
The Bottom Line
Introduction
UPDATE - Please note that drive is now named Exos 7E2000.
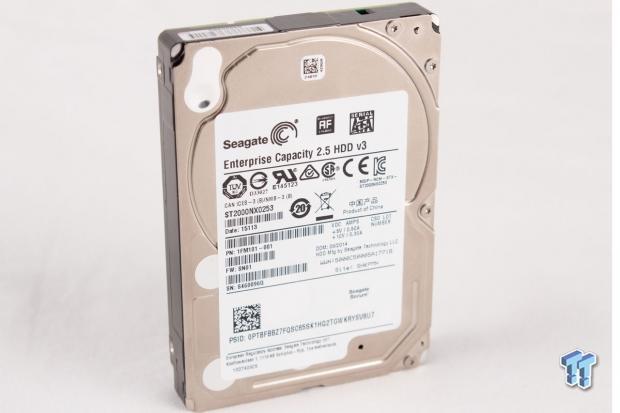

Seagate's new Enterprise Capacity 2.5" HDD v3 offers up to 2TB of density in the compact 2.5" form factor. The 7,200-RPM Enterprise Capacity v3 is geared for the capacity segment, but also offers impressive best-in-class performance, and a 50% improvement in watts-per-TB. The third-generation Enterprise Capacity 2.5 is designed for maximum capacity entry-level servers, blade servers, SAN, and NAS applications.
SSDs are unquestionably penetrating further into the performance 2.5" segment. While SSDs are coming in larger capacities as of late, 2TB capacity points have not become pervasive, and overall NAND production is not even close to providing enough Exabytes of storage to unseat the venerable HDD. Another advantage for the Enterprise Capacity v3 lies in its High Availability features delivered via 6GB/s SATA, or dual-port 12Gb/s SAS connections.
One of the primary reasons for the surge in SSD adoption is fierce competition between foundries, leading to more palatable price points for consumers, but many of the value segment SSDs continue to feature the SATA connection. SAS SSDs also have value options, but they command a higher price point, which leads plenty of room for higher-capacity SAS HDDs in the datacenter. Offering 2TB in a small form factor also opens up more opportunities in dense system designs, and incorporates well into slim 1U and 2U servers.
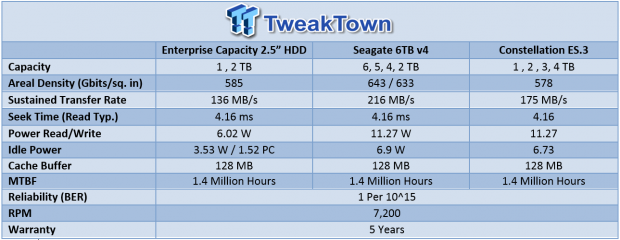
The Enterprise Capacity v3 also offers lower power consumption during active and idle operating states. With Seagate's proprietary PowerChoice technology, the Enterprise Capacity v3 can idle as low as 1.52 watts. We cover PowerChoice in more detail on the following page. Seek times remain similar to the 3.5" class SSDs, but the sequential performance is somewhat lower than larger HDDs at 136 MB/s. This is still an 18% performance improvement over the previous generation. The v3 supplants the Constellation.2, which also offered both 6Gb/s SAS and SATA. The new v3 version also features a 128MB multi-segmented cache.
Reliability weighs in with a standard 1.4 million hours MTBF, and a one per 10^15 UBER rating. The Enterprise Capacity also features a five-year warranty. SED (TCG-compliant) and FIPS 140-2 options protect data, and ease drive-retirement and repurposing. The v3 also features Seagate Instant Secure Erase, which renders all data on the drive unreadable in less than one second.
The Enterprise Capacity v3 also supports RAID Rebuild. RAID Rebuild is part of the SAS standard that is now supported by the major RAID controller vendors. RAID Rebuild enables communication between the drive and the RAID controller to perform surgical rebuilds in lieu of rebuilding the entire array. This can alleviate the lengthy performance-sapping rebuild process in many cases.
In today's article, we compare the diminutive 2TB Enterprise Capacity v3 to its larger companion, the 3.5" 6TB Enterprise Capacity v4, and a previous-generation 4TB Constellation ES.3. This Seagate-only test pool will highlight the difference between the 2.5" and 3.5" offerings, and analyze improvements over previous generation drives. First, let's take a closer look at the Enterprise Capacity v3.
Enterprise Capacity 2.5 HDD Internals and Specifications
Enterprise Capacity 2.5 HDD Internals

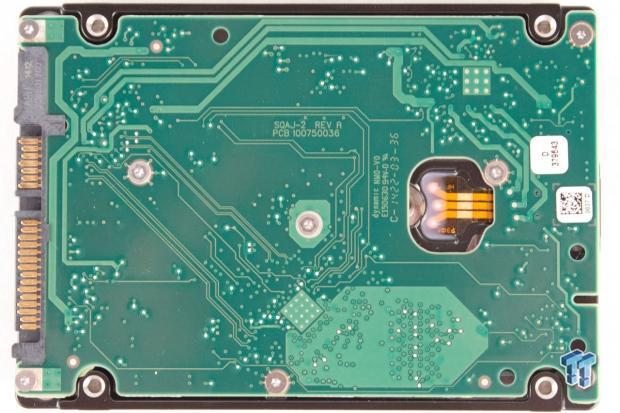
The Seagate Enterprise Capacity 2.5 HDD v3 comes in the familiar 2.5" form factor. The PCB covers the bottom of the drive.
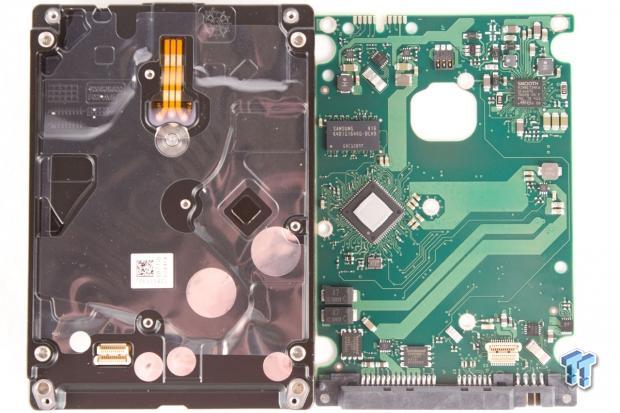

The large PCB is isolated from the case of the drive by a thin plastic covering. There is a mount point on the case that mates with the thermal pad on the controller to shed heat into the case.
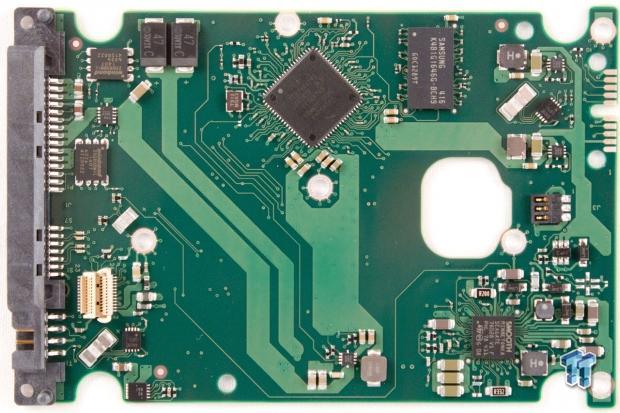
A large Seagate branded controller sets near the edge of the PCB. A SMOOTH motor controller is on the bottom right, and the large Samsung 128MB multi-segmented cache chip is near the upper right. We note several power capacitors to the upper left, and accelerometers occupy opposing corners of the PCB.
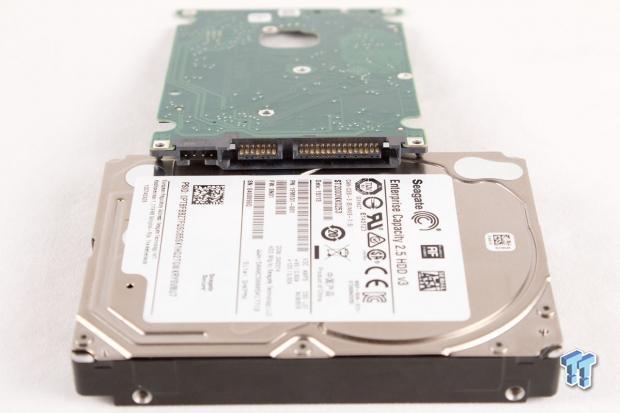

The drive features a standard 6Gb/s SATA port, which helps keep cost low, and provides wide compatibility.
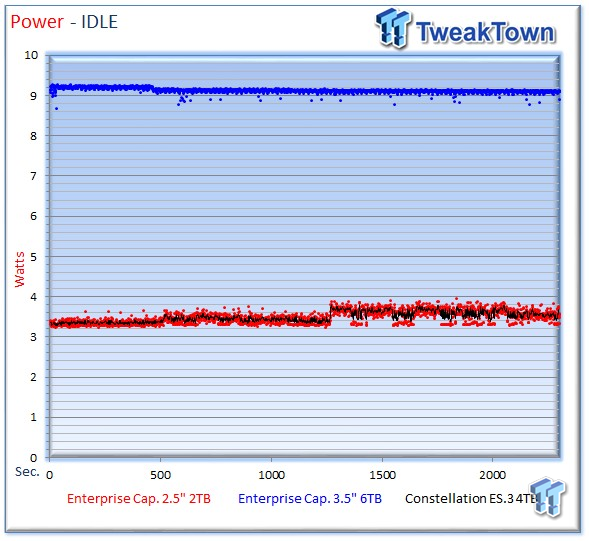
Idle power consumption is a pain point in the datacenter. The Seagate Enterprise Capacity 2.5 HDD v3 utilizes PowerChoice Technology, Seagate's proprietary implementation of the T10/T13 Approved Standard. PowerChoice provides four enhanced idle modes that place the drive into deeper quasi-sleep cycles to conserve power. The feature is enabled with a SAS Mode Page, or SATA Set Feature command in a typical implementation.
Once enabled, PowerChoice places the drive into successively deeper idle states triggered by the length of drive inactivity. There is also the option for immediate host-initiated power transitions with SAS/SATA commands, but each consecutive sleep mode requires more time for resumption. We did not test with enhanced PowerChoice states enabled.
