CPU, APU & Chipsets News - Page 118
Qualcomm unveils Snapdragon 450
At MWC Shanghai Qualcomm announced a bunch of new products including the new mid-range processor, the Snapdragon 450.
This processor is designed to be put in mid-range smartphones, with a heavy focus on the Chinese market and Chinese manufacturers.
The Snapdragon 450 has an improved CPU and GPU with a 25% increase to both over the Snapdragon 435. It will feature an eight-core processor and Adreno 506 GPU which should offer better performance at lower power thanks to also being a 14nm FinFET chip.
Continue reading: Qualcomm unveils Snapdragon 450 (full post)
The new iMac Pro might feature server-grade co-processor
Apple is preparing their next-gen iMac Pro systems, which can be configured with Intel's new Purley-based CPUs rocking up to 18C/36T and ECC RAM for the best you can get in an AIO desktop PC.
These are the configurations we should expect for the new iMac Pro:
But, there's now news coming from Pikeralpha that one of the most interesting parts of Apple's new iMac Pro could be the fact that it uses an ARM co-processor. The use of an ARM co-processor would allow the iMac Pro to perfect regulate the power going through the machine, perfectly tweaking the CPU and GPU management to keep power draw down, and thus temperatures. This is incredible important for an all-in-one that rocks a 18C/36T processor, 128GB of ECC RAM, and a bunch of PCIe-based NVMe SSDs, and AMD's new Radeon Vega GPU architecture.
Continue reading: The new iMac Pro might feature server-grade co-processor (full post)
AMD EPYC: 64C/128T dual-CPU against Intel 56C/112T CPUs
AMD has been making some pretty serious waves with its Zen CPU architecture, but now that the enterprise/server-grade EPYC processors are here, Intel is in for a big fight - even with its spiffy new Xeon Platinum line of CPUs.
AMD's new EPYC 7601 comes in 32C/64T, but has been used in a dual-CPU server with a total of 64C/128T for some serious computational power - with SiSoft Sandra and Cinebench R15 2P benchmarks. We're seeing a competition between Intel's new 28C/56T processors in both single- and dual-CPU configurations, with a dual-CPU rig with Intel's new Xeon Platinum 8180 and a total of 56C/112T of power.
The benchmarks saw an average all-core CPU clock of 2.7GHz on all 64C/128T of AMD's dual EPYC 7601 system, while the dual Intel Xeon Platinum 8180 had 3.4GHz across all of its dual-CPU goodness at 56C/112T. In the Cinebench R15 performance, we're looking at AMD's EPYC 7601 scoring around 6879 points, while Intel's new Xeon Platinum 8180 pushes 8301.
Continue reading: AMD EPYC: 64C/128T dual-CPU against Intel 56C/112T CPUs (full post)
Major flaw found in Intel CPUs and HT, needs BIOS fix
If Intel wasn't already in enough trouble with AMD's constant onslaught of products with Ryzen and now Ryzen ThreadRipper, the company is now going to have a huge storm surrounding it over a newly-discovered flaw in Intel's Skylake and Kaby Lake architectures with Hyper-Threading.
The HT-enabled processors with critical flaws were discovered on the Debian Linux user list, and sent out without a warning notification - but these issues extend to Windows, and other operating systems, too. The errors with HT-enabled Skylake/Kaby Lake CPUs can lead to various issues ranging from your entire system locking up, major data corruption or loss, or even more. As HotHardware points out: "the replication conditions are very specific and are unlikely to be encountered by most users in the wild". Still, it's not a good thing to see a company the size of Intel experiencing major issues like this, especially with AMD now competing in a big way in the CPU market again.
The problems surrounds Intel errata documentation, explained as:
Continue reading: Major flaw found in Intel CPUs and HT, needs BIOS fix (full post)
Intel's next-gen 6C/12T: competes with AMD Ryzen 5 1600X
Intel has been reacting to AMD's new Ryzen CPUs with the tease and release of their new Core i9 processors, but the mainstream Coffee Lake CPUs that are set for a reported launch early next year are being teased more and more.
