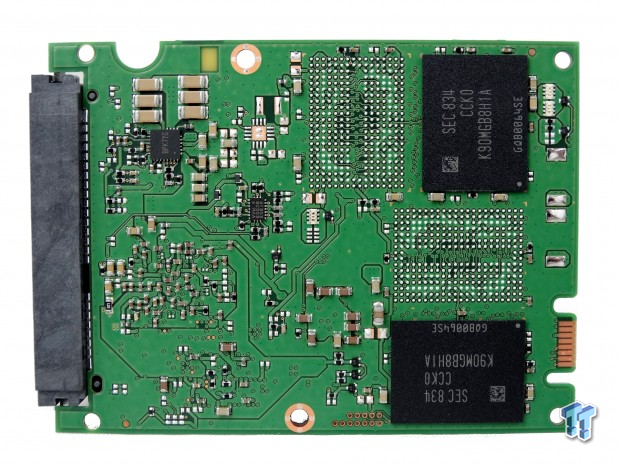
The Samsung 883 DCT uses a standard 2.5" 7mm design that allows companies to fit more drives in servers compared to the older 9.5mm z-height design.
We rarely take enterprise SSDs apart since so many use thermal transfer epoxy. We were forced to split the 883 DCT case to find if this series uses capacitors to host power failure protection. The drive does, and that separates it from the Samsung 860 DCT and the 860 consumer products like the 860 EVO and 860 Pro.

Synthetic Performance Testing
Product Comparison
We brought all three 883 DCT capacities to this review. Joining the 883 DCT models, we included a Samsung PM863a and Seagate Nytro 1351, both in 3.84GB capacities.
Sequential Read Performance
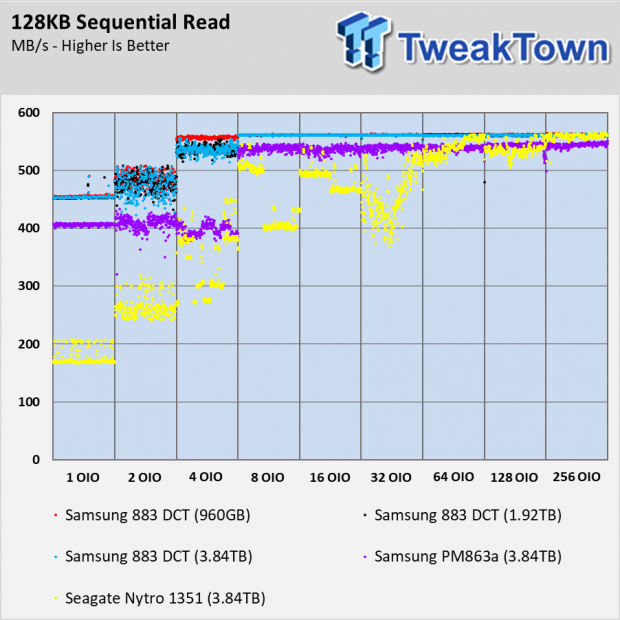
Through most of the review, you will find all three Samsung 883 DCT drives perform nearly identical. There are a few places where the 3.84TB performs slightly better due to more overprovisioned area, and the 1.92TB is in the middle with the advantage coming in more write-intensive workloads.