The Enterprise Capacity 2.5 immediately displays its excellent power characteristics with a low 3.83 watts average power draw during the idle power state. It is important to note this measurement is without PowerChoice technology activated; the diminutive 2TB offering can idle as low as 1.52 watts when using PowerChoice. Even without PowerChoice, we can observe a notable difference in comparison to the larger 6TB version. The 3.5" HDD requires more power, but its larger capacity offers a similar watts-per-TB measurement.
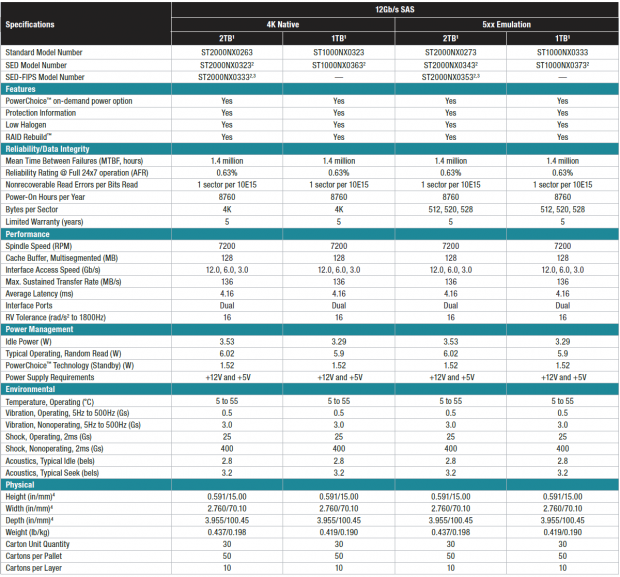
Enterprise Capacity 2.5 HDD Specifications
The 12Gb/s Seagate Enterprise Capacity 2.5 HDD we are testing today is the 512e variant with the ST2000NX0353 part number. There are 4KN, SED, and FIPS variants available with different part numbers.
Test System and Methodology

Our approach to storage testing targets long-term performance with a high level of granularity. Many testing methods record peak and average measurements during the test period. These average values give a basic understanding of performance, but fall short in providing the clearest view possible of I/O QoS (Quality of Service).
While under load, all storage solutions deliver variable levels of performance. "Average" results do little to indicate performance variability experienced during actual deployment. The degree of variability is especially pertinent, as many applications can hang or lag as they wait for I/O requests to complete. While this fluctuation is normal, the degree of variability is what separates enterprise storage solutions from typical client-side hardware.
Providing ongoing measurements from our workloads with one-second reporting intervals illustrates product differentiation in relation to I/O QoS. Scatter charts give readers a basic understanding of I/O latency distribution without directly observing numerous graphs. This testing methodology illustrates performance variability, and includes average measurements during the measurement window.
IOPS data that ignores latency is useless. Consistent latency is the goal of every storage solution, and measurements such as Maximum Latency only illuminate the single longest I/O received during testing. This can be misleading, as a single "outlying I/O" can skew the view of an otherwise superb solution. Standard Deviation measurements consider latency distribution, but do not always effectively illustrate I/O distribution with enough granularity to provide a clear picture of system performance. We utilize high-granularity I/O latency charts to illuminate performance during our test runs.
We conduct our tests over the full LBA range to allow each HDD to highlight its average performance. All three HDDs spin at 7,200 RPM and feature varying capacity points, which should be taken into consideration when analyzing performance and power metrics. The first page of results will provide the key to understanding and interpreting our test methodology.
Benchmarks - 4k Random Read/Write
4k Random Read/Write
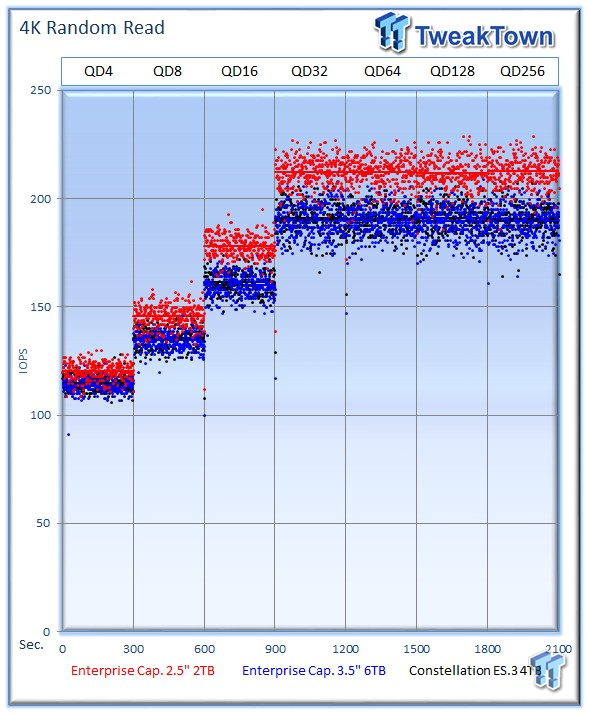
Each level tested includes 300 data points (five minutes of one second reports) to illustrate performance variability. The line for each queue depth represents the average speed reported during the five-minute interval. 4K random speed measurements are an important metric when comparing drive performance, as the hardest type of file access for any storage solution to master is small-file random. 4K random performance is a heavily marketed figure, and is one of the most sought-after performance specifications.
The Enterprise Capacity 2TB starts out with an impressive average of 212 IOPS at QD256, trailed by the ES.3 with 190 IOPS, and the 6TB Enterprise Capacity with 189 IOPS. The smaller platter provides a significant boost in average speed during the measurement window.
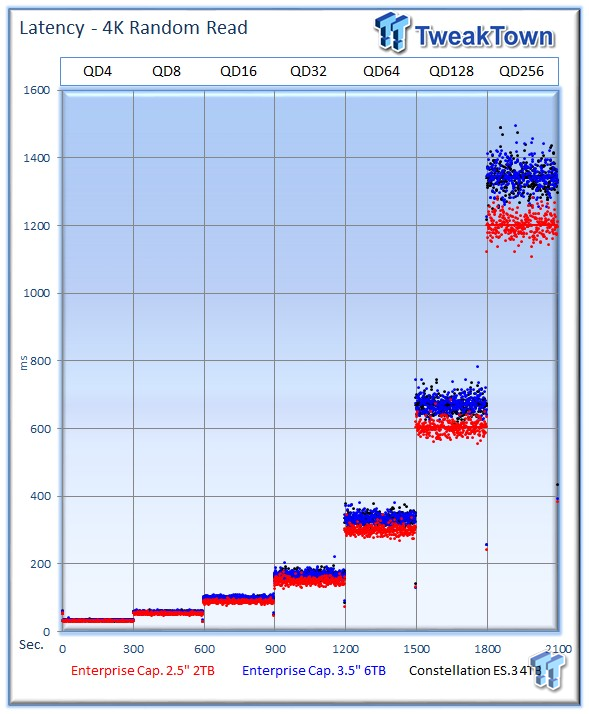
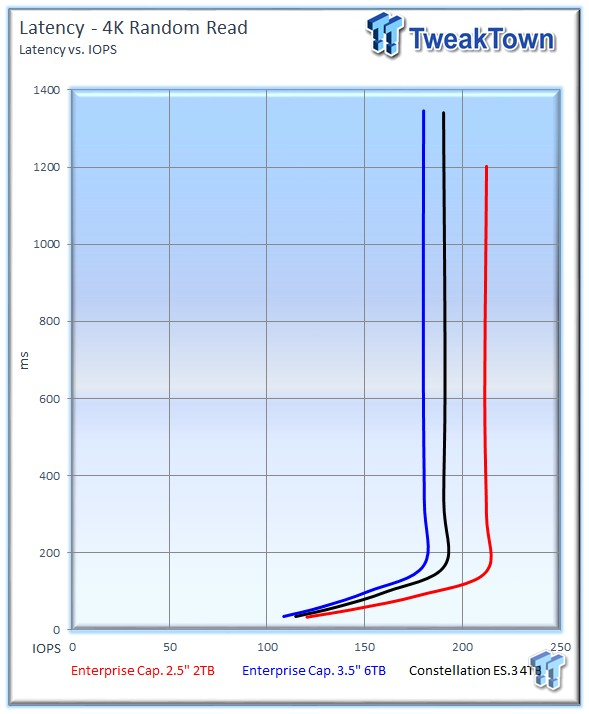
Our Latency vs IOPS charts compare the amount of performance attained from each solution at specific latency measurements. Many applications have specific latency requirements. These charts present relevant metrics in an easy-to-read manner for readers who are familiar with their application requirements. The HDDs that are lowest and furthest to the right exhibit the most desirable latency characteristics.
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity also delivers an enhanced latency profile during the measurement window.
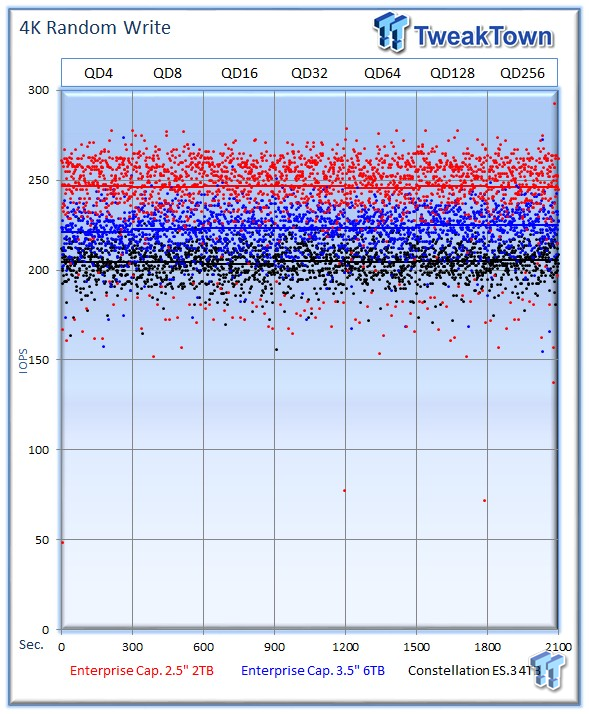
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity leverages its smaller platters to deliver another impressive performance with an average of 246 IOPS at QD256. The 6TB 3.5" drive comes in second with 224 IOPS, and the ES.3 averages 205 IOPS.