The latest on Intel's upcoming Coffee Lake-based Core i7 processors is that they will come out in 6C/12T flagship models, with similar to performance of AMD's Ryzen 5 1600X, which is also a 6C/12T processor. There's now a listing on the Geekbench database of a few new Intel processors, with a 6C/12T model with 1.5MB of L2 cache and 12MB of L3 cache. We should expect the 6C/12T processor to come with up to 3.5GHz base and 4.2GHz boost clocks, which is hefty for a 6C/12T mainstream CPU, especially from Intel.
With the Geekbench entry, the chip is clocked at 3.2GHz base, and has a single-core score of 4619 and multi-core score of 20,828. If we compare this against a retail AMD Ryzen 5 1600X processor, we have a single-score of 4574, and multi-core score of 20,769. Right on the money against the Ryzen 5 1600X.
Continue reading: Intel's next-gen 6C/12T: competes with AMD Ryzen 5 1600X (full post)
Intel's next-gen Coffee Lake: 6C/12T @ 4.2GHz or more
Intel just launched its new Core i9 range of processors, but Coffee Lake news continues to roll out, as Coffee Lake is a refresh/optimized slice of Kaby Lake that supports more than 4 CPU cores.
A new engineering sample has turned up on the SiSoft Sandra benchmark database, showing that Intel will have 6C/12T CPUs at 3.5GHz, and over 4.2GHz with Turbo enabled. We should expect 256KB of L2 cache per core, and 9MB of shared L3 cache. There's also a variant of Coffee Lake that will include a larger 12MB of L3 cache, too.
We should expect the Coffee Lake-S series to come in 4C/8T with GT2 graphics, as well as 6C/12T with GT2 graphics. There will be Coffee Lake-S and Coffee Lake-H series processors, but we might see Intel change the socket from LGA 1151 to something else with Coffee Lake, but let's hope they don't - alright?
Continue reading: Intel's next-gen Coffee Lake: 6C/12T @ 4.2GHz or more (full post)
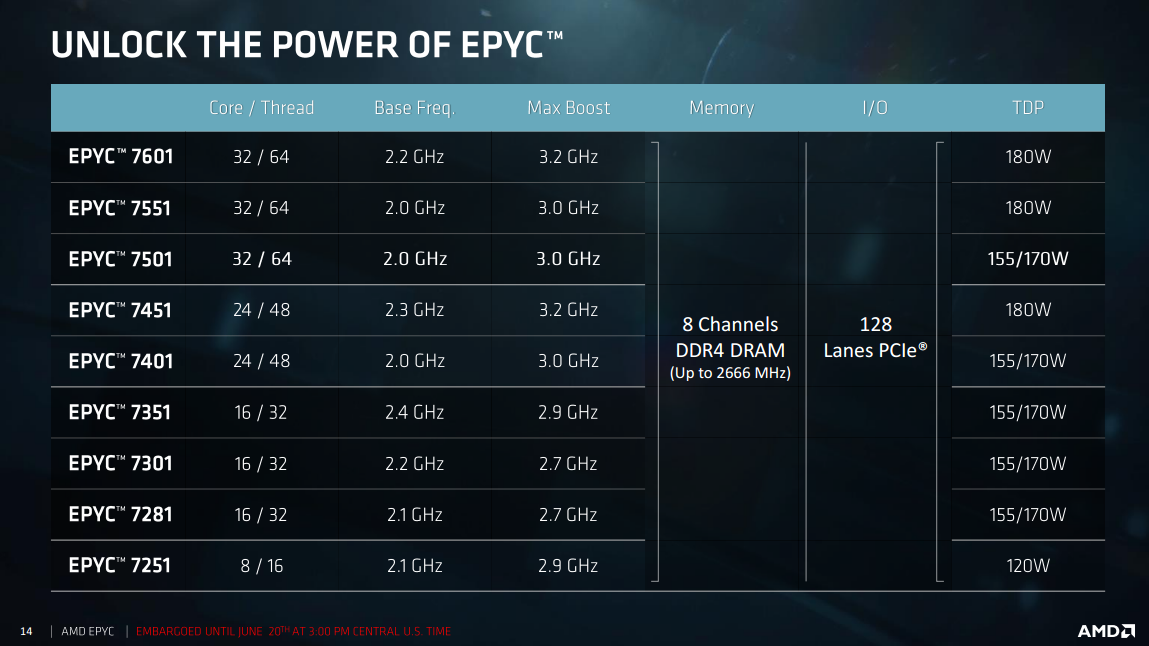
AMD EPYC: 32C/64T flagship CPU costs $4200, monster perf
The NDA has lifted on AMD's next-gen Epyc CPU range of processors, with the company detailing some of the pricing on its Xeon CPU competitors - with some hefty pricing at the flagship end of the scale.