Sequential Write Performance
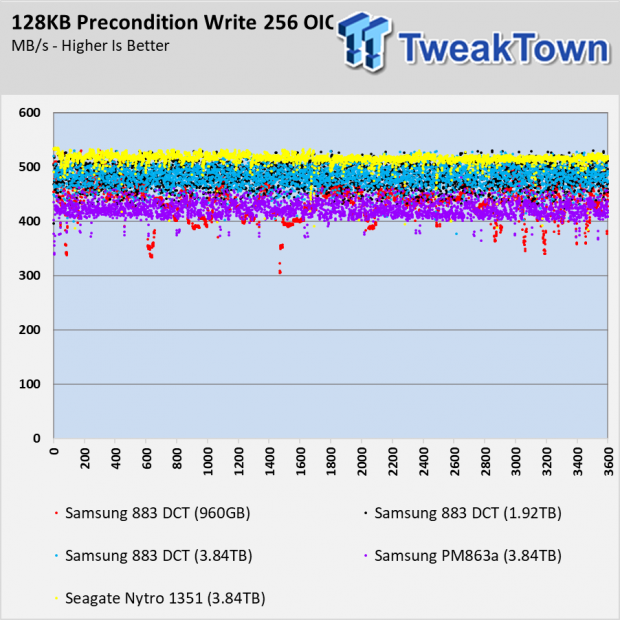
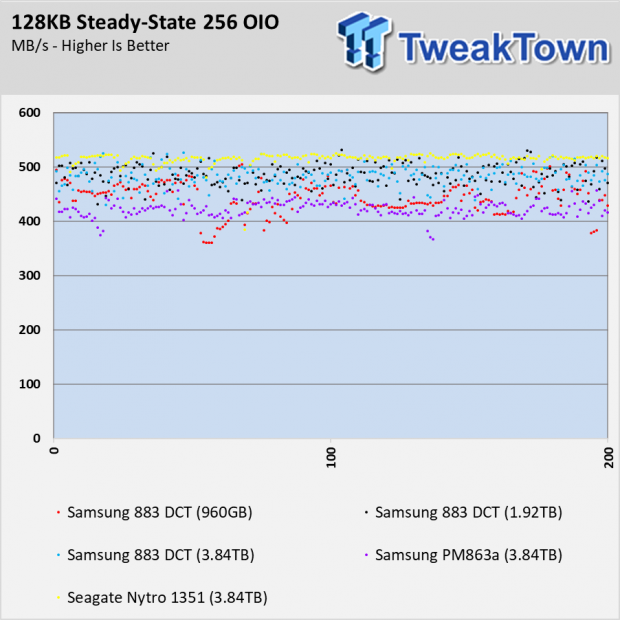
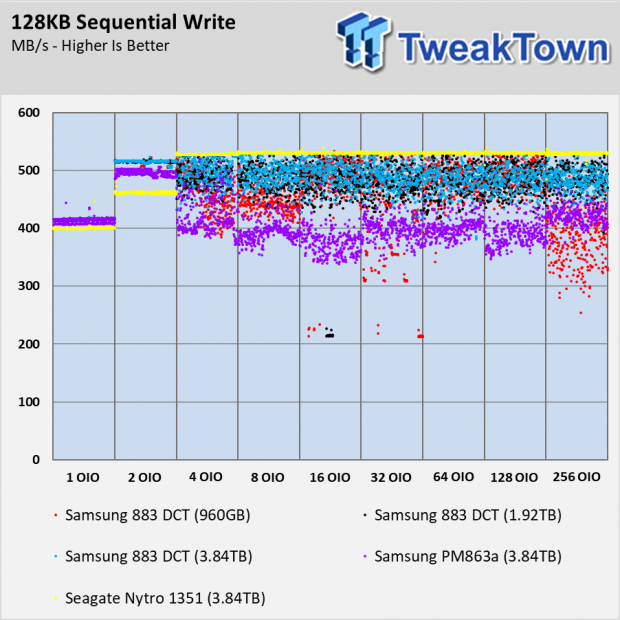
After testing a number of enterprise SSDs over the previous months, we've noticed the SATA models generally show less performance consistency compared to those using NVMe. The Seagate Nytro 1315 in the 128KB Sequential Write chart with the OIO scaling shows consistent performance. The IO dots converge to form a line.
The Samsung 883 DCT drives, as well as the older PM863a, show more variation in the IO in this write test.
Sequential Mixed Workload Performance
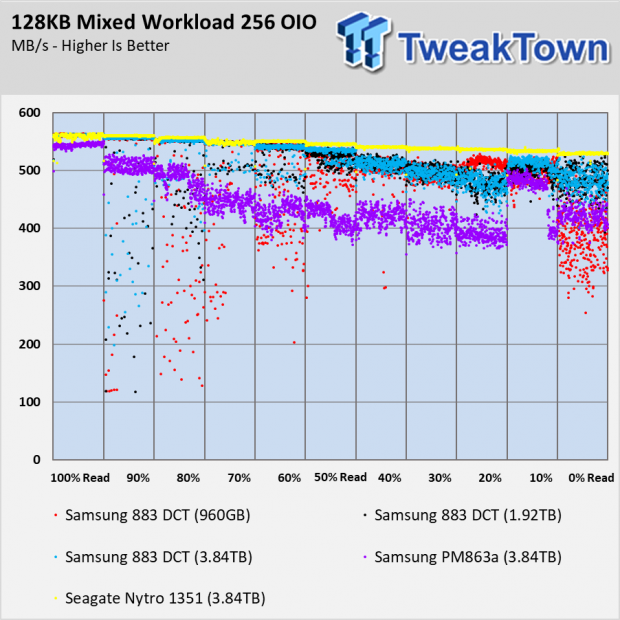
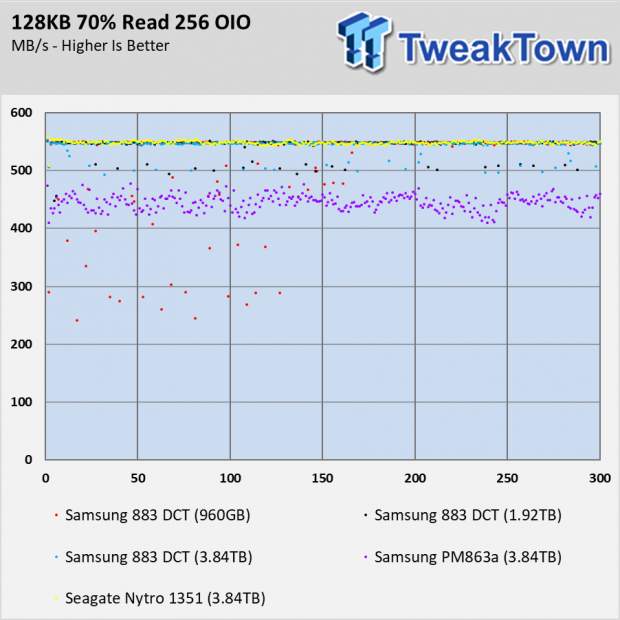
The mixed workload results show the deviation with the 883 DCT drives at 90% and 80% reads. The drives clean much of that up by 70% reads. You will also notice there isn't a heavy bathtub curve with any of the drives tested today. With consumer SATA SSDs, we usually see a deep performance dip in the middle of the chart with progressive increases to the edges.
