AMD has made its new Ryzen 7040U series official, with the launch of two parts of that series: the Ryzen 5 7545U and Ryzen 3 7440U processors, which will both feature smaller Zen 4c cores that is currently used in the EPYC family of processors.

The special thing about AMD's new Ryzen 7040U series CPUs is that they're the first to feature a hybrid-style architecture with performance-focused and efficiency-based cores, similar to how Intel uses a hybrid design with P-Cores and E-Cores on their Core CPUs.
Now, AMD is saying it has even better performance with its new processors over the competitor, and they all feature "AMD Ryzen AI" technology. AI will be a huge focus moving forward on CPUs over the coming months -- Intel's new Meteor Lake packs an AI chip -- and Microsoft will change to "AI PC" recommendations and scores on systems in 2024.
What does the 'c' stand for? The 'c' in Zen 4c stands for 'Cloud' as the Zen 4c cores are borrowed from AMD's datacenter-focused EPYC family of processors.
Starting with how the Zen4c cores work, where they share the same instruction set as the regular Zen 4 cores, where both sets of CPU cores run at the same frequency. The Ryzen 5 7545U processor features 6 cores and 12 threads at up to 4.9GHz, with 22MB of cache, the Radeon 740M GPU, and a 15-30W TDP. Under that, we've got the Ryzen 3 7440U processor with 4 cores and 8 threads at up to 4.7GHz, also with Radeon 740M graphics, 12MB of cache, and a 15-30W TDP. Both of these processors include "Zen 4c".
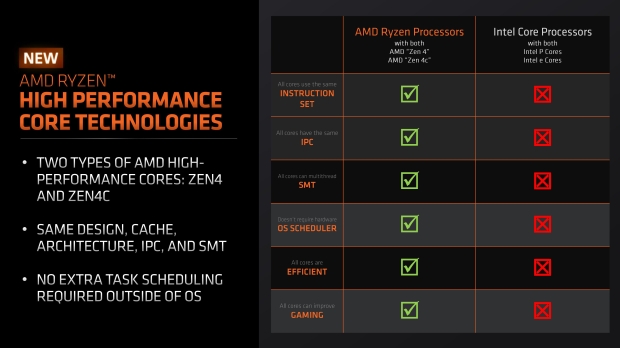
Do you need to do anything to make Zen 4c cores work? Nope, there's no OS scheduler activation, the operating system doesn't need to do anything or any software needs to be installed to work out where the cores go and how they're used when you're gaming on a Zen 4c-based Ryzen 7040U series CPU. Awesome.
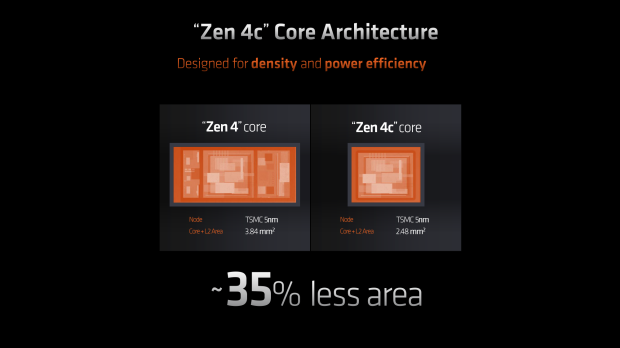
The new Zen 4c cores are designed for density and power efficiency, with Zen 4c cores using 35% less area than regular Zen 4 cores, while both are made at TSMC on the 5nm process node.
AMD is using its Zen 4c cores in notebooks for a few reasons: efficiency, scalability for premium products, and scalability for entry-level products. With efficiency, the smaller Zen 4c cores with the same IPC can use less power, all while providing more performance below that impressive 15W TDP.
While on higher-end products, the smaller Zen 4c cores with the same IPC will open up potential future core count increases of processors in the premium segment. The lower-end will use the smaller cores of Zen 4c while the same IPC allows AMD to deliver more options for consumers.
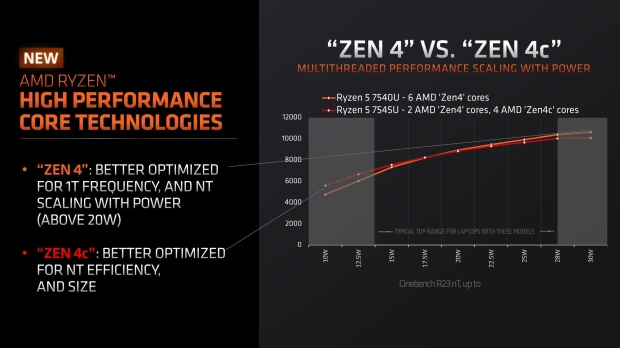
AMD's new high-performance core technologies are split into two: Zen 4, which is better optimized for 1T frequency, and NT scaling with power (above 20W); meanwhile, the Zen 4c cores are better optimized for NT efficiency and size.
We'll see new products featuring the AMD Ryzen 7040U series shortly.