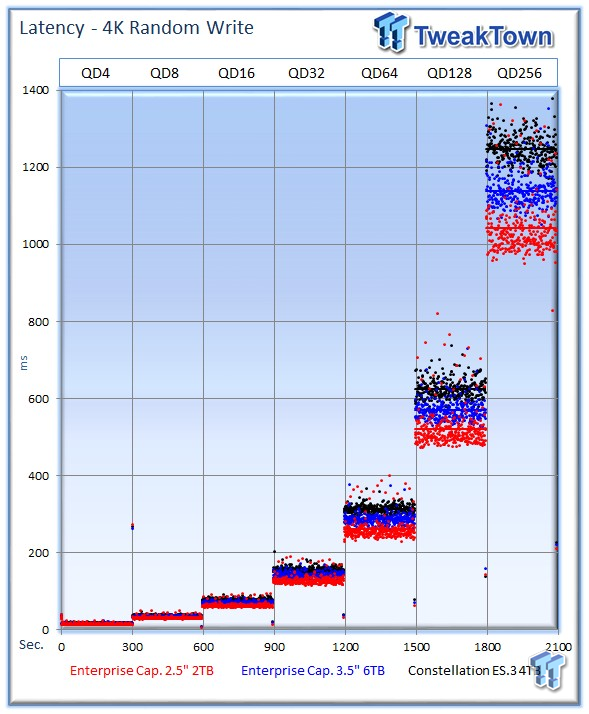
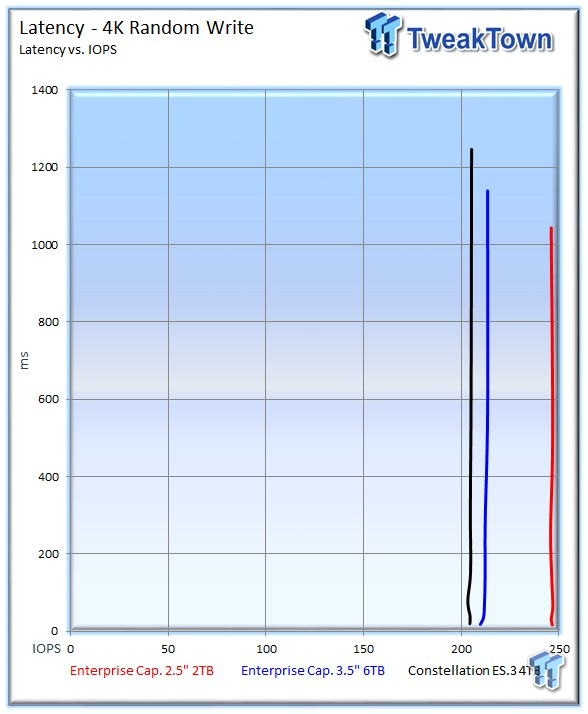
The 2TB drive distances itself from the larger capacity drives in IOPS-v-latency measurements.
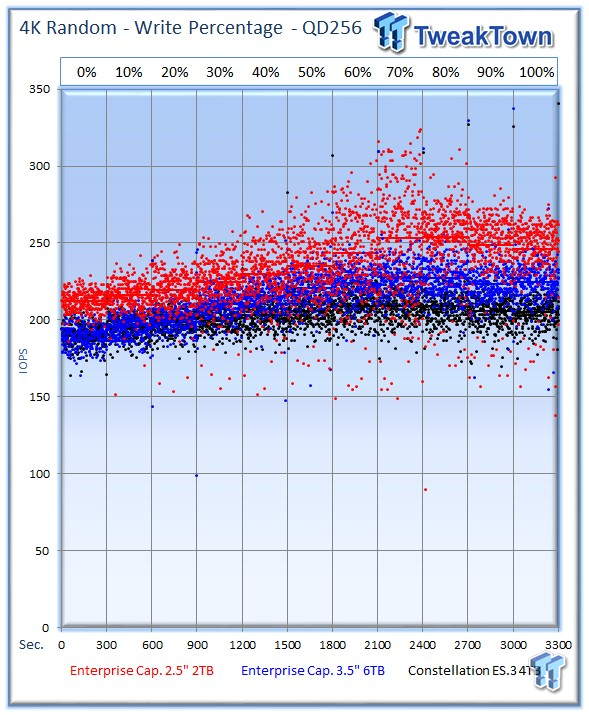
Our write percentage testing illustrates the varying performance of each solution with mixed workloads. The 100% column to the right is a pure write workload of the 4k file size, and 0% represents a pure 4k read workload.
The nimble 2.5" 2TB Enterprise Capacity offers robust performance that leads the test pool across the board.
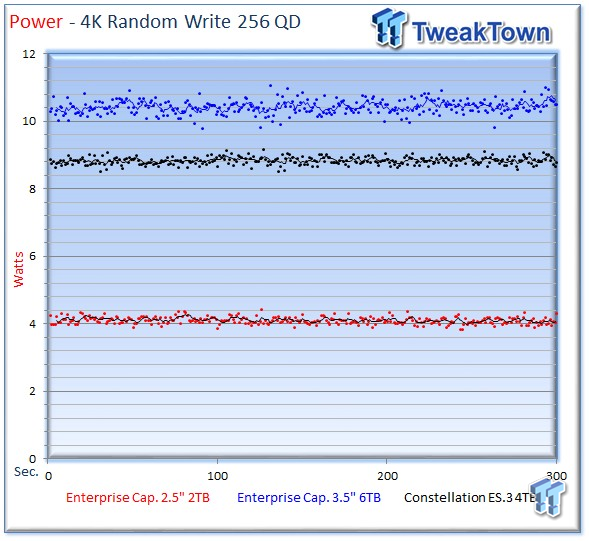
We record power consumption measurements during our test run at QD256. It is important to note the difference in RPM between the WD Red Pro at 7,200 RPM, in comparison to the lower RPMs featured in the 4TB and 6TB WD Red's, and the Seagate NAS HDD. The higher-RPM drive will predictably feature higher power consumption.
The 2TB HDD only requires a miserly 4.11 watts during the test. This is much lower than the higher-capacity offerings, though the 6TB Enterprise Capacity offers a better watts-per-TB ratio.
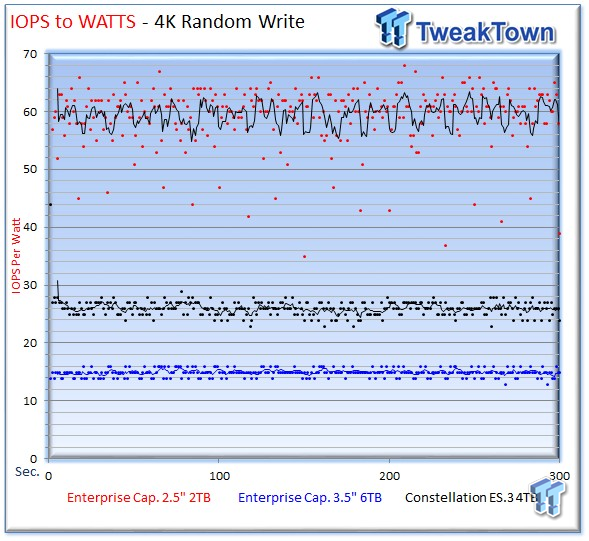
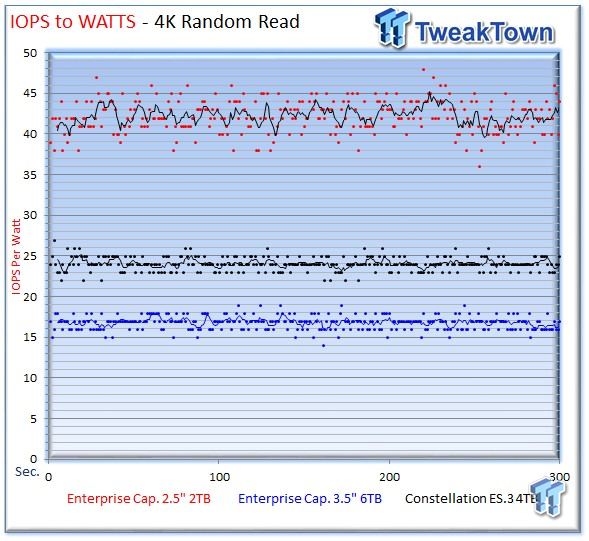
We generate IOPS-to-watts measurements from data recorded during the test period. The 2TB drive is incredibly efficient with a chart-topping average of 59 IOPS-per-watt during the write workload, and 42 IOPS-per-watt during read activity.
Benchmarks - 8k Random Read/Write
8k Random Read/Write
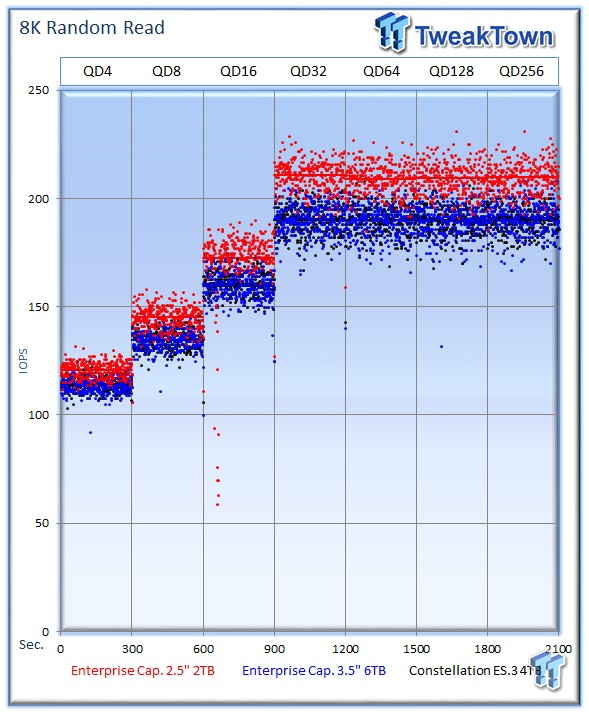
Server workloads rely heavily upon 8k performance, and we include this as a standard with each evaluation. Many of our server workloads also test 8k performance with various mixed read/write workloads.
