
The Bottom Line
Introduction and Packaging

Today we will be looking at the Lenovo ThinkServer RD640, which is a larger capacity server compared to the Lenovo ThinkServer RD340, which we reviewed recently.
The feature list of the ThinkServer RD640 also follows the same basic concepts the RD340 brings to the table. The RD640 comes equipped with large storage capacity with up to 32TB on internal storage in a 2U server. All drives can be configured as hot swap SAS, SATA hard drives, or SSDs.
Optimized for virtualization workloads, the RD640 is perfect for databases, analytics, and other business applications. The RD640 can have two processors with up to 24 cores total, and large memory bandwidth. The RD640 also has plenty of I/O upgrade options, making it a true workhorse for business critical applications.
If you require more storage, there are options that allow up to 16x 2.5" drive bays that are also hot-swappable. Additional storage adapter options include the LSI ThinkServer RAID 710 adapter with 1GB write back cache, and LSI MegaRAID CacheCade Pro 2.0 and Fastpath for additional IOPs performance.
The server itself features tool-less rail kits, and Lenovo Smart Grid power management technology that uses Intel Node Manager, so it is easy to scale up power management in the data center. These features give the administrator the ability to manage up to 1,000 server nodes.
For virtualization workloads, the RD640 is vSphere-optimized and network equipped. Complete virtualization management uses VMware vSphere Operations Manager, LenovoEMC storage technology, and is vSphere 5 Certified. The management tool suite with the latest plug-ins from VMware allows virtual machine setup, and optimized VM performance. Let's start unboxing the Lenovo ThinkServer RD640, and then we will run the server through our tests.
Packaging

The shipping box is standard for Lenovo server products. The foam inserts provide ample protection for the contents inside. There are about five to six inches of foam and air space between the outer box and the server contents. This does well to protect the server from drops, punctures, and mishandling by mail couriers.

Here we have the accessory boxes laid out, and the rail kit. The two boxes come neatly packed in the shipping box, and are easy to remove before taking the server out.

The accessory box has two power cords, a software and manual disk, plus installation instructions.

Upon opening the rail kit box, we get a chance to see the contents.

The kit comes with everything you need to install the rails, including two sliding rails, two mounting screw packages, and instructions for how to install the rails.
PRICING: You can find the ThinkServer RD640 70AY0006UX 2U Rack Server for sale below. The prices listed are valid at the time of writing but can change at any time. Click the link to see the very latest pricing for the best deal.
United States: The ThinkServer RD640 70AY0006UX 2U Rack Server retails for $1199.99 at Amazon.
Specifications, Layout, and Installation
Specifications
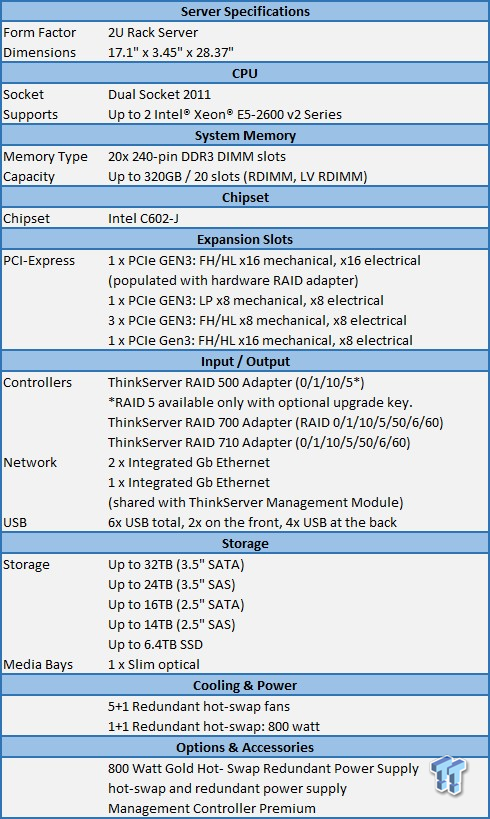
The RD340 has a wide range of storage options, and plenty of LAN ports for connectivity. Optional Raid adapters can greatly increase storage performance. The RD340 can also use an impressive 192GB of RAM.
Layout

The front of the RD640 is dominated by eight storage bays that can give up to 32TB of storage. These bays can be configured as either hot-swap SAS, SATA hard drives, or even solid state drives.
The right of the server has one slim optical drive. On the left side of the server there are two USB ports, a com port, status LEDs, and power button.

Looking at the back of the server, we can see the I/O layout. The power supply on the left slides out by unlocking the red lever and pulling the power supply outward.
To the right of the power supply we see the green serial port, and the LAN/Remote management port. Next, there is another LAN port, and the VGA output, followed by four USB ports and the last LAN port. Above these ports are two knockouts that can be removed to allow for expansion cards. Expansion slots allow for up to five additional PCIe expansion cards to be mounted inside the server.
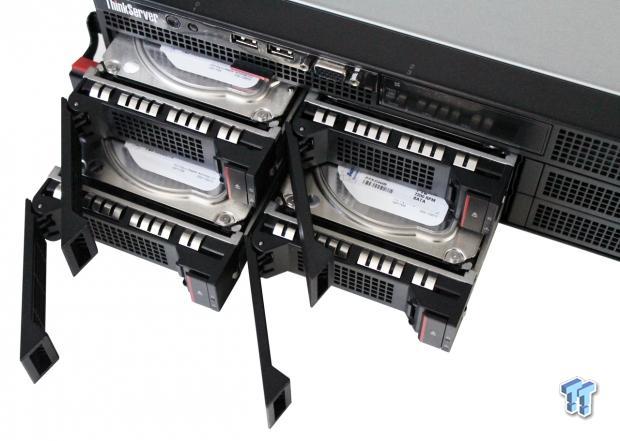

The RD640 we received had four 1TB drives installed. Each of the drives can be removed by pressing the button on the right side of the drive. Pressing the button releases the locking arm, and once the arm releases, the drives pull out easily.

To remove the top of the server, there is a simple latch that pops open and allows you to slide the server lid right off. We prefer this method of accessing the insides of the server over other methods like having to remove screws on the sides to take the lid off. When the server is installed in a rack, it is very easy to access the inside.

After taking the lid of the server off, we get our first look at the air shroud that directs airflow from the fan banks and across the CPU heat sinks.
The square holes allow for some air to pass through and provide cooling for expansion cards. To remove the air shroud, simply lift up on the support ribs and set aside. It will lock in place when reinstalled later.
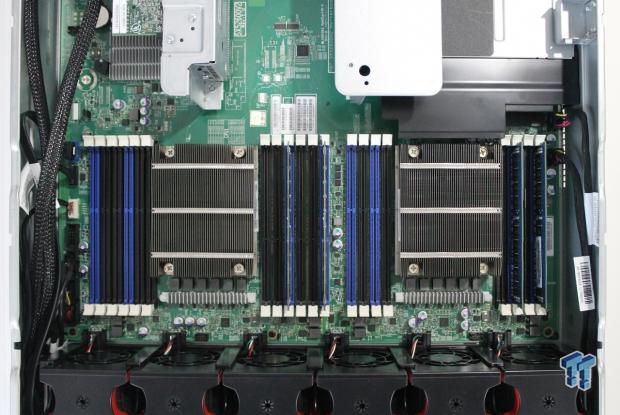
After removing the air shroud, we see the CPU heat sinks and RAM slots. It is rather simple to add more RAM if needed; nothing is in the way of the RAM slots, so simply pull back the white locking retainers, and insert the RAM sticks.

At the back of the server, we find expansion bays for PCIe cards. These come with PCIe riser cards, and mounting frames to install expansion cards. There are five expansion bays available in the RD640; two are on the left bay, two are in the middle bay, and one is on the far right side, above the PSU.
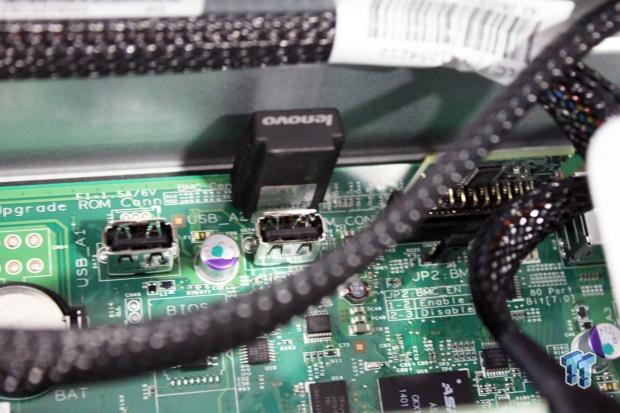

Looking from the back of the server on the left side, we see the TPM module to the right, and behind the first USB port is where the Lenovo Management Controller Premium is located.