Random Read Performance
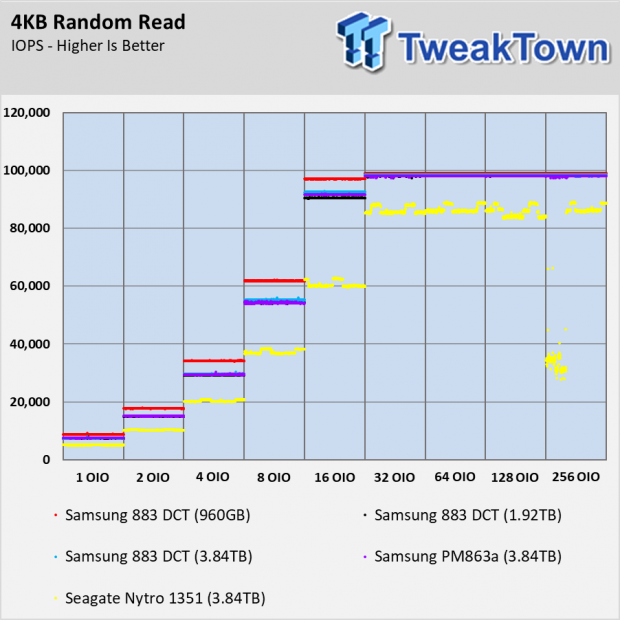

The 960GB 883 DCT shows slightly better random read performance over the other two 883 DCT capacities. The three drives all level off around 100,000 IOPS, but at lower queue depths, the 960GB shows superior performance.
In an upcoming article, we will show the performance of several SATA and NVMe SSDs as read cache in a new enterprise NAS system. The 883 DCT performs remarkably well in this role thanks to its high random read performance.
Random Write Performance
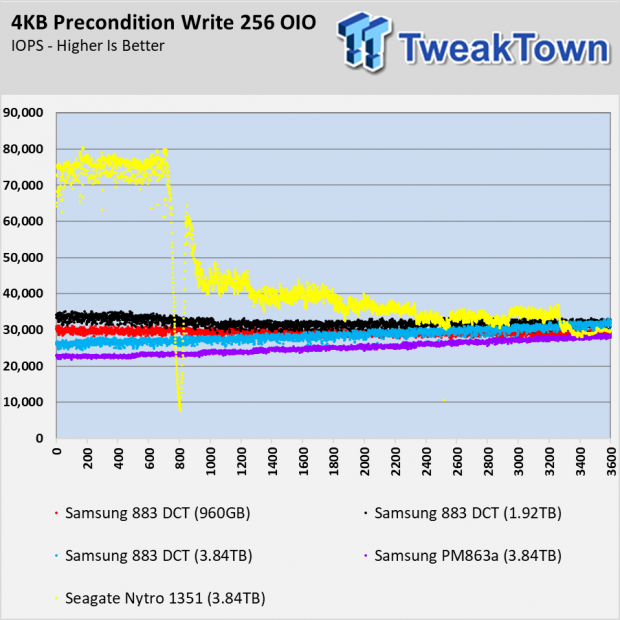
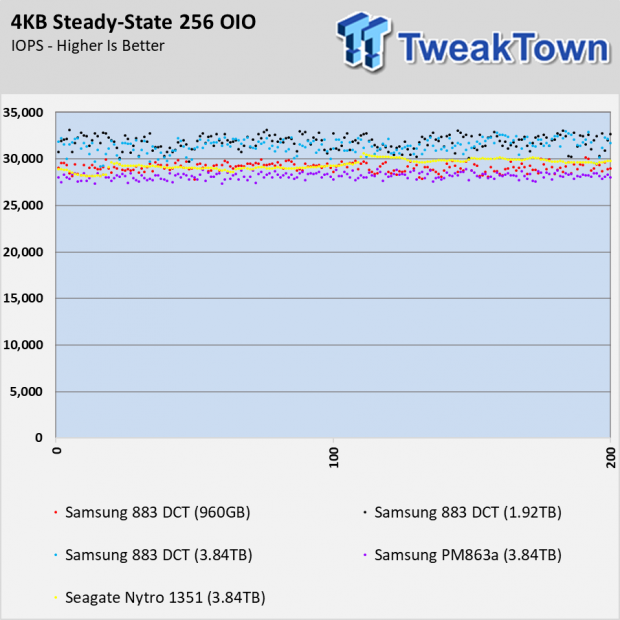
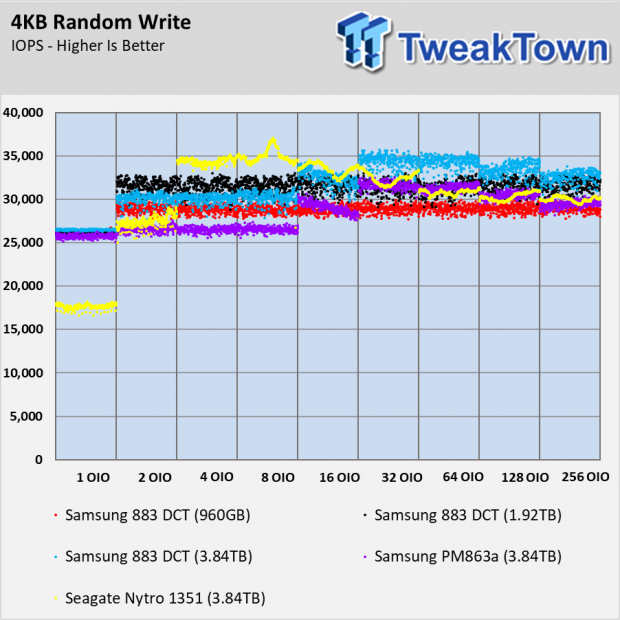
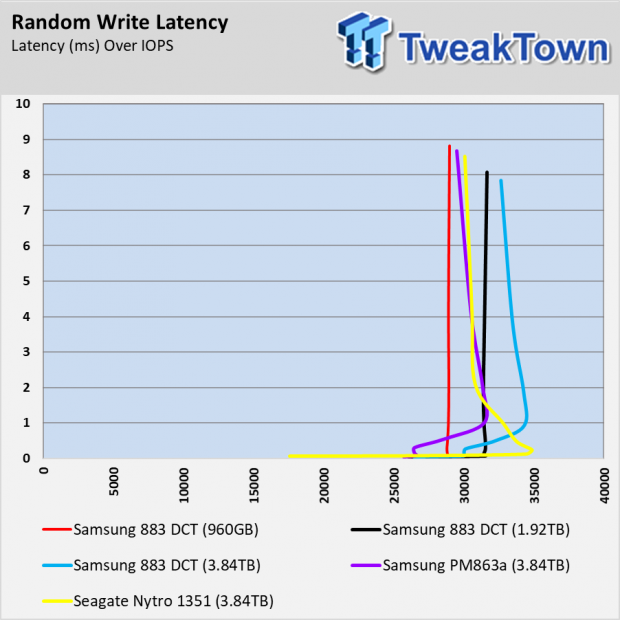
The 883 DCT series doesn't use an SLC cache like consumer models like the 860 EVO and 860 QVO. The Seagate Nytro 1351 does use a SLC buffer, and you can see how the cache runs out of steam in the preconditioning chart. What you don't see is the amount of processing power that goes into managing the SLC in an environment that doesn't take advantage of the feature.