The average 8k random read speed of the 2TB drive is 209 IOPS at QD256, and the 6TB comes in second with 226 IOPS. The 4TB ES.3 comes in third with 199 IOPS at QD256.
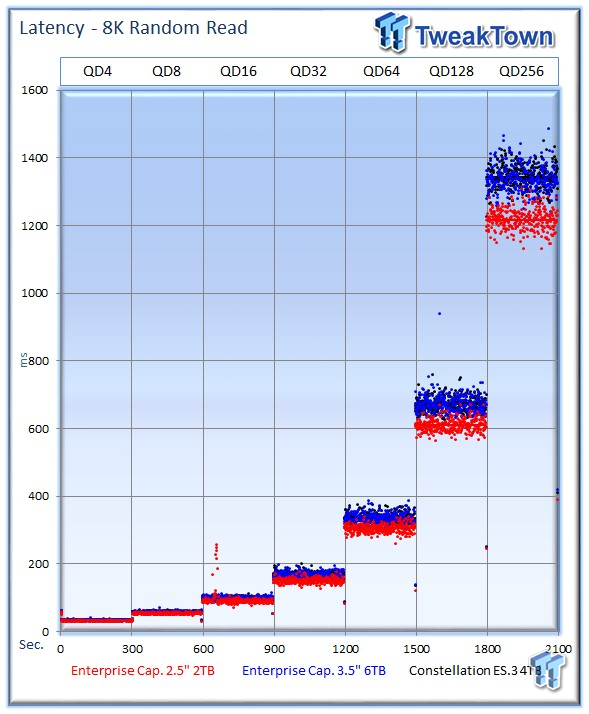
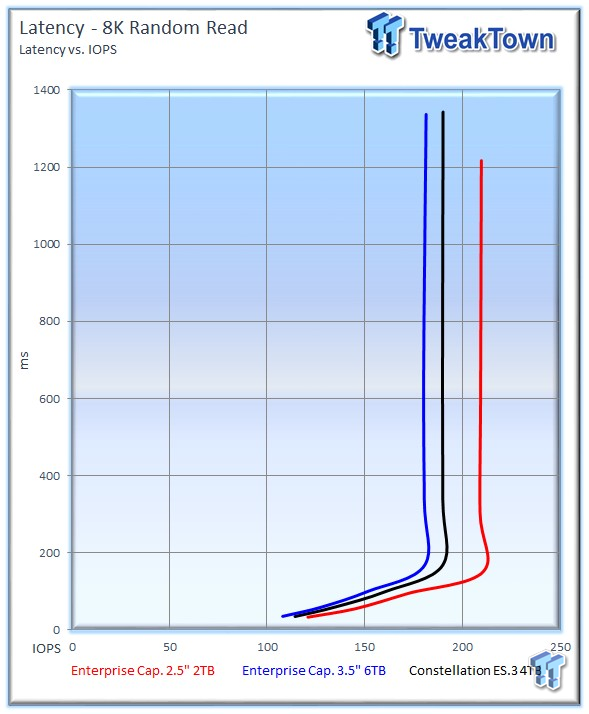
The 2TB drive continues to take a solid lead in latency-v-IOPS measurements.
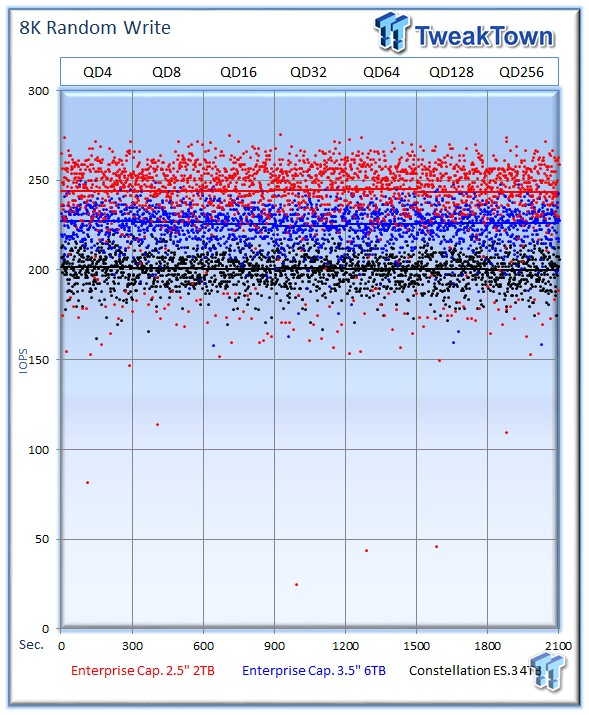
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity averages 243 IOPS at QD256, and the 6TB provides 226 IOPS. The ES.3 lags behind the newer drives again with an average of 199 IOPS.
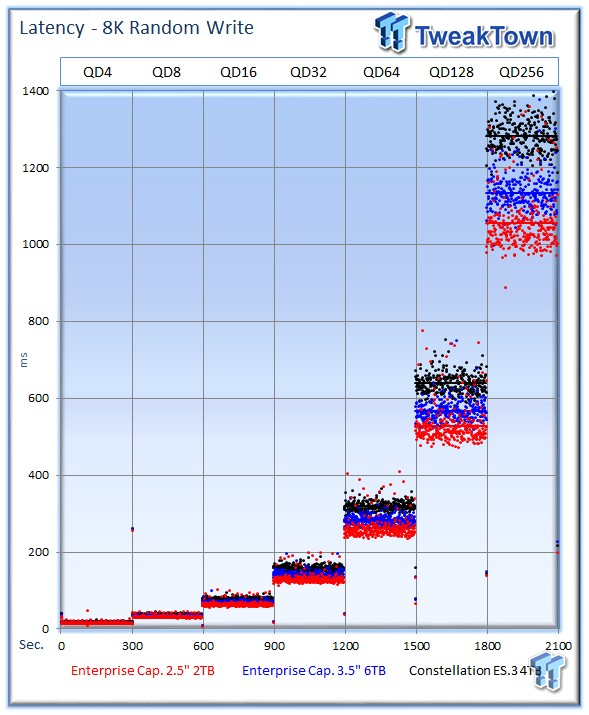
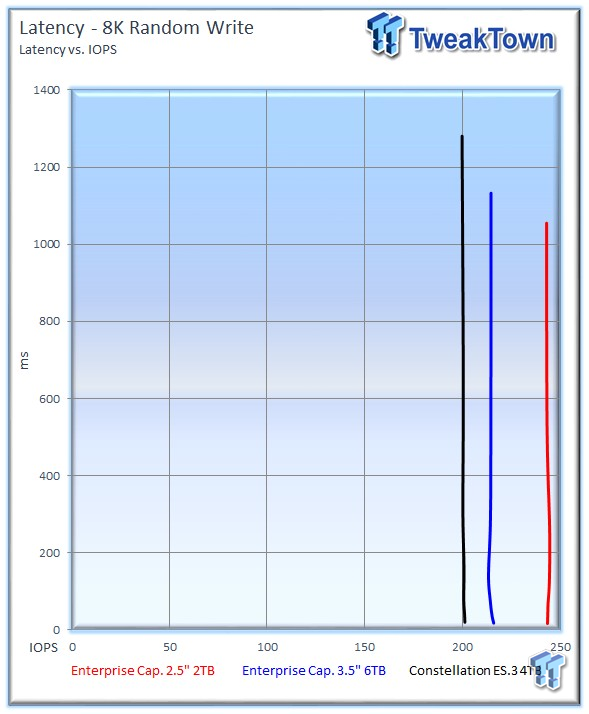
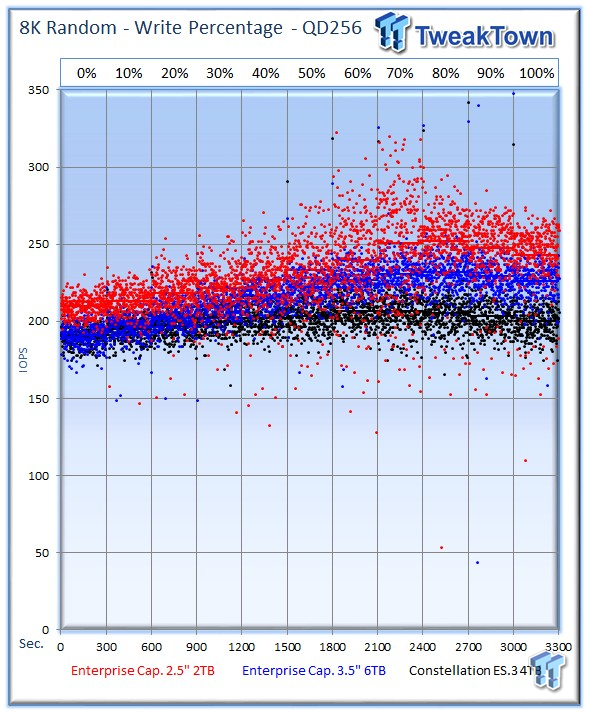
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity continues to deliver excellent mixed-random performance.
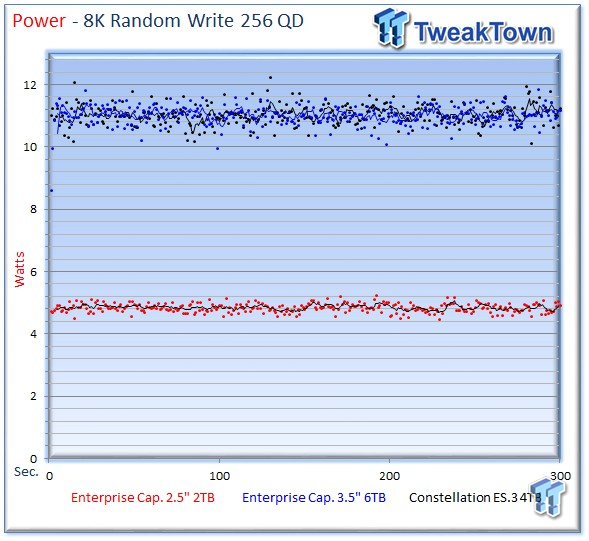
Power consumption for the 2TB drive is very impressive with an average of 4.84 watts.