The Lenovo Management Controller Premium is an optional accessory, which appears to be a simple dongle type of device. This unlocks KVM abilities through IPMI remote management. If you do not use this module, you will still have IPMI, but you will not be able to remote in by KVM.

The server that we have uses only one power supply. The power supply simply unlocks and slides out for replacement, if ever needed.
If needed, an optional redundant power supply can be ordered.
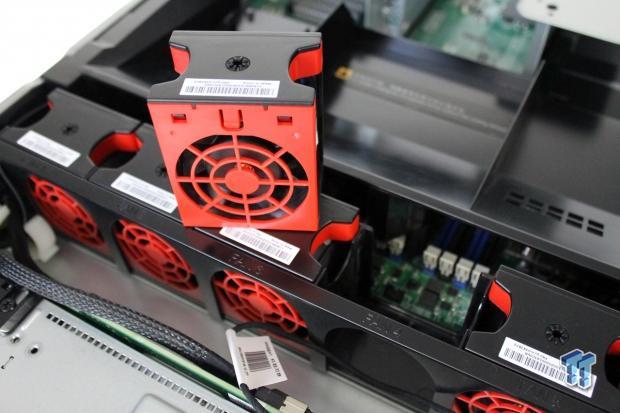

The fans on the cooling bar are simple to replace. Simply pull up on the tab, and lift the fan out.
These fans are designed to move large amounts of air, and do not make a lot of noise. Even when running at 100% speed, the RD640 is not loud, and can be run in an office enviroment.
Installation
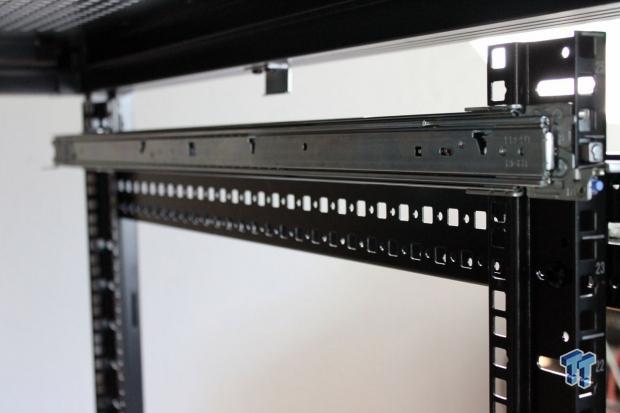

Position the back of the rail into the slots where you want the server to go. There is a locking lever, and a blue release button at the bottom.
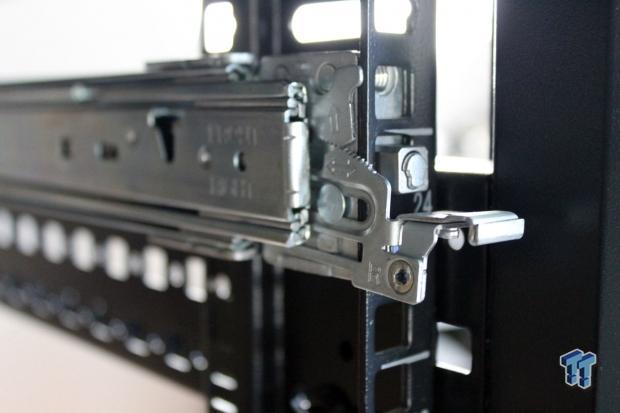

On the front end, push down on the rail lock lever and insert it into the rack, then lift the lever to lock it in place. At the top of each rail, there is a mounting screw hole. After you get the front and back of the rail locked in place, screw in a retaining screw to finish installing the rails.
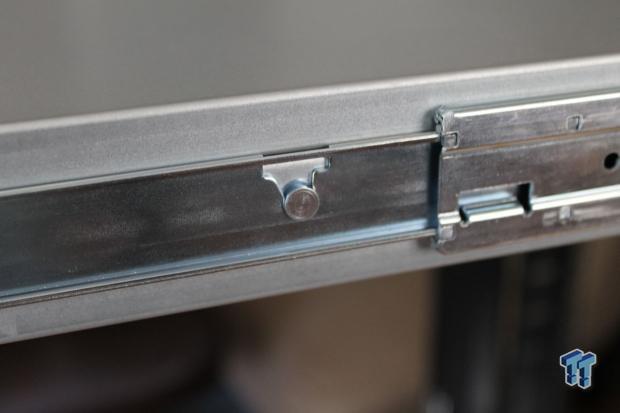

Each rail has three grooves that line up with guides on the sides of the server. Lift the server in place so the guides line up with all three grooves, and lower it into place.