Random Mixed Workload Performance
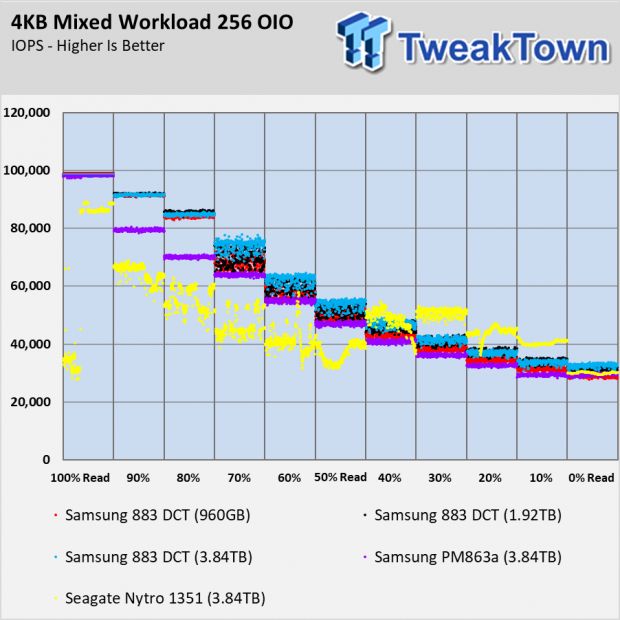
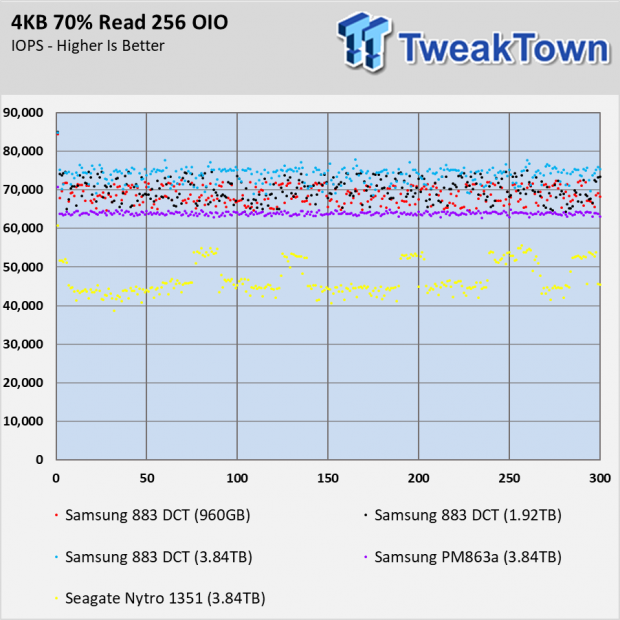
The more the Samsung 883 DCT SSDs get away from a 100% read or write load, the more inconsistent the performance. This is very common with all SSDs as the mix increases the latency. NVMe SSDs generally have a tighter performance cluster since the interface is bidirectional, unlike SATA.
The important takeaway from these two charts is the improvement from the older PM863a. You can see the largest gains in the 90% and 80% read workload.