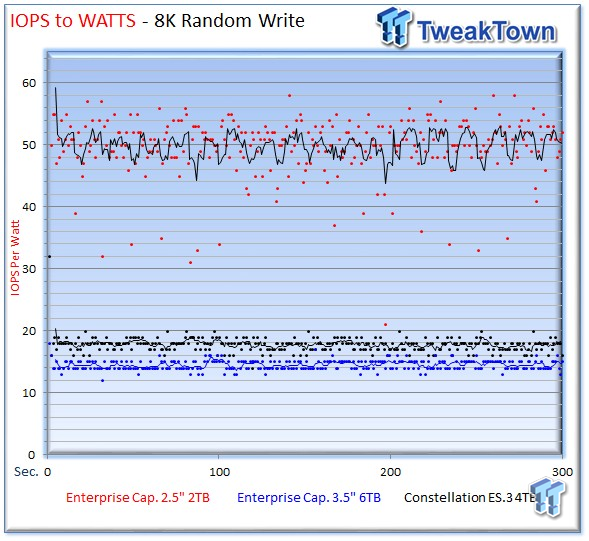
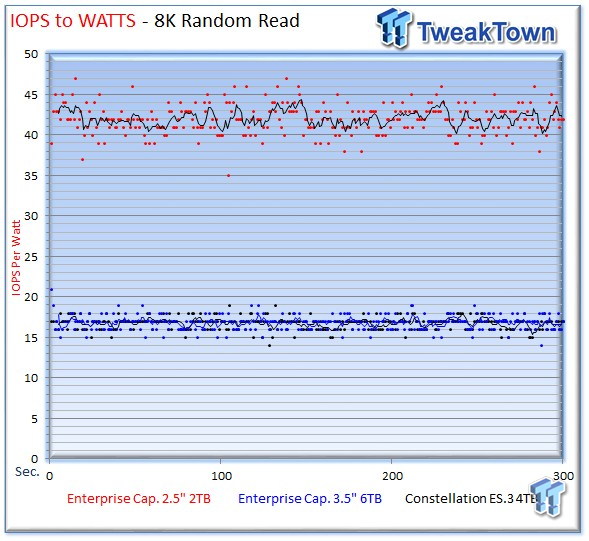
The 2.5" Enterprise Capacity provides 50 IOPS-per-watt with 8k write activity, and 42 IOPS-per-watt during read activity.
Benchmarks - 128k Sequential Read/Write
128k Sequential Read/Write
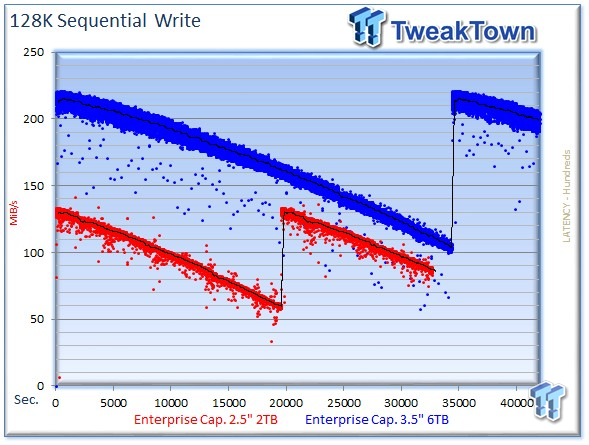
We write to every LBA to highlight performance degradation from the outer to inner tracks of the drive. The drives begin with much higher speed on the outer tracks, and lose speed as it works inward. It required 9.7 hours to write the entire capacity of the 3.5" 6TB Enterprise Capacity drive, and 5.2 hours for the 2TB variant.
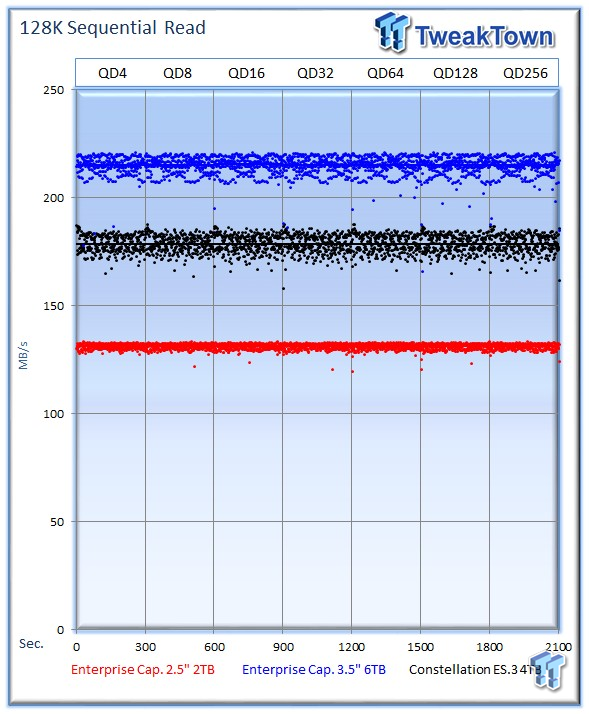
128k sequential speed reflects the maximum sequential throughput of the HDD, and is indicative of performance in OLAP, batch processing, streaming, content delivery applications, and backup scenarios. Today's HDDs are increasingly used for sequential workloads as SSDs encroach upon the application space.
The 2TB drive has an advantage in random workloads, but during the sequential read workload, it lags behind the competitors with an average of 131 MB/s at QD256. The 6TB version tops the chart with an outstanding 215 MB/s, and the previous-gen ES.3 offers 178 MB/s.
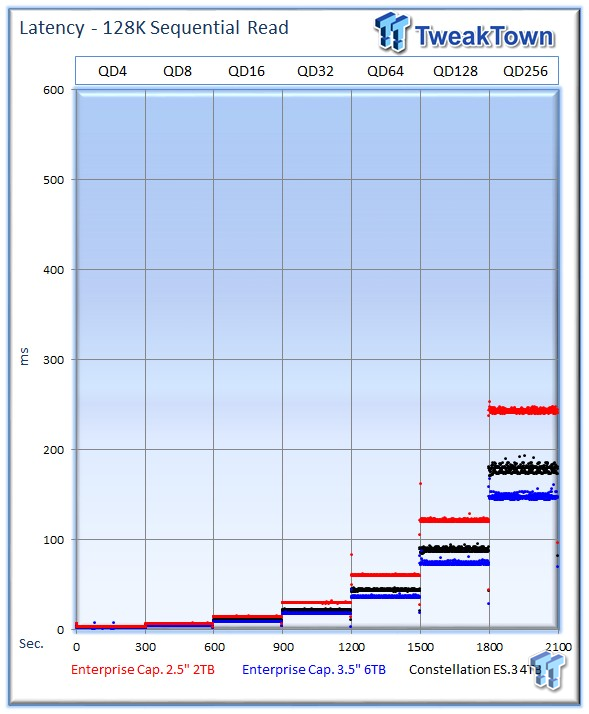
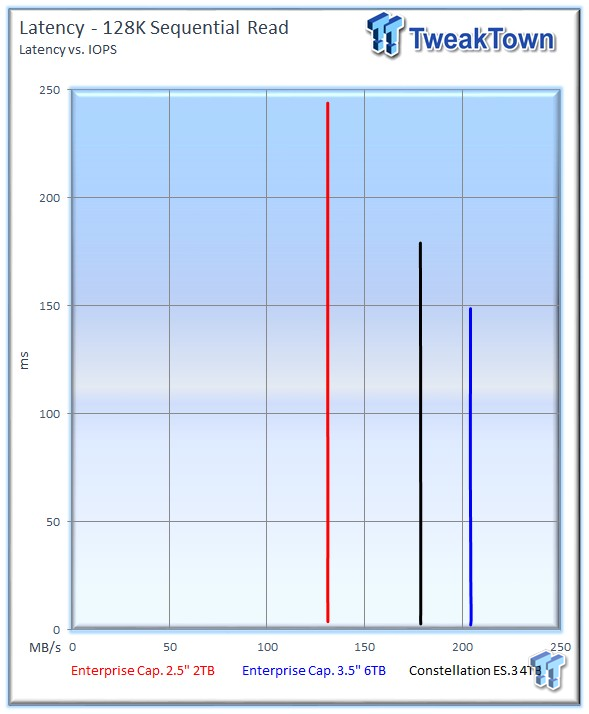
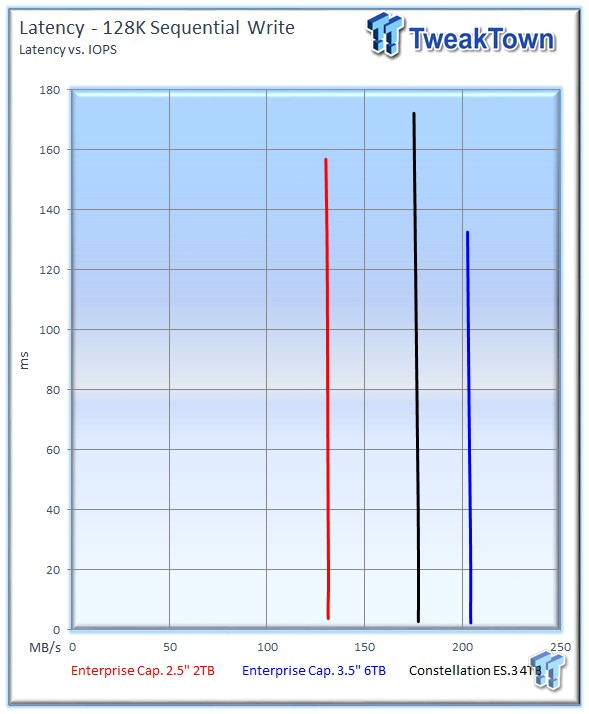
The faster sequential performance of the 6TB version equates to much lower latency during the test.