The very front of the rail has a lock that snaps into place when installing the server. To remove the server, slide the lock to the front. You can now lift the server up, and out off the rails. The RD640 weighs in at ~35.3 pounds, which is not a lot, but we do advise using two people to assist installing the server, or removing one.
The complete racking process took us a little while to figure out, but overall, the process was rather simple.
BIOS, Software, and Remote Management
BIOS
The BIOS for this server is typical, so we will only show key BIOS screens.
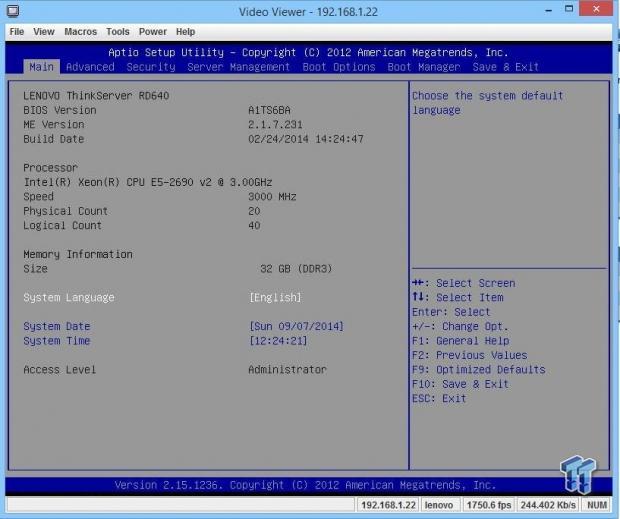
This is the main BIOS screen you see when you first enter the BIOS.
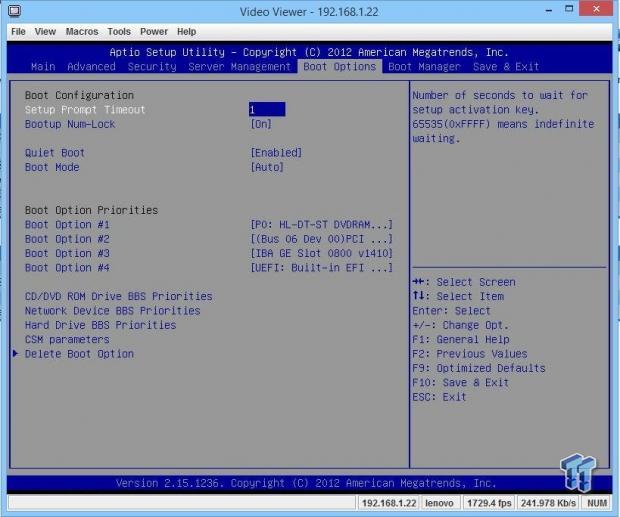
This is the Boot Options menu. This allows you to set which devices you want to boot from, and the boot order priorities.
Moving along to the Advanced menu, we can see the adjustable settings.
This is the Advanced Processor Configuration tab. We set this server up so speed step and other power features are turned off; this will allow us to get maximum performance out of the server while we test.
In the Advanced Power Management tab, we turn off all power saving features for our tests.
Here we see adjustment in the memory configuration.
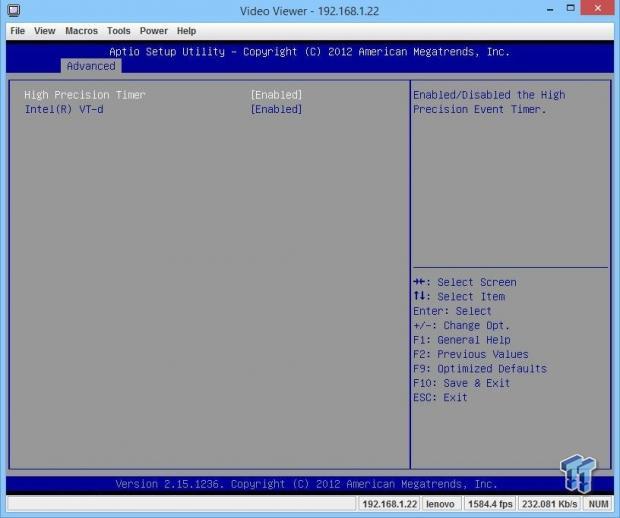
Here we can enable or disable the High Precision Timer and VT-d.
Software
The Lenovo RD640 ThinkServer comes with two disks. One disk has drivers and setup programs to aid you in setting up this machine.
Simply insert this DVD into the DVD drive, and boot the machine. It will take you to the ThinkServer EasyStartup program.
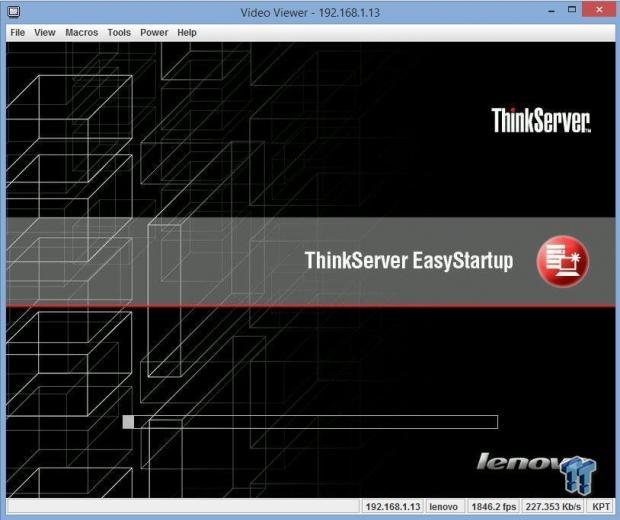
When booting from the software DVD, you will enter the ThinkServer EasyStartup program, which will guide you through the process of getting the machine up and running.
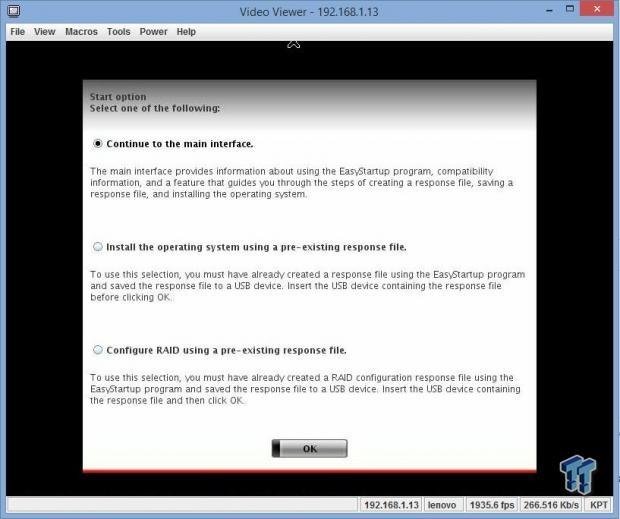
After this boots, you go through two other screens, agree to terms and conditions, enter the date and time, and then you will come to this screen. Much of this process is self-explanatory, so there is no need to show every screen that you will encounter - many screens are just confirming settings and hitting the next button.
Continue to the main interface if you are setting up a new server for the first time. After you work through that, you can create a response file on a USB drive that you can use for other servers. This includes raid drivers, OS type, and everything else you would need. You would then use this USB drive for any other new servers.
If you have one of these already made, then pick the second option. If you need the same setup, but wish to use a different type of RAID, then use the last option.
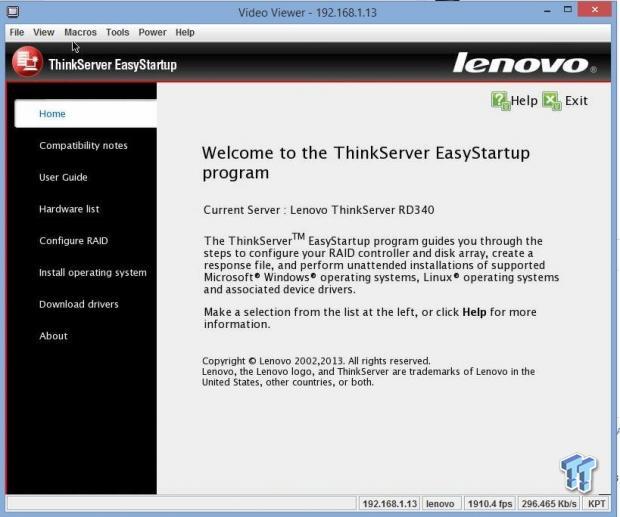
This is the home screen you will see after you select the first option from the step before this. On the left hand side you can see all the steps you will need to go through to complete this procedure.
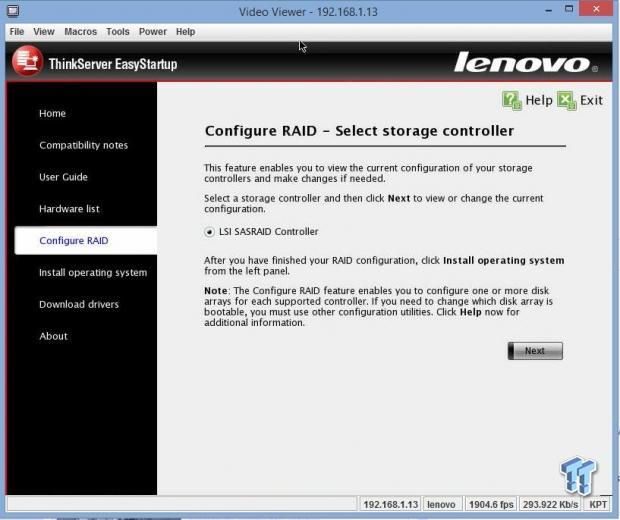
We skipped ahead a few steps to show you how the RAID is set up.
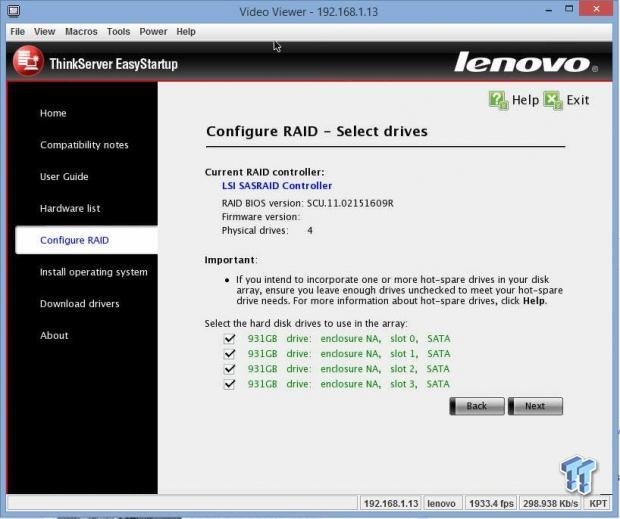
The ThinkServer R6340 that we received had four Western Digital 1TB hard drives installed. Here you can see how they show up in EasyStartup. We selected all four drives for our RAID.
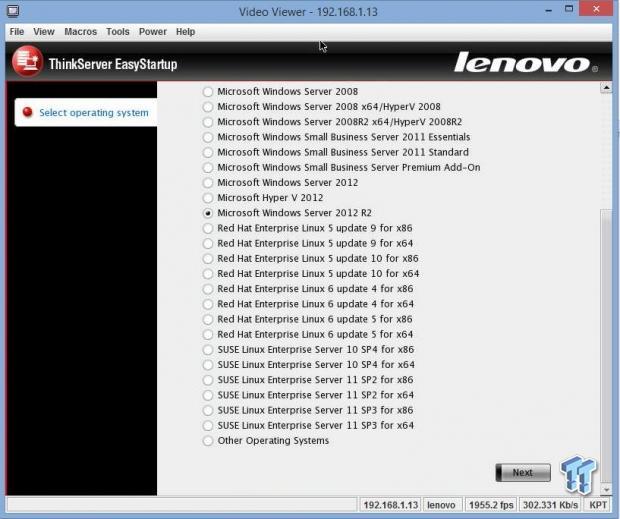