Workload Performance Testing
Database Workload
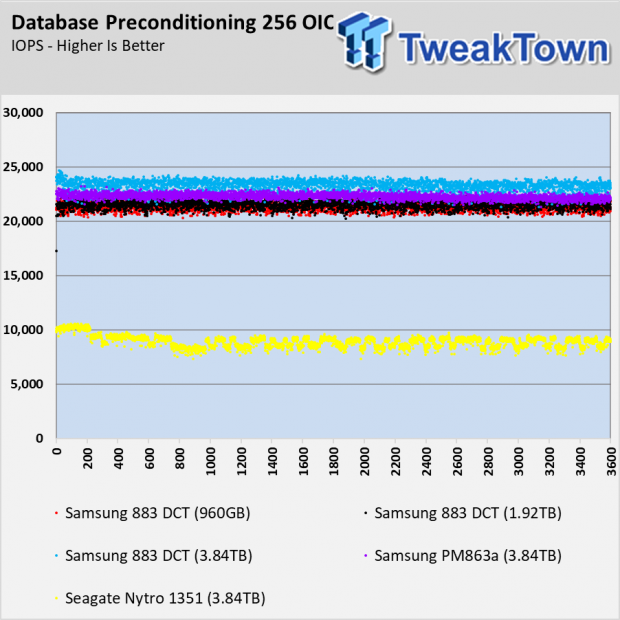
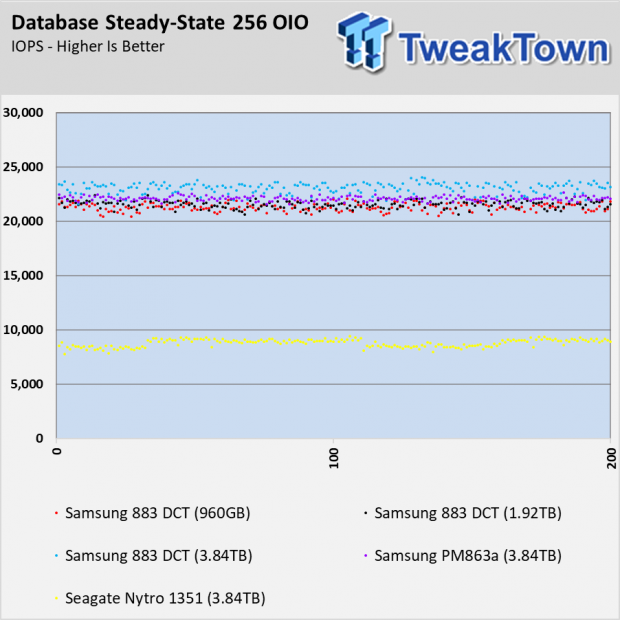
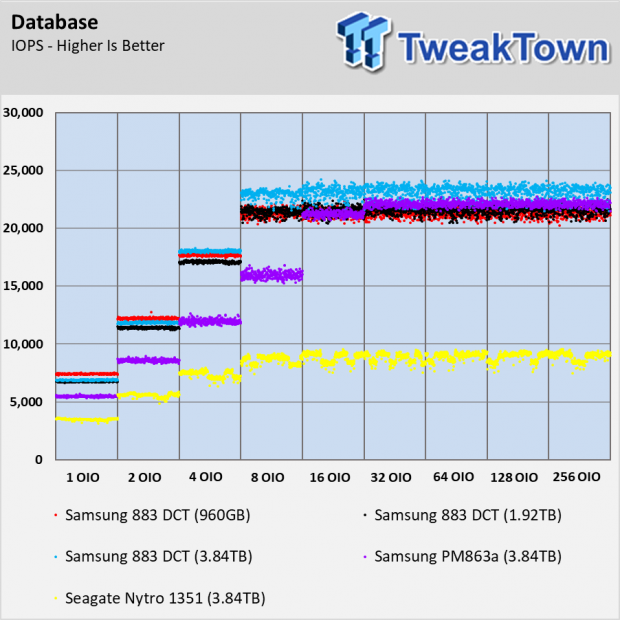
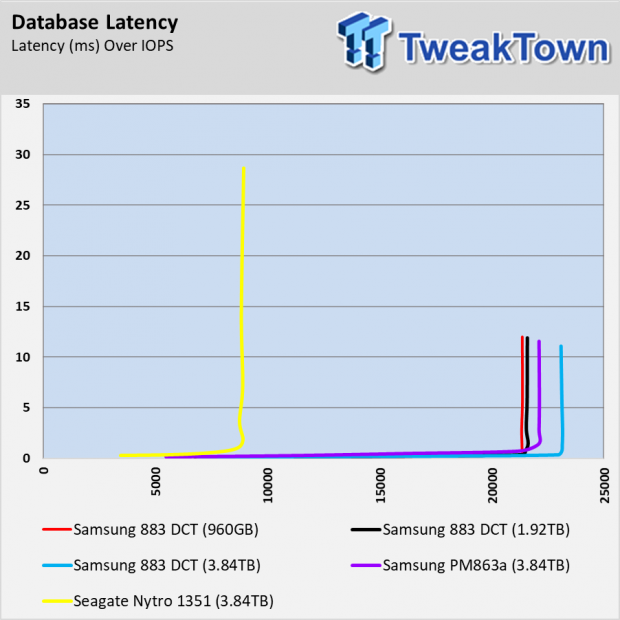
As we mentioned, there are some workloads where the extra overprovisioning allows the 3.84TB 883 DCT to outperform the other capacities in the series. The database test is one example where the performance stair steps with the capacity.