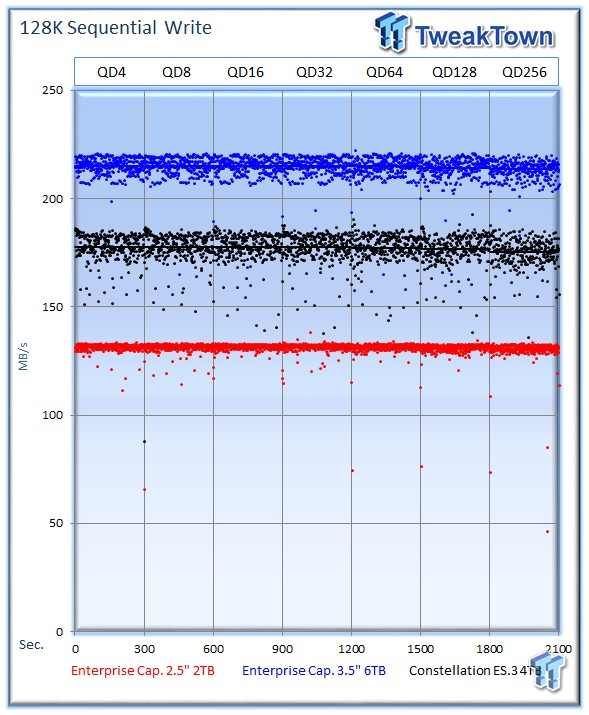
Sequential write performance is important in tasks such as caching, replication, HPC, and database logging. The 2TB drive averages 130 MB/s, well below the 213 MB/s for the 6TB version, and 175 MB/s for the 4TB ES.3.
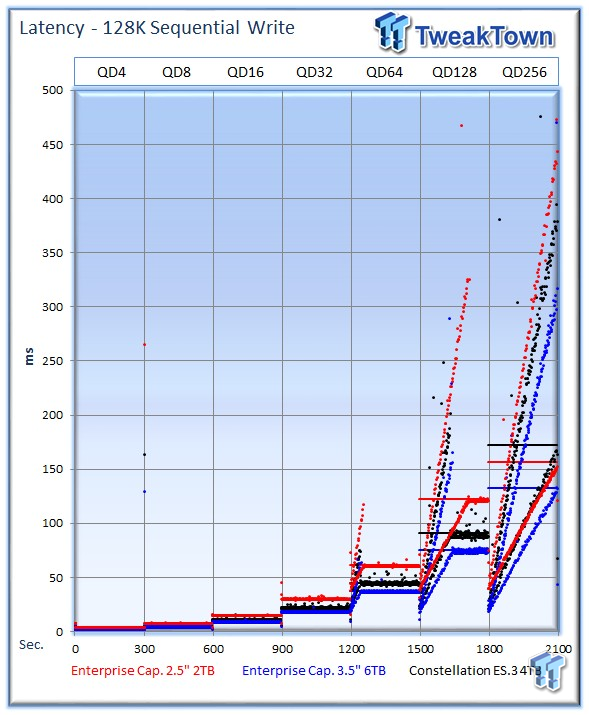
The 6TB Enterprise Capacity delivers the best IOPS-v-Latency performance.
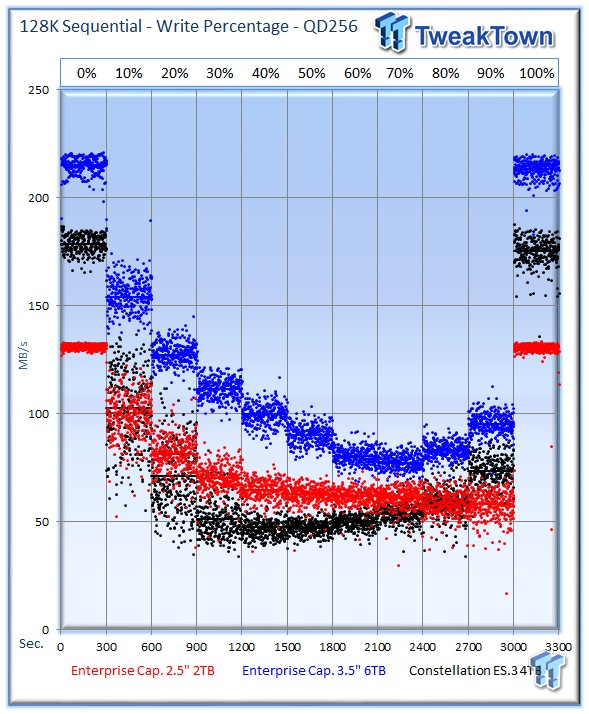
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity manages to best the ES.3 during the mixed sequential testing, but lags behind its larger 6TB counterpart.
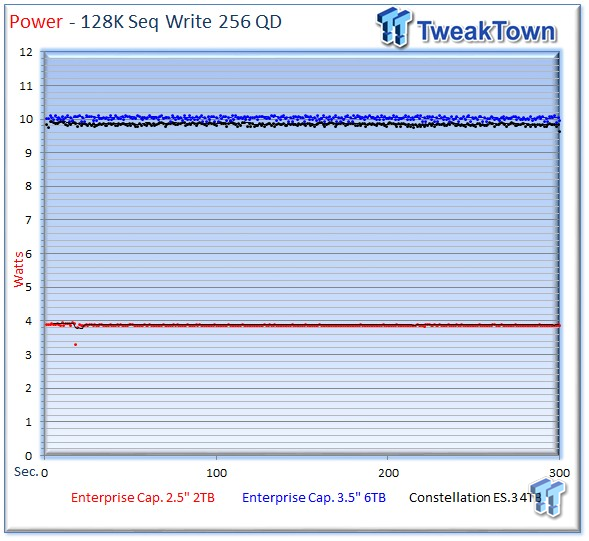
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity averages a mere 3.88 watts.
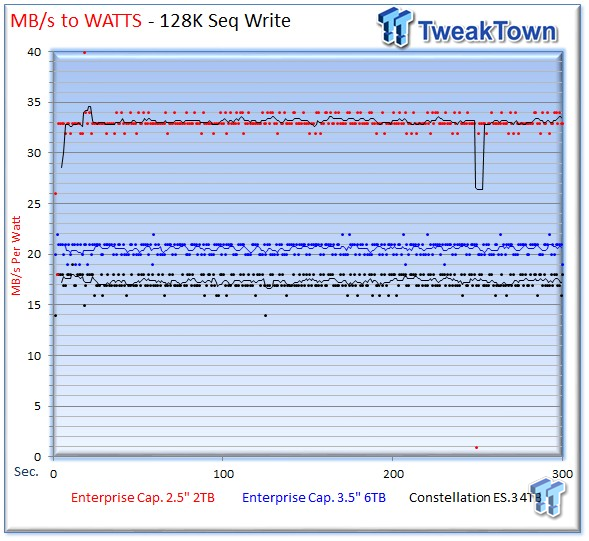
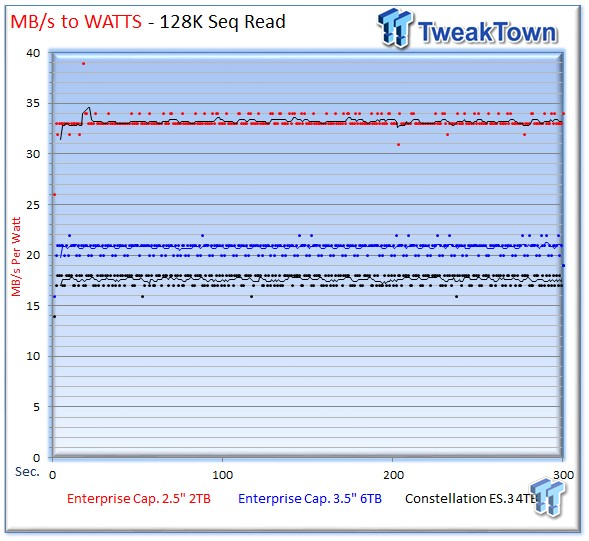
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity still manages to offer incredible efficiency in spite of the slower performance, with an impressive average of 33 MB/s for read, and 32 MB/s-per-watt for write.
Benchmarks - Database/OLTP and File Server
Database/OLTP
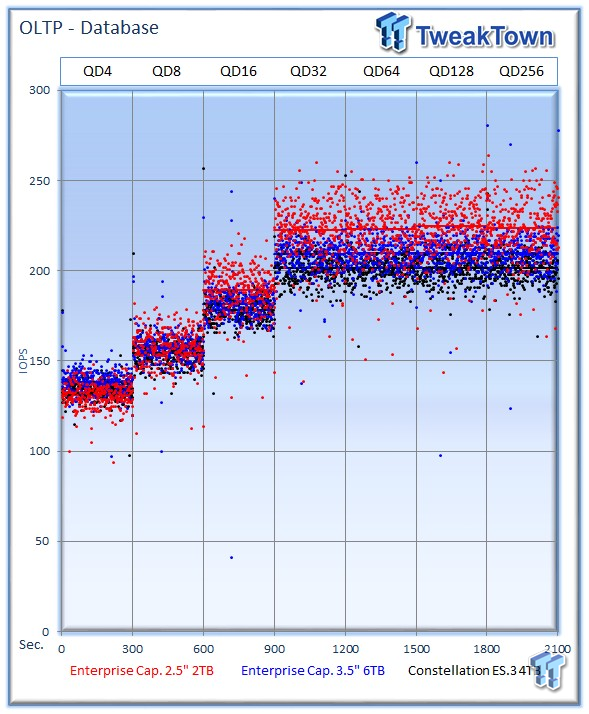
This test consists of Database and On-Line Transaction Processing (OLTP) workloads. OLTP is the processing of transactions such as credit cards and high frequency trading in the financial sector. Databases are the bread and butter of many enterprise deployments. These demanding 8k random workloads with a 66 percent read and 33 percent write distribution bring even the best solutions down to earth.
The 2TB drive delivers an impressive 223 IOPS at QD256 during this demanding test. The 6TB also offers great performance with 210 IOPS, and the ES.3 provides 201 IOPS.