Here you can select the OS you want to install; we will be using Windows Server 2012 R2. After this step, you can proceed to enter your OS Key, admin user name, password, and a few other pieces of information. Afterward, you will have the option to write all of this to a response file on a USB stick to use on future installations.
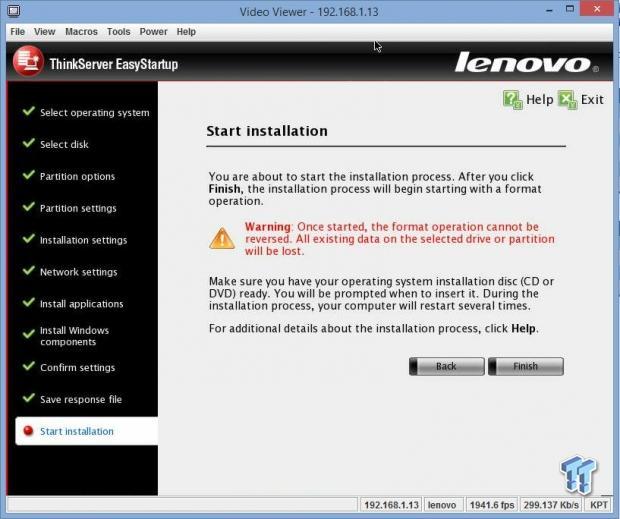
This is the last step in the EasyStartup process. Once you click finish, the install procedure will take over and get everything set up for you.
There are other ways to set up the RD640 if you wish to do it manually. The supplied software disk should have all the drivers that you would need, and that process is very much like setting up any other server you would run across.
The EasyStartup program makes this an easy process for anyone just starting out setting these up.
Remote Management
There are several ways to do remote management and IPMI on the RD340. Just like any server with IPMI, its simply enter in the IP address that you find in the BIOS under server management/BMC network configuration into your web browser. In our case, that was 192.168.1.13. After that, you see the login screen.
On the back of the RD340, there is a dedicated LAN port for BMC, and we connected to that for our tests.
The login information for the Lenovo ThinkServer RD640 is as follows:
Username: lenovo
Password: len0vO
Then hit ok. As a best practice, Administrative users should change factory default Username/Password logins before connecting any new server to their network.
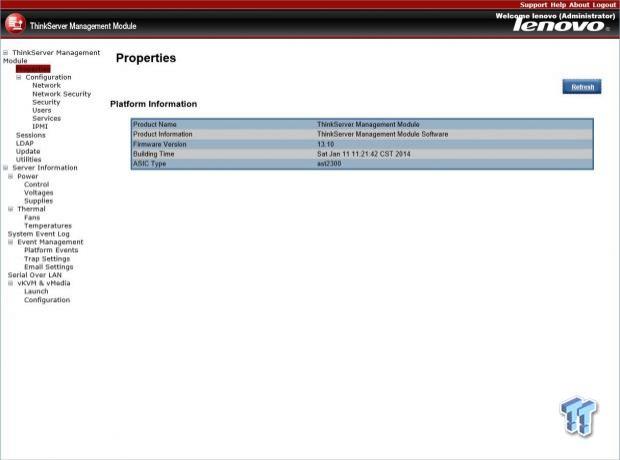
Here we are looking at the home screen for the ThinkServer management. The rest of the menus are typical for IPMI/BMC setups, so we will not show all of them.
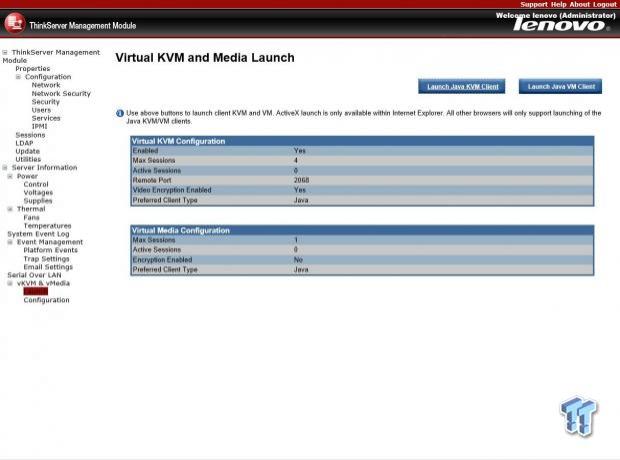
If you have the Management Controller Premium module installed, you will see the menu options for KVM. These will not show up if there is no module installed. Now hitting the launch java KVM client will allow you to remote right into the server.
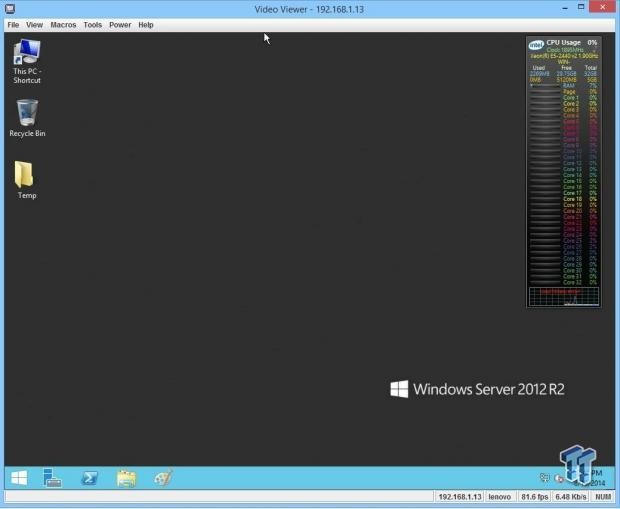
After entering the java KVM client, we can now control the machine from the BIOS level all the way to the desktop.
The next method to control the server is with a software package called Easymanage. Installed EasyManage on your host machine and use this to control many servers in your network. After installing EasyManage and then running it, enter login information.
Login: server
Password: manager
This is a typical screen for EasyManage. This program has many features that are useful in managing a number of different servers.
Test System Setup
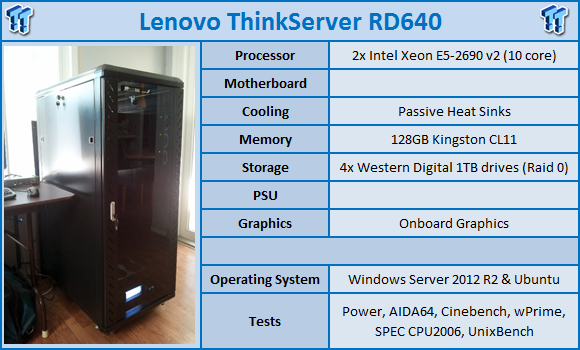
We would like to thank Lenovo, SPEC, Yokogawa, AIDA64, and Kingston for their support in providing parts for our test system.
For all tests that we have run, we used optimized BIOS settings for max performance.
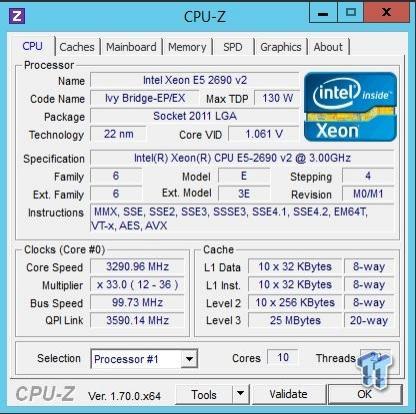
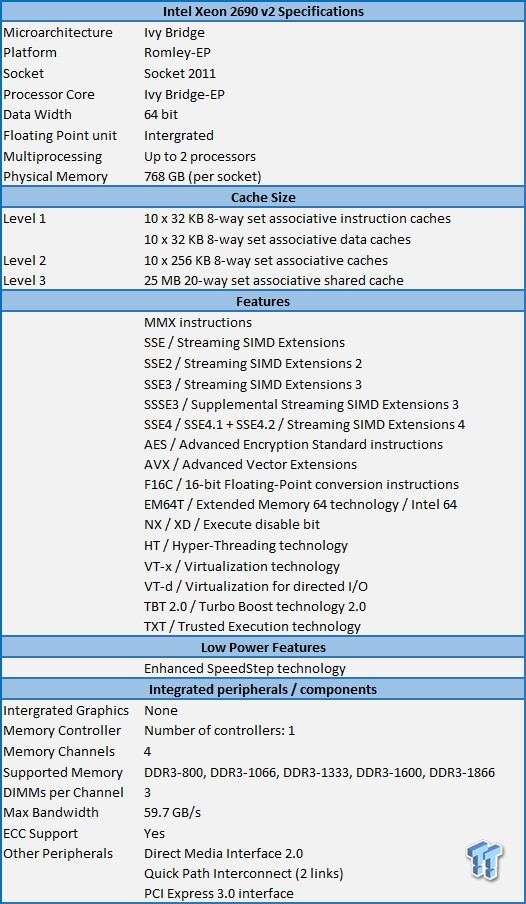
This is the CPUz screen, showing the various stats of the Xeon E5-2690 v2 CPUs. As you can see, this CPU has a Max TDP of 130 watts, and core voltage of 1.061V. Each CPU has ten cores, and we will be running a dual CPU system. This gives it 20 cores/40 threads total.