OLTP Workload
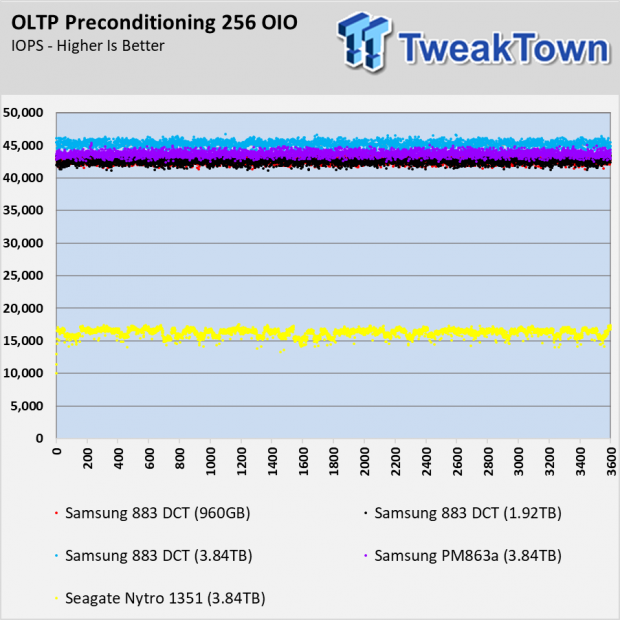
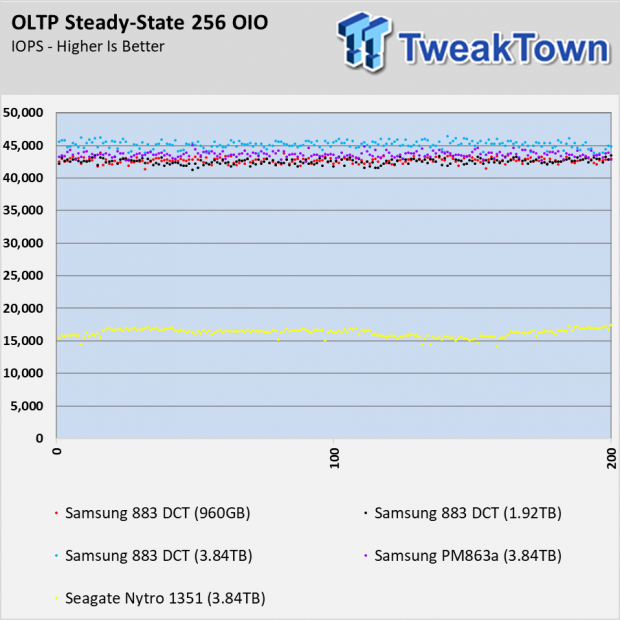
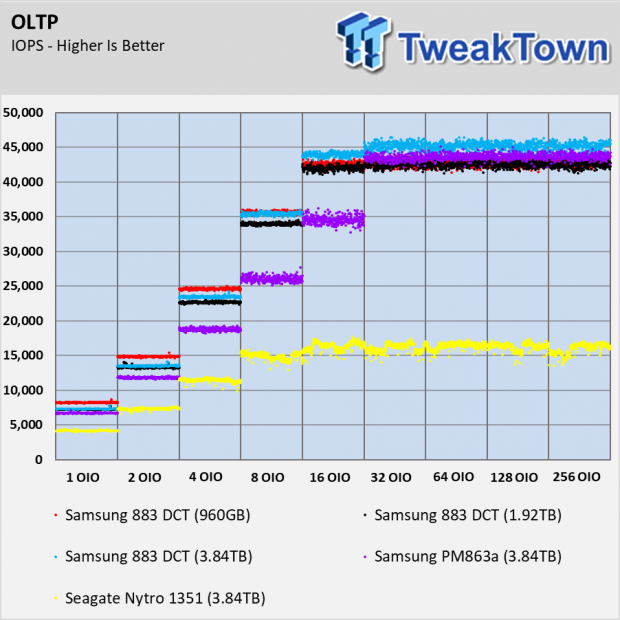
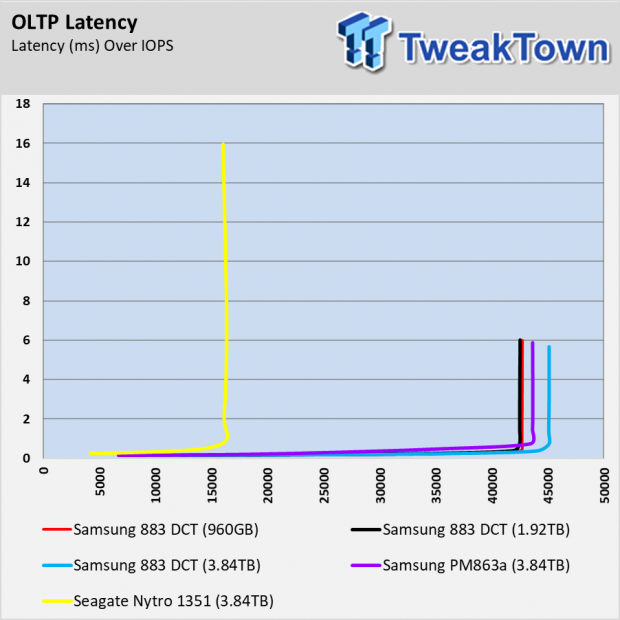
The OLTP workload is similar to the database workload. The blocks double in size and that allows the performance to double with most SSDs. The 883 DCT SATA SSDs perform very well in this test. At higher OIO, the 883 DCT drives nearly triple the performance of the Seagate Nytro 1351.