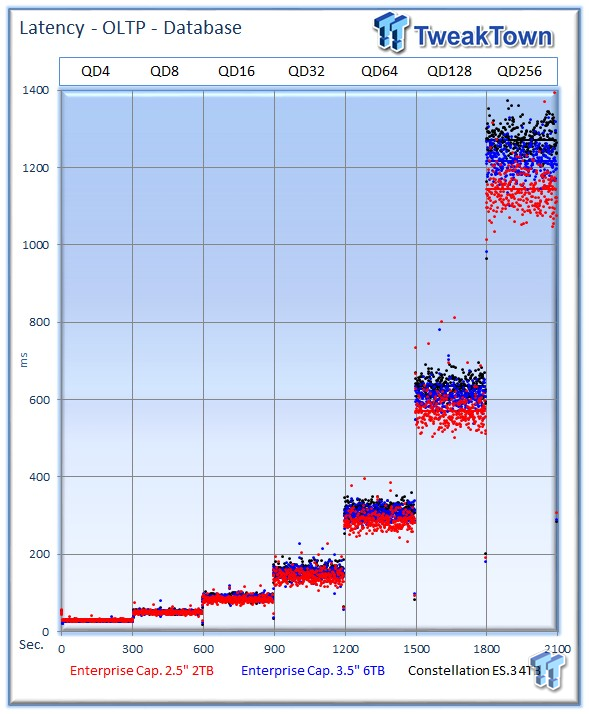
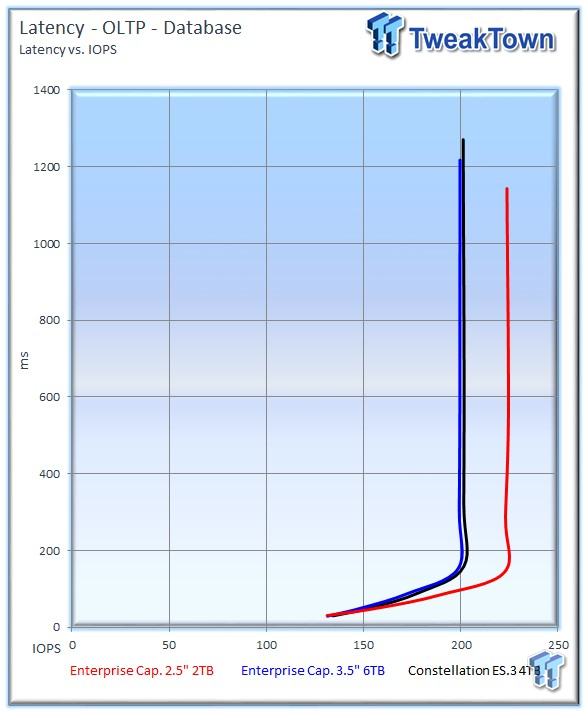
The 6TB Enterprise Capacity came close in performance, but the 2TB version manages to deliver better latency-v-IOPS characteristics.
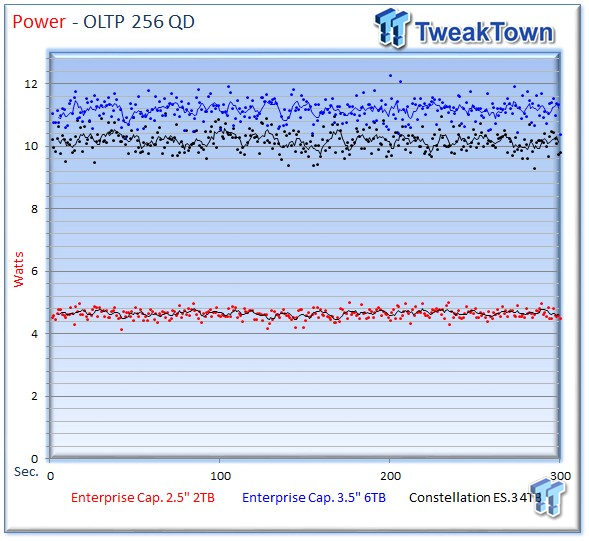
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity requires an average of 4.65 watts during the transactional workload.
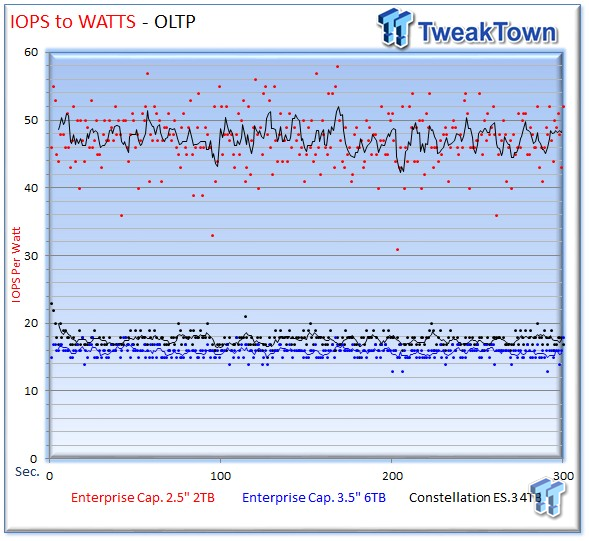
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity provides an outstanding 47 IOPS-per-watt.
File Server
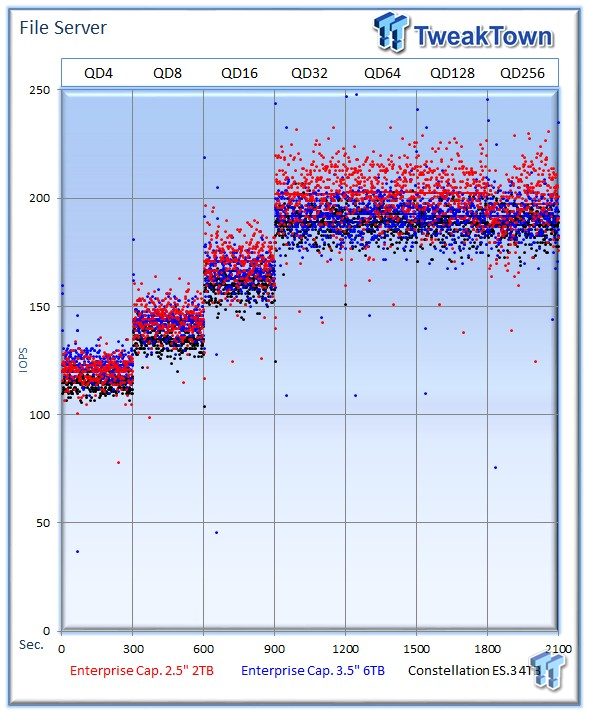
The file server workload consists of typical file server activity. This profile tests a wide variety of different file sizes simultaneously, with an 80% read and 20% write distribution.
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity provides 197 IOPS at QD256, followed closely by the 6TB variant with 191 IOPS. The ES.3 averages 187 IOPS.
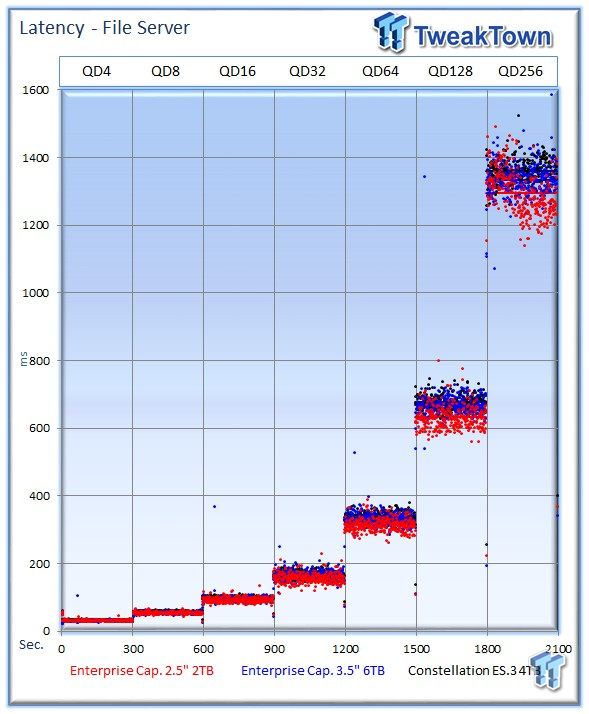

The ES.3 manages to come in second in latency-v-IOPS measurements.
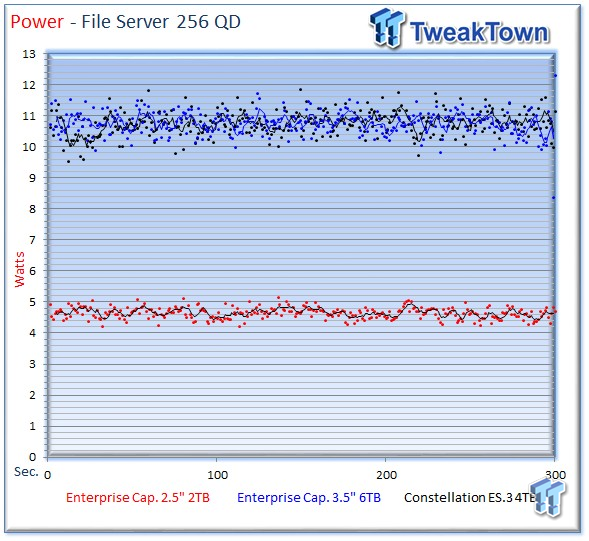
The 2TB drive continues to offer amazingly low power consumption with an average of 4.65 watts during the fileserver workload.