The E5-2690 v2 processors based on Ivy Bridge architecture released on Sept 14, 2013. The Xeon E5-2690 v2 CPUs are built on more optimized and energy efficient 22nm Ivy Bridge-EP microarchitecture, and feature up to 50% more cores, and up to 25% more cache at the same power envelope as previous generation of Xeon E5 products.
These processors incorporate a Digital Random Number Generator, new Float 16 instructions, and have higher memory bandwidth due to added support for DDR3-1866 memory. The E5-1600v2 and E5-2600v2 CPUs are backwards compatible with existing socket 2011 motherboards. Features of the E5-2690 v2 processor are as follows:
The memory we used in our tests is 128GB of Kingston KVR-16R11S4/8HA DDR3 1600MHz ValueRAM Server Memory.
The Lenovo ThinkServer RD640 can support memory with speeds up to 1866MHz ECC RDIMMs. Let's move forward with testing the Lenovo ThinkServer RD640. We will show test results from actual servers we have tested, and not just motherboards. Server load outs can effect scores vs motherboards that have far less options installed. We will also keep this on same socket setups, so we won't mix up processor classes.
System and CPU Benchmarks
CINEBENCH 11.5
CINEBENCH is a real-world cross platform test suite that evaluates your computer's performance capabilities. The test scenario uses all of your system's processing power to render a photorealistic 3D scene. This scene makes use of various different algorithms to stress all available processor cores. You can also run this test with a single-core mode to give a single-core rating.
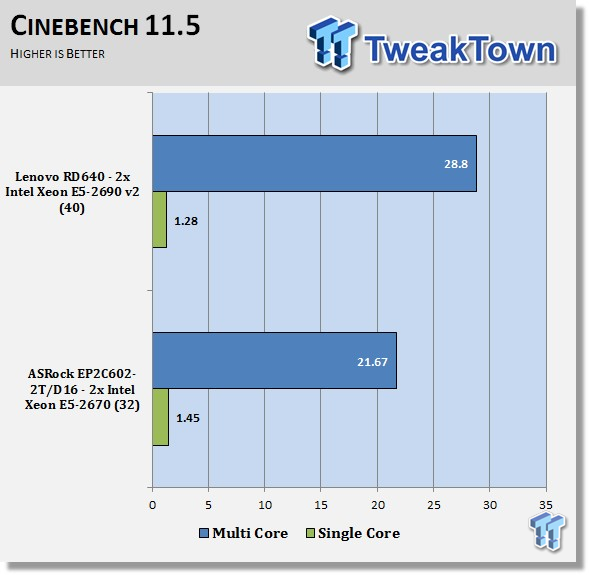
The E5-2690 v2 processors have a core advantage over the E5-2670's, so we expect to see better multi-threaded scores with these. We see an additional four to eight points increase in these scores for the RD640.
This is a simple test to run, and it gives an overall look at the processing power of the RD640. Most of the scores we have gotten on dual CPU systems are in the same range of numbers shown with the RD640 at the top end.
CINEBENCH R15
CINEBENCH R15 is a real-world, cross platform test suite that evaluates your computer's performance capabilities. CINEBENCH is based on MAXON's award-winning animation software CINEMA 4D, which is used extensively by studios and production houses worldwide for 3D content creation.
The test scenario uses all of your system's processing power to render a photorealistic 3D scene (from the viral "No Keyframes" animation by AixSponza). This scene makes use of various algorithms to stress all available processor cores.
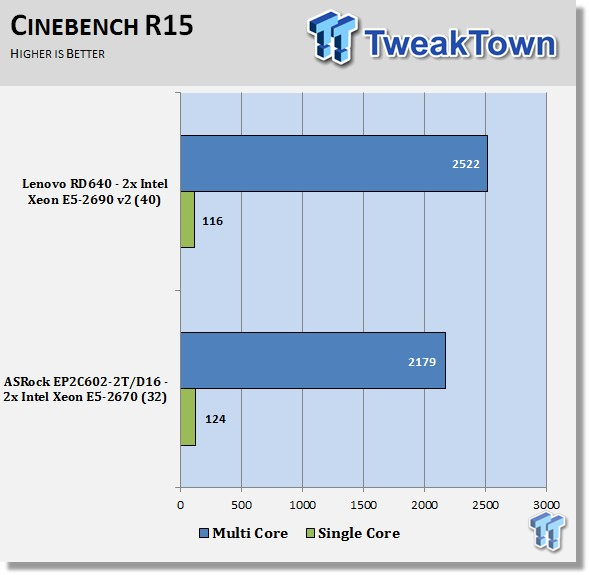
We like the multi-threaded scores on this server; it really shows a lot of power can be installed into a 2U server. In many of our tests shown here, a simple CPU upgrade will improve results. In our case, we had the Intel Xeon E5-2670 in the lab for the bulk of our testing, and results shown are for reference only.
wPrime
wPrime is a leading multi-threaded benchmark for x86 processors that tests your processor performance. This is a great test to use to rate the system speed; it also works as a stress test to see how well the system cooling is performing.
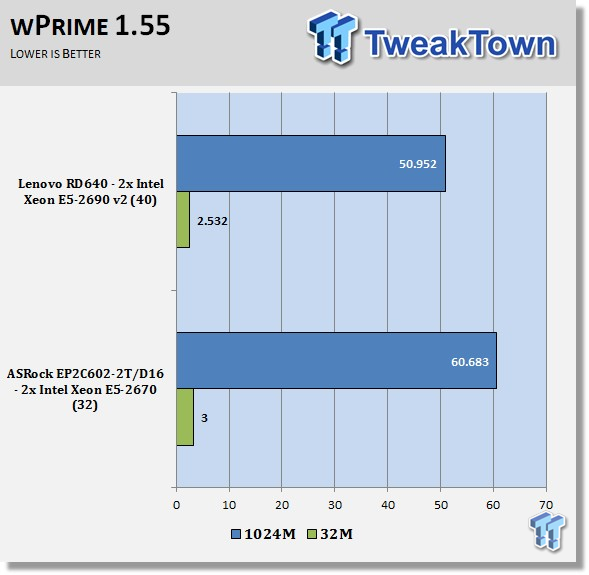