AMD will have a bunch of 32C/64T options, with the Epyc 7601 flagship CPU that is available right now for $4200. Under that, we have the Epyc 7551 without pricing yet, but the Epyc 7501 is priced at $3400 and also available today. Towards the end of July, there will be the Epyc 7401 for $1850, the Epyc 7301 for $825, Epyc 7281 for $650, and Epyc 7251 for $475.
Our resident CPU editor Steven Bassiri, has detailed AMD's new Epyc CPUs here - with a more detailed piece on the way very soon.
Continue reading: AMD EPYC: 32C/64T flagship CPU costs $4200, monster perf (full post)
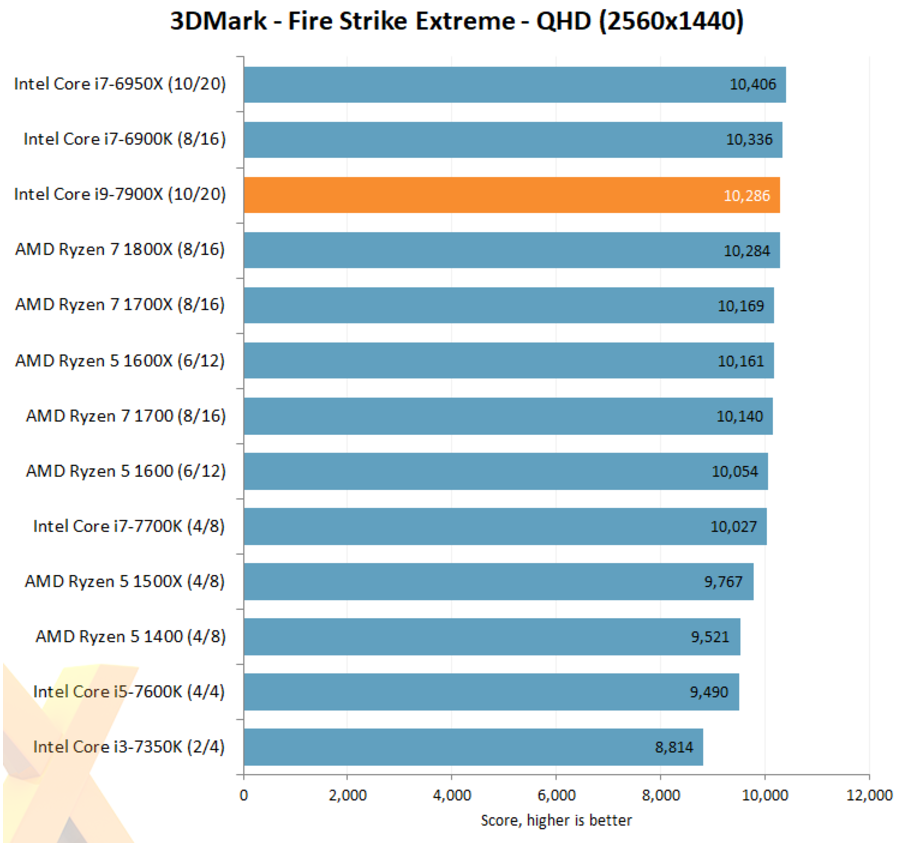
Intel Core i9-7900X reviewed: 10C/20T @ up to 4.8GHz
The massive multi-threaded consumer CPU war is now starting thanks to AMD hitting Intel where it hurts with Ryzen and hitting 8C/16T @ $499... but Ryzen ThreadRipper with up to 16C/32T is on the way, so the preemptive strike from Intel with Core i9 happened.