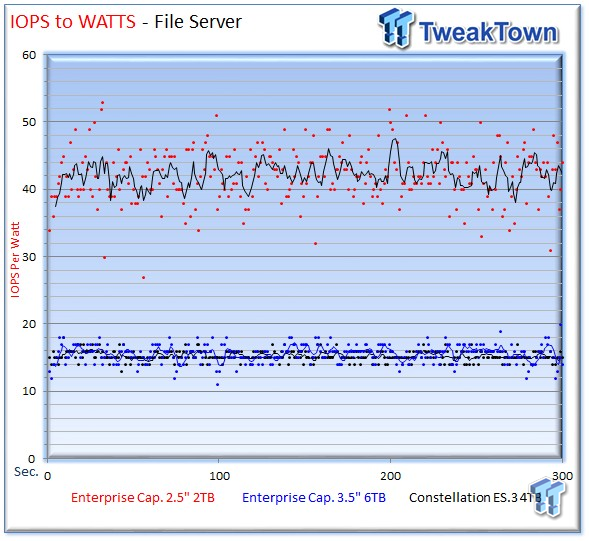
The 2TB drive offers 42 IOPS-per-watt during the measurement window.
Benchmarks - Email Server
Email Server
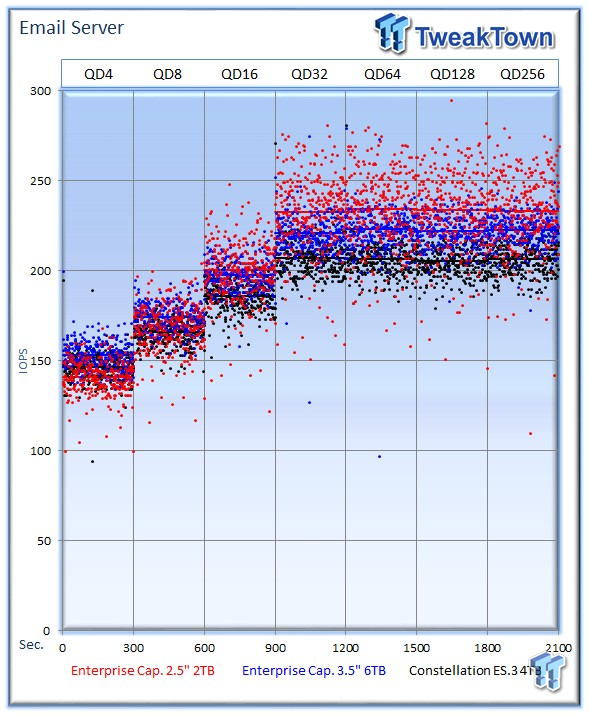
The email server workload is a demanding 8K test with a 50% read, and 50% write distribution. This application is indicative of the performance in heavy write workloads.
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity leads the charts again with an average of 232 IOPS at QD256. The 6TB comes in a close second with 222 IOPS, and the ES.3 delivers 206 IOPS.
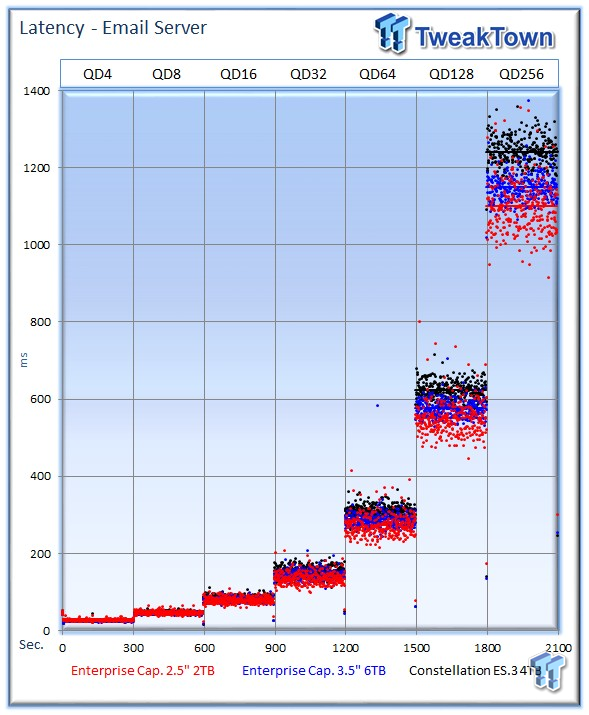
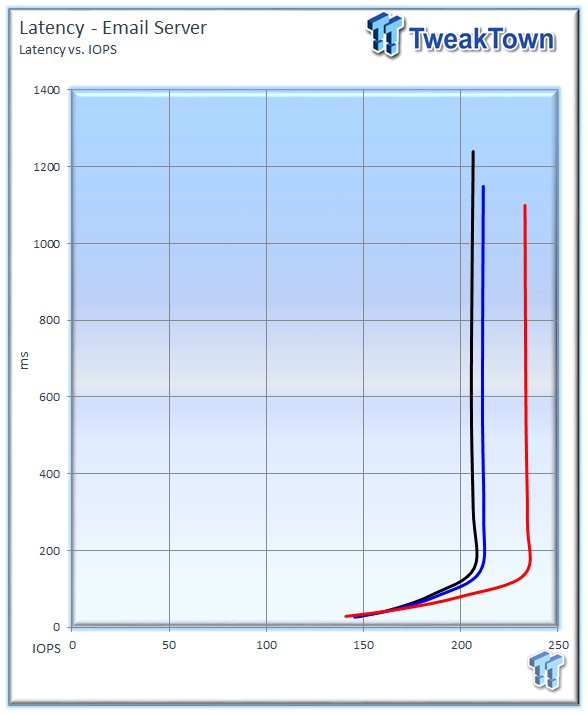
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity delivers much better latency during the measurement window.
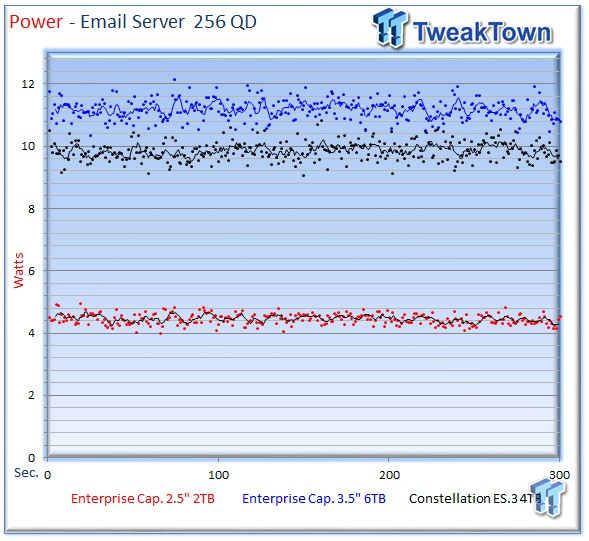
The 2TB averages 4.46 watts during the email server workload.
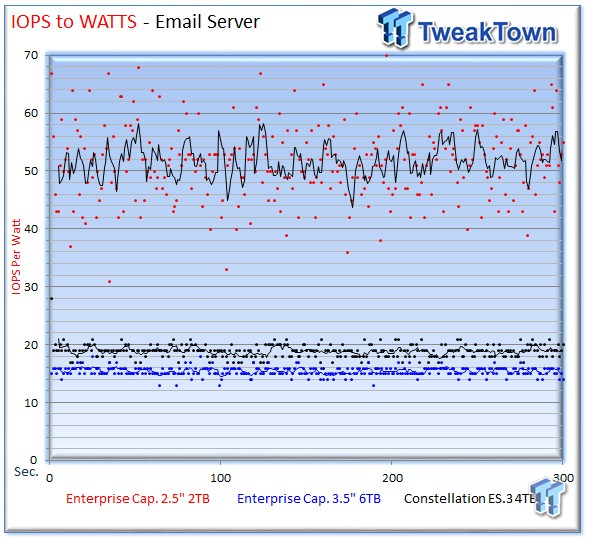
The 2TB Enterprise Capacity offers 51 IOPS-per-watt during the measurement window.
Final Thoughts

HDDs are experiencing increased competition from SSDs in many aspects, but remain the go-to solution for capacity applications. The two technologies are destined to co-exist in the datacenter, and caching and tiering solutions merge the positive aspects of both solutions to accelerate workloads, and provide robust storage capacity. Datacenters are evolving to accommodate both forms of media and leverage their respective strengths to deliver the best overall solution.
New architectures, such as the Open Compute initiative, and new VSAN architecture, are designed from a system level to rely upon both forms of media, furthering intertwining the two technologies. These approaches also offer administrators wide latitude in the type of solutions they deploy into their architecture.
The Seagate Enterprise Capacity 2.5 HDD v3 steps in and offers a big capacity boost for space-constrained server and NAS/SAN applications. The slim form factor provides flexibility to deploy the drives into a number of applications, and enhanced density and lower power consumption address several pain points in the datacenter.
The Enterprise Capacity touts an 18% increase in sequential workloads, and best-in-class performance for the 2.5" 7,200-RPM segment. In our sequential testing, we found that the Enterprise Capacity v3 delivers fast sequential speed, and performance in mixed sequential workloads actually beat out the Constellation ES.3. The Enterprise Capacity v3 performance came in second to the speedy 6TB Enterprise Capacity.
In random testing, the Enterprise Capacity 2.5 HDD v3 delivered tremendous performance that surpassed the other drives in the test pool. Random workload performance was incredibly impressive with 4k and 8k workloads, and the v3 also demonstrated impressive strength in mixed random workloads.
The Enterprise Capacity v3 delivered excellent performance in our OLTP, fileserver, and email server workloads. The Enterprise Capacity v3 also exhibited excellent latency characteristics in our random workload latency-to-IOPS comparisons that easily outpaced the larger capacity drives in the test pool.
The most impressive test results actually came during power testing. The Enterprise Capacity v3 delivered a massive win in idle power draw, and even under heavy workloads, the gap remained large between it and the competition. The radically lower power consumption in tandem with increased performance contributed to a big win in every IOPS-per-watt test. Even with expected lower sequential speed, the Enterprise Capacity v3 managed to score a win in IOPS-to-MB/s measurements.
The Seagate Enterprise Capacity v3 offers the features we have come to expect from enterprise-class HDDs, such as an available dual-port 12Gb/s SAS connection, SED and FIPS options, Seagate Instant Erase, support for the RAID Rebuild functionality, and a five-year warranty. Pairing high performance with low power consumption, and a hefty dose of capacity in a small form factor, creates a compelling offering with class-leading attributes, winning the TweakTown Editor's Choice Award for the 2.5" capacity segment.