wPrime shows similar results to our CINEBENCH scores. The 2470 v2s do not have high clock speeds in order to keep heat down, but it still has a lot of potential. There is also a substantial speed difference between the E5-2670 and E5-2690 v2 processors; this shows the impact of moving to newer gen processors.
Memory Benchmarks
AIDA64
AIDA64 memory bandwidth benchmarks (Memory Read, Memory Write, and Memory Copy) measure the maximum achievable memory data transfer bandwidth.
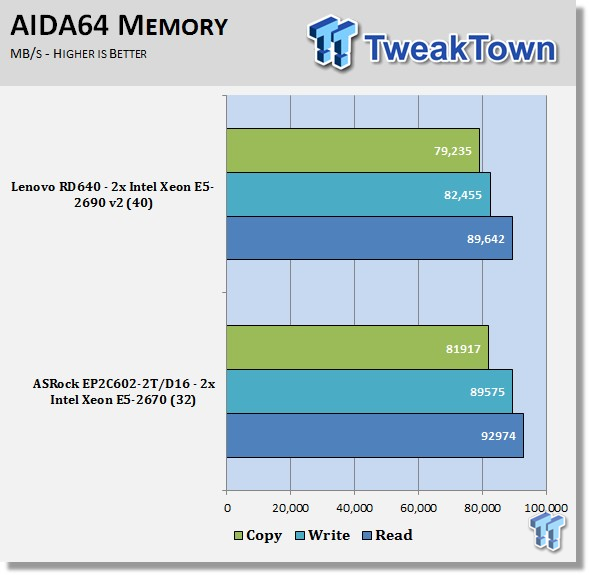
AIDA64 memory tests show the RD640 using Quad-Channel memory has good memory bandwidth. Higher speed memory sticks would help to improve memory bandwidth.
Linpack
Intel Optimized LINPACK Benchmark is a generalization of the LINPACK 1000 benchmark. It solves a dense (real*8) system of linear equations (Ax=b), measures the amount of time it takes to factor and solve the system, converts that time into a performance rate, and tests the results for accuracy.
LINPACK is a measure of a computer's floating-point rate of execution ability and measured in GFlops (Floating-point Operations per Second), ten billion FLOPS = ten GFLOPS. LINPACK is a very heavy compute application that can take advantage of the new AVX2 instruction. Since it puts a very high load on the system, it is also a good stress test program.
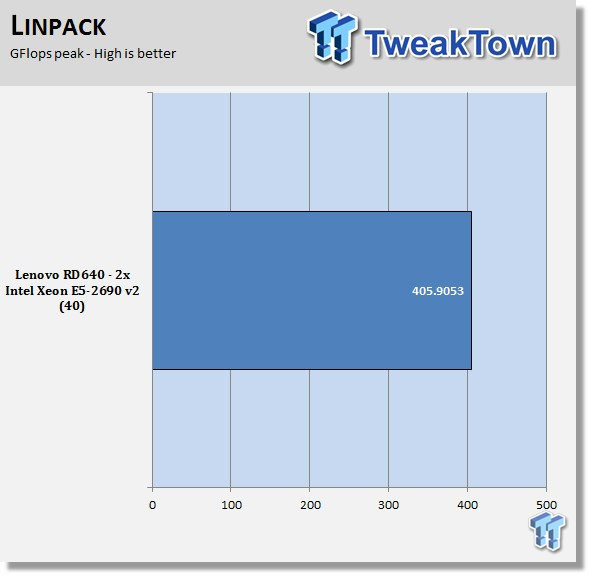
Back when we did the review of the ASRock 2U12L6SC-2TS6 server, we did not use LINPACK, so we have no data to compare with.
The E5-2690 v2 processors have very good bandwidth results that are relative to all Ivy Bridge CPUs tested here. Peaking slightly over at more than 405 GFlops shows a very strong processor IMC and memory setup. We are very pleased with the results from LINPACK on the RD640 server.
UnixBench 5.1.3 and SPEC CPU2006v1.2
UnixBench
UnixBench has been around for a long time now, and is a good general-purpose bench to test on Linux based systems. This is a system benchmark, and it shows the performance of single-threaded and multi-threaded tasks.
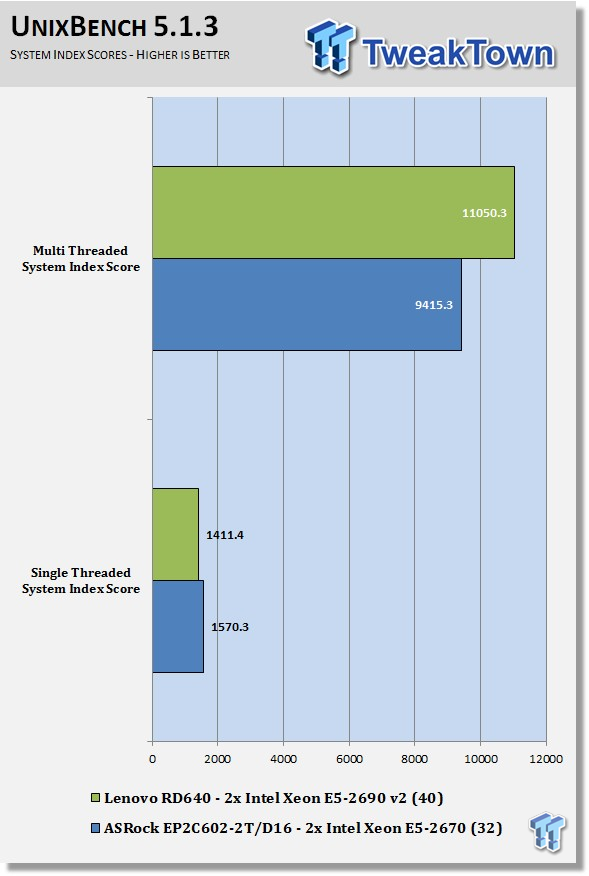
This shows the system indexes after a complete UnixBench run. Here we get an idea of how much performance gain we get using multi-threaded applications. However, many applications use single- threaded, so this number is really the base, and a higher clock speed will increase both indexes.
Now we are seeing that the E5-2690 v2s in the RD640 come very close to other systems we have tested. This is starting to look very good for the RD640.
SPEC CPU2006v1.2
SPEC CPU2006v1.2 measures compute intensive performance across the system using realistic benchmarks to rate real performance.
In our testing with SPEC CPU2006, we use the following basic commands to run these tests:
Runspec -tune=base --config=tweaktown.cfg, then int, or fp
To do multi-threaded, we add in --rate=40 on the RD640.
When SPEC CPU first came out, these tests could take up to a week to run, but as computers become faster, our tests now take up to four days for a full run. The user can do many thing to effect the results of CPU2006 runs, such as compiler optimizations, add-ons like Smartheap, and different commands used in to start the tests.
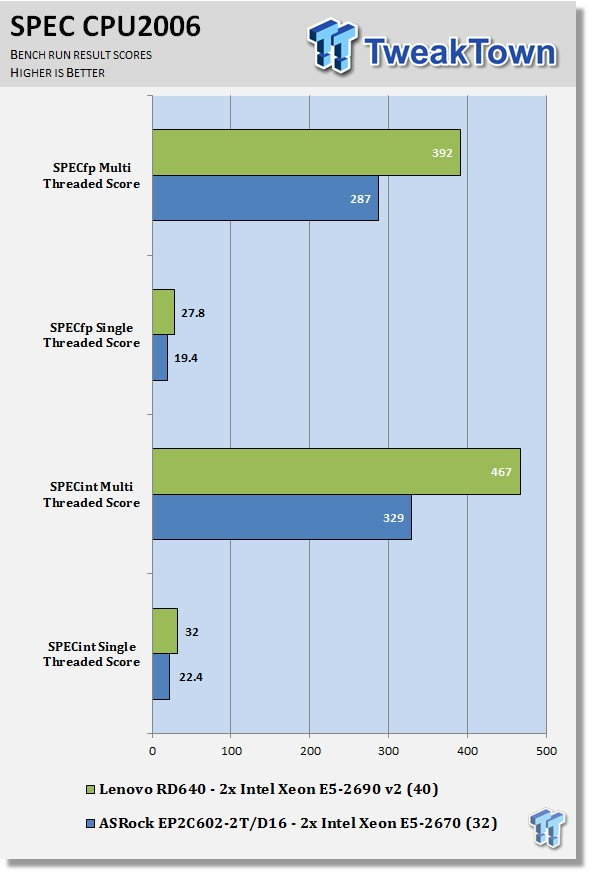
Here you can see the SPEC scores after full runs for Integer (int) and Floating Point (fp) tests.