Now we're seeing the first review of Intel's upcoming Core i9-7900X, their new X299-based Core-X series processor with 10C/20T of CPU performance that seems to perform well, overclock well, but is priced pretty high. Hexus has published their review from an Intel CPU sample that was not provided to them by Intel - so they could throw the review online and not worry about Intel's legal team emailing them saying they've broken NDA.
We can see that the fresh X299 chipset needs some more time to mature, but we have some gaming and overclocking charts for you to gander over - and consider buying the 10C/20T chip in the form of the Core i9-7900X over the upcoming Ryzen ThreadRipper range from AMD. My tip: wait.
Continue reading: Intel Core i9-7900X reviewed: 10C/20T @ up to 4.8GHz (full post)
AMD Epyc: 32C/64T @ 3.2GHz, 2TB RAM and 128 PCIe lanes
AMD is killing it with their new Zen CPU cores, with Ryzen already a success and Ryzen ThreadRipper going for Intel's throat - but what about the server market? This is where Epyc comes into play, with the upcoming Epyc 7000 series from AMD. VideoCardz picked up the news, with some details on the Epyc 7000 series:
No compromise 1-Socket
There's some huge performance increases over Intel's Xeon E5-2699A v4 processor, which is a 22C/44T @ 3.6GHz CPU, with 55MB of cache, and a price of $4000+. We have 47% more performance over the single socket CPU, but given there are 18 more CPU threads (albeit at 400MHz slower clocks), AMD is going to send some massive shocks throughout the server market with Epyc.
Continue reading: AMD Epyc: 32C/64T @ 3.2GHz, 2TB RAM and 128 PCIe lanes (full post)
Intel's Skylake-X to use an Integrated Voltage Regulator
Remember the fully integrated voltage regulator (FIVR) introduced with Haswell CPUs? Turns out that news of Intel axing the technology was not completely true. Intel's previous FIVR was implemented to reduce motherboard voltage regulator (VR, VRM, or MBVR) complexity, as it fed the CPU a single voltage and the CPU then internally branched off, reduced, and controlled the other voltages needed for other CPU domains (graphics, system agent, cache, IO, etc.).
Traditionally, CPU voltage regulators are fed 12v from your main system power supply, and then they reduce it down to voltages below 2v for the CPU and its different domains. However, as CPUs became more complex they required multiple separate VRs, each with their own controllers (PWM Controller). Adding more external VRs not only increases motherboard costs because of the need for each VR to be individually controlled, but also more importantly, it takes up motherboard real estate which is scarce on a motherboard with eight memory DIMMs surrounding the CPU. Over the past week, Intel quietly made public volume 1 of the Skylake-X datasheet, and you can find it here: Intel Skylake-X Datasheet Volume 1 of 2.
In table 1-1 on page 14 we find that "IVR" will be referenced in the datasheet, and it stands for "Integrated Voltage Regulation (IVR): The processor supports several integrated voltage regulators." Later in the datasheet we find reference to the fact that the IVR is related to the previous FIVR through a signal name called "FIVR_Fault", which "Indicates an internal error has occurred with the integrated voltage regulator. The FIVR_FAULT signal can be sampled any time after 1.5 ms..." We then learn further down about the VCCIN signal, "1.8 V - 1.55 V input to the Integrated Voltage Regulator (IVR) for the processor cores, lowest level caches (LLC), ring interface, PLL, IO, and home agent. It is provided by a VR 13.0 compliant motherboard voltage regulator (MBVR) for each CPU socket.
Continue reading: Intel's Skylake-X to use an Integrated Voltage Regulator (full post)