Email Workload
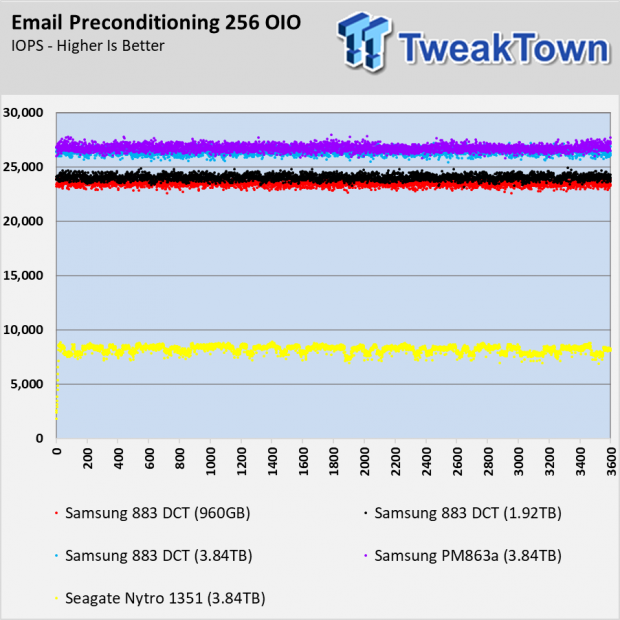
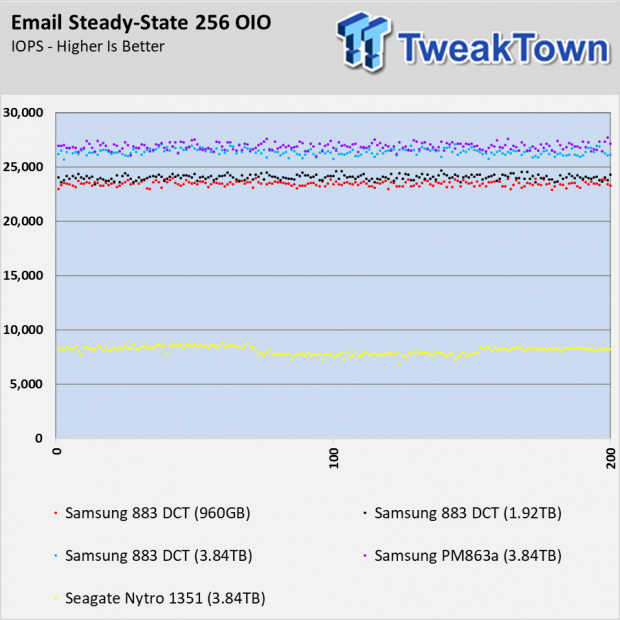
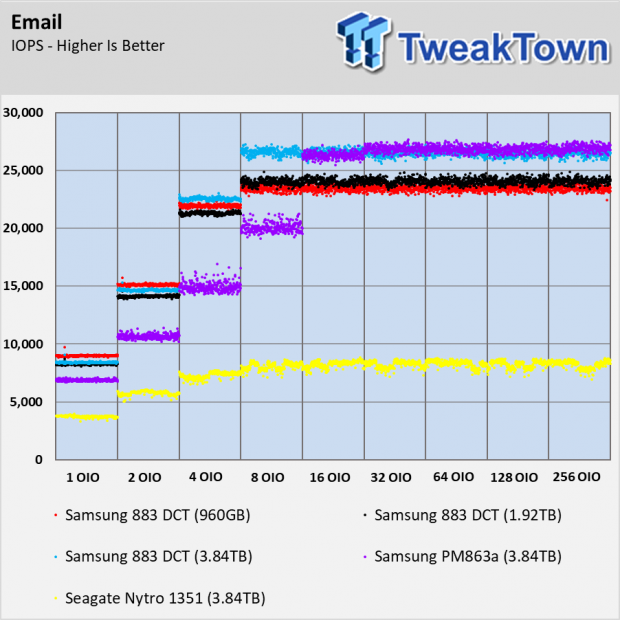
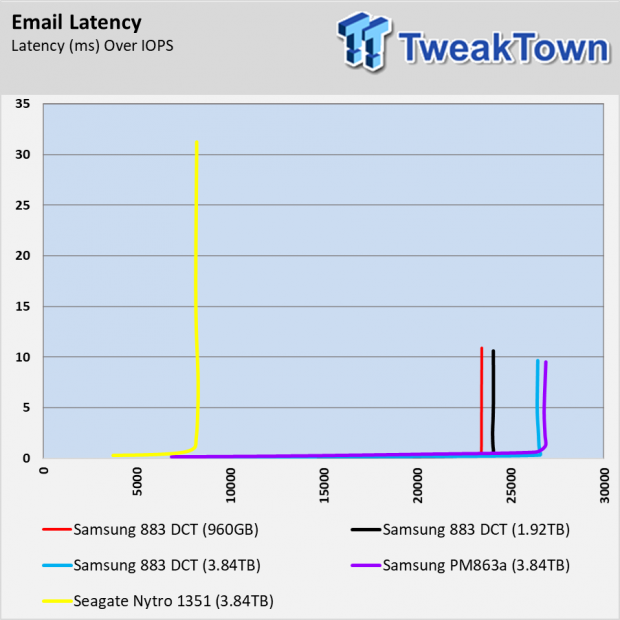
The email workload test shows a familiar story that seems to repeat in this review. The Samsung 883 DCT SSDs perform flawlessly with fairly predictable cadence between the capacities. The largest size, 3.84TB, has a slight edge over the others and all three sizes outperform the Nytro 1351 by a sizable margin.