Single-core runs show how fast (speed) a CPU can perform a given task. In the multi-core runs, we set SPEC CPU2006v1.2 to use all threads, and this is a measure of the throughput of the system.
The additional core/threads of this system have a huge impact on performance in these tests, and really show the amount of horsepower that a dual socket system has over a single socket board. Single-threaded results are still very important, but when you need lots of those to run, moving to a dual socket setup is the way to go.
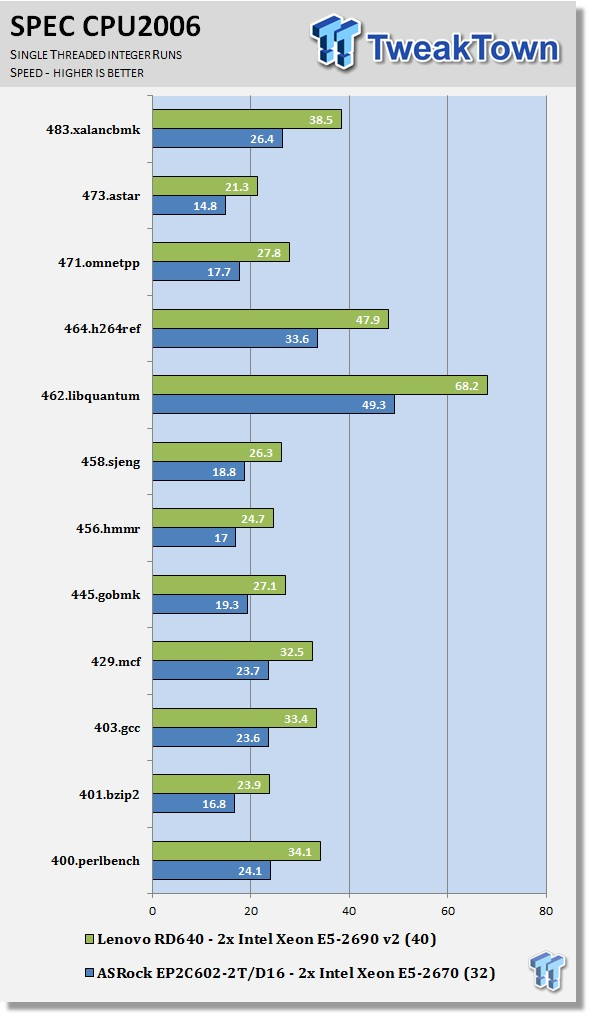
Looking at the results of single-threaded integer runs, we can get an idea of the speed at which the Intel Xeon E5-2690 v2s can crunch through the different integer tests. Not all CPUs are equal here, and ones that have a higher speed will perform these tests faster. In this case, this is the stock speed of the Intel Xeon E5-2690 v2s. Naturally, using an overclocked system, or CPUs with a higher stock speed, will generate higher results.
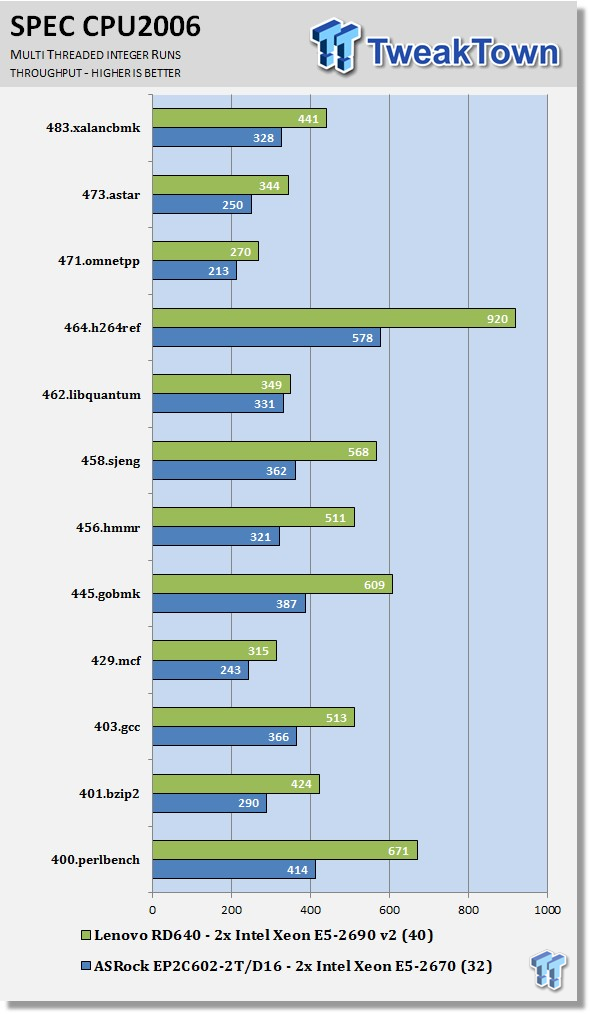
Now we run the test using all 40 threads of the Dual Intel Xeon E5-2690 v2s, to measure the throughput of the system. In this test, more cores/threads will have a greater effect on the outcome.
We can see a big difference here using the dual socket setup over single socket systems, with a three to four times performance boost in many cases.
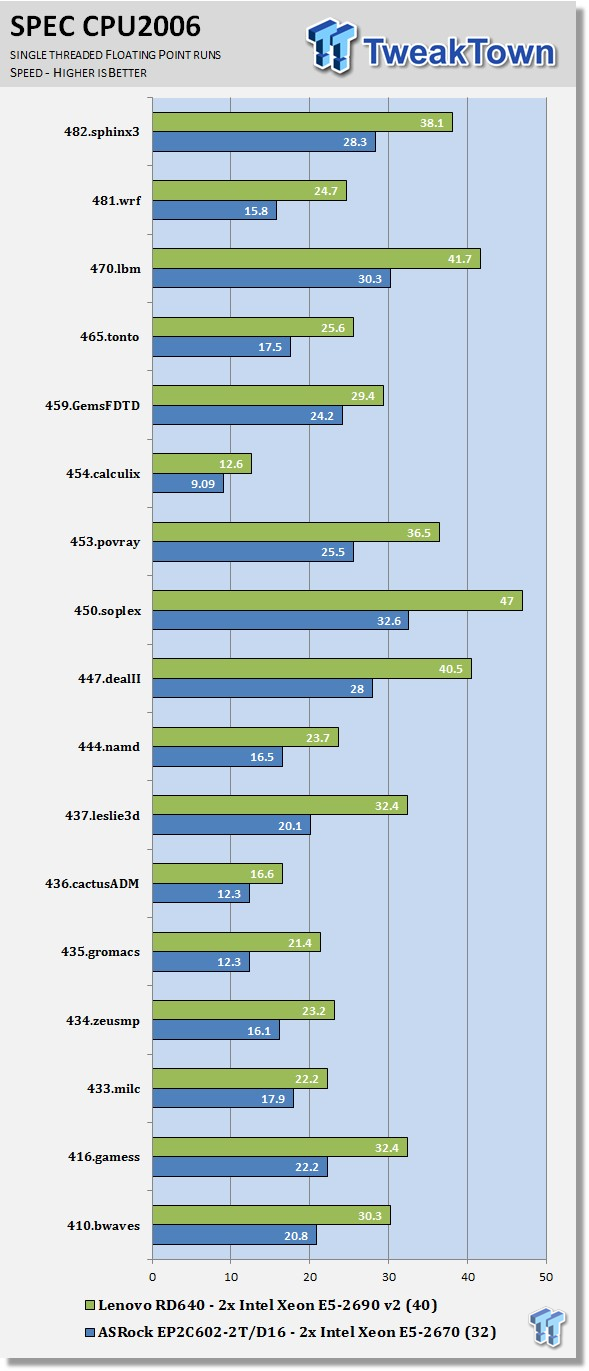
Just like the integer tests, we now run the floating-point tests in single (speed) mode. The lower clock speeds of the Intel Xeon E5-2670's also hold this bench back. We do see a strong advantage with using Ivy Bridge-EP E5-2690 v2s in this test.
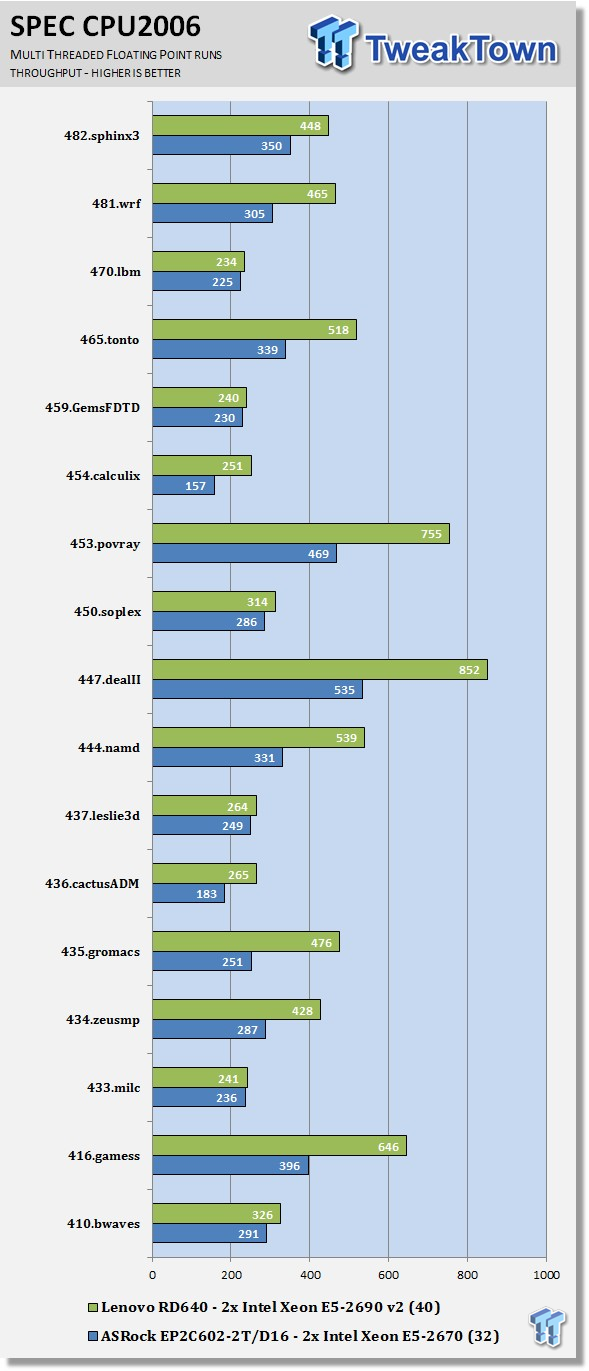
Here we see the results of the multi-threaded floating-point run that uses all 40 threads of the Dual Intel Xeon E5-2690 v2s. Like the multi-threaded integer test, more cores/threads will have a greater impact on the test.
Just the single-threaded FP runs, we see a strong advantage using Ivy Bridge-EP E5-2690 v2s in this test.
Power Consumption and Final Thoughts
Power Consumption
We have upgraded our power testing equipment and now use a Yokogawa WT310 power meter for testing. The Yokogawa WT310 feeds its data through a USB cable to another machine where we can capture the test results.
To test total system power use, we used AIDA64 Stability test to load the CPU, and then recorded the results. We also now add in the power use for a server from off state, to hitting the power button to turn it on, and taking it all the way to the desktop. This gives us data on power consumption during the boot up process.
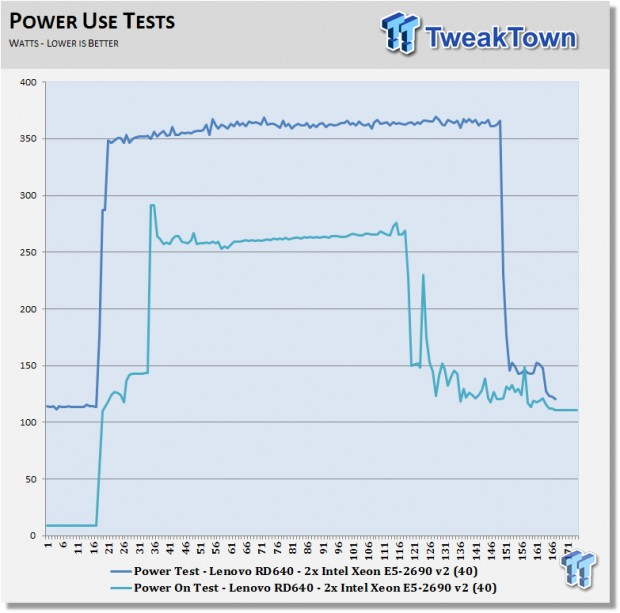
With dual socket systems, power use can be rather high when fully loaded. The Lenovo ThinkServer RD640 did peak out at about 360 watts under load, and about 280 watts on boot up. Setting the server power features and CPU speed step will lower these numbers. Overall, the RD640 does not use a lot of power compared to bigger systems. This is good, as it also lowers heat output and makes for a cool running server.
Idle power use is in the range of ~110 watts, which is very good for a server of this type. Lower idle power use means less running costs in the long run, making the RD640 inexpensive to run over time.
Final Thoughts
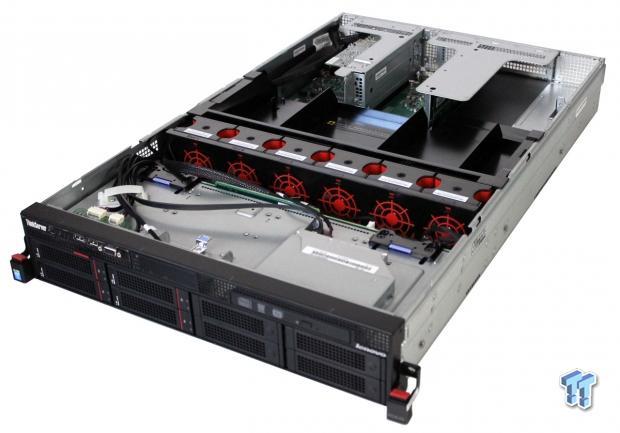

The Lenovo ThinkServer RD640 is a powerful server that is well suited for heavy VM workloads, and offers a complete virtualization management solution.
With a large number of storage bays and onboard or optional storage adapters, the RD640 is able to handle the increasing demands of the datacenter with a wide range of options. High-speed network access comes pre-installed, and optional expansion cards can increase the capacity if needed.
The EasyStartup DVD simplifies setup of one server to many servers; it is simple to use, and walks you through a compete server OS install. We have now used EasyStartup on several Lenovo servers, and find it a breeze to use now. After the first server is configured with EasyStartup, the settings can be saved to a USB drive to set up additional servers without having to go through the whole process again. You can still do the install the manual method if you wish; everything that you will need is included on the software DVD.
Server management provided though IPMI, or the optional Lenovo Management Controller Premium Module for iKVM abilities. This allows server management just like any other server you would run into. Extended management abilities using EasyManage allow a larger number of servers to be managed with ease.
Lenovo's line of servers offer simple tool-less operation; simply unlock the server lid, pull out the air shroud, and install RAM or upgrade expansion cards. This is very simple to do, and can be done while the server is installed in a rack without any problems. Just like the server itself, the rail kit is tool-less and snaps into place, but you still need to screw in a retaining screw to lock everything into place. Once you figure out the rail install, it is rather simple to do.
It is hard to find things to not like about the RD640; we had no issues installing the OS, adding RAM, or reconfiguring the hard drives. The RD640 is open standards based, which allows it to easily fit into your existing network and work flows, and its high performance, so it will not be a bottle neck to your system.
PRICING: You can find the ThinkServer RD640 70AY0006UX 2U Rack Server for sale below. The prices listed are valid at the time of writing but can change at any time. Click the link to see the very latest pricing for the best deal.
United States: The ThinkServer RD640 70AY0006UX 2U Rack Server retails for $1199.99 at Amazon.