Archive Workload
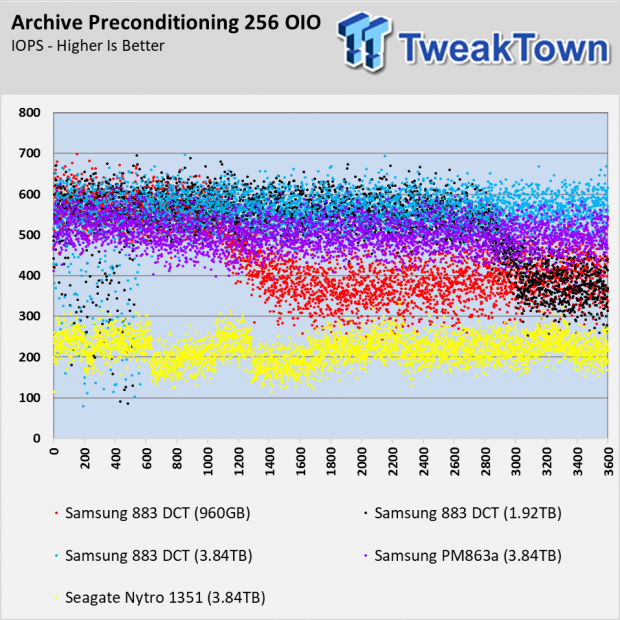

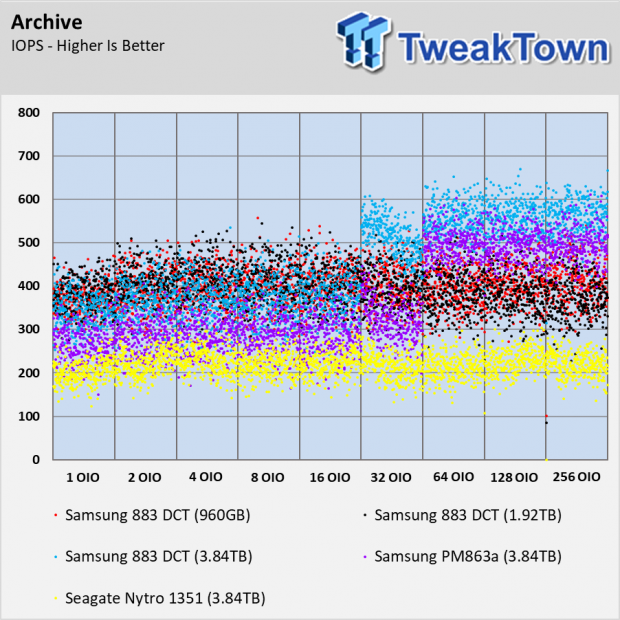
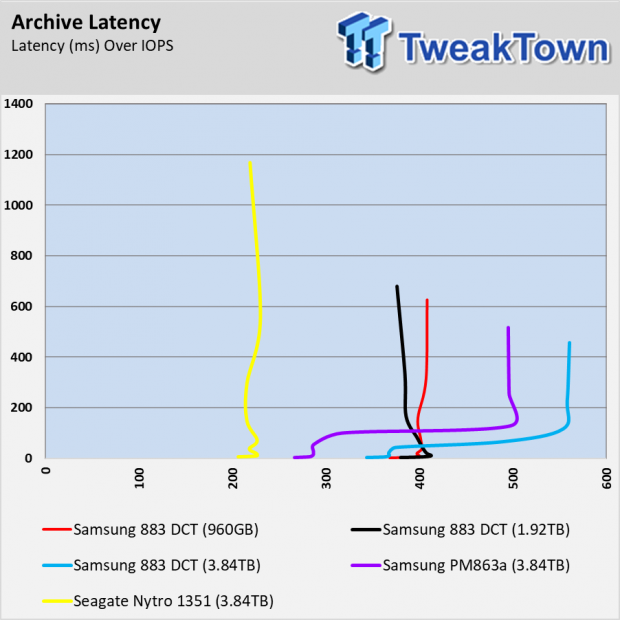
The archive test doesn't have the providence like the other tests. It wasn't embedded in the older Iometer suite but it does have credibility. The test comes from Dell's performance lab and is one of my favorite tests because it mixes reads and writes, block sizes, and sequential with random data. This test shows us what it's like to run multiple workloads on the same drive or a general file server role.
None of the drives delivers consistent performance here, and it's not just the products in this test. Even the Intel Optane SSDs and Samsung 983 ZET (Z-NAND) SSDs have a difficult time taming this workload.
Final Thoughts
Of the data center SATA SSDs we've tested, the Samsung 883 DCT delivers the highest performance thus far. The series will appear in a number of future reviews where we use the drives in application NAS systems for read and write cache. The low price and wide availability opens this series to a number of users, not just the targeted data center racks.

The Samsung 883 DCT series bridges the gap between the 860 DCT and the 983 DCT NVMe series. The 883 DCT includes features not found on the 860 DCT, like host power-loss protection, higher QoS, and more endurance. The series also features Class 0 AES 256 encryption and end-to-end data protection. These are also features found on the 983 DCT NVMe series.
In our testing, we observed higher performance with the 883 DCT compared to the older Samsung PM863a and Seagate Nytro 1351, all in 3.84TB capacity. At high queue depths, the older Samsung PM863a delivered equal performance in our synthetic workloads. At lower queue depths and in our applications tests, the 883 DCT walked away from the PM863a when comparing equal capacities. The 883 DCT also smashed the peak performance of the Seagate Nytro 1351. The Seagate often delivered better performance consistency, but at the cost of peak performance under heavy workloads.
Performance |
97% |
Quality |
95% |
Features |
95% |
Value |
92% |
Overall |
95% |
The Samsung 883 DCT series provides the highest performance possible to date over a SATA interface. The series includes features not found on entry-level data center SSDs but doesn't break the budget.

Similar Content
Related Tags
