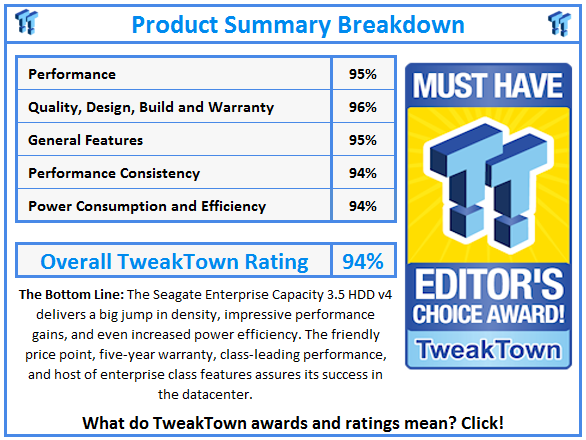
Introduction
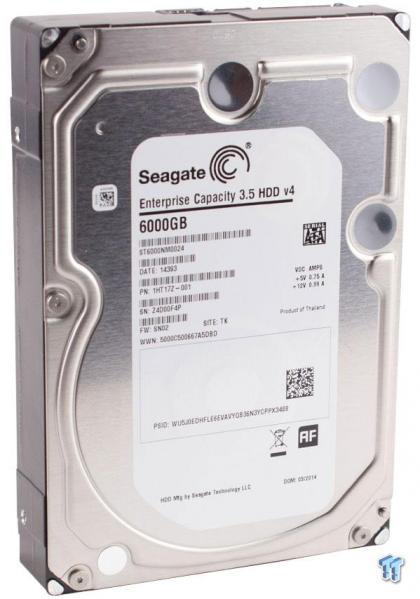

The amount of data in the world is endlessly multiplying, heading towards a projected 40 trillion gigabytes by 2020, but IT budgets are not increasing at such a rapid clip. Seagate's release of their 6TB nearline Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 addresses the need for more capacity in the datacenter. Comparisons to the only other available 6TB drive, the HGST Ultrastar He6, are unavoidable. While HGST only extends the benefits of their helium-infused He6 to the 6TB capacity, Seagate has brought an entire family of 7,200 RPM drives in capacities of 6, 5, 4, and 2TB in the familiar 3.5-inch form factor. The v4 features either a dual-port 12GB/s connection or SATA 6Gb/s.
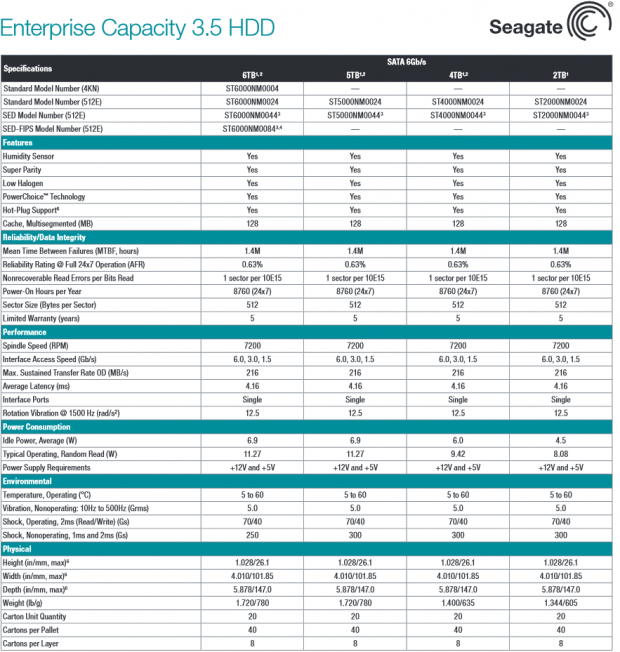
Seagate took an evolutionary tack with their eighth generation platform, while HGST went with a revolutionary new design that relies heavily upon the advantages of helium. Seagate utilizes standard PMR and increased areal density to deliver the 50 percent capacity boost. Areal density jumps 25 percent to 643 Gbits/square-inch, and the new Advanced Format 4KN format helps provide an increase to 1000GB per platter.
The combination of industry-leading areal density and ingenious design leads to a rather conventional approach to capacity expansion. Several architectural design modifications enable the addition of a sixth platter, one fewer than the HGST drive. Seagate added another inertia actuator to reduce coil size and reduced the thickness of the base plate. Adding two more heads required a novel approach to combat turbulence-induced head flutter and vibration. Seagate employed a top disk separator plate to improve airflow, a less radical design than the helium in the HGST design.
One of the immediate concerns with larger capacity HDDs are RAID rebuild times. These can stretch into days with current 4TB drives. This has led to the exploration of new approaches, such as object storage, to remove the requirement for RAID. The Seagate v4 has RAID Rebuild functionality built-in. RAID Rebuild, part of the SAS standard, allows communication between the drive and a RAID controller to perform targeted rebuilds. These surgical rebuilds can remove the requirement for rebuilding an entire array. This technology is offered on some previous-generation Seagate HDDs, but widespread support from RAID controller vendors is just now becoming a reality. The Seagate Enterprise Capacity v4 is also faster than its 6TB competitor, which significantly reduces rebuild time.
The Seagate v4 supports Super Parity, which adds an extra parity bit to improve data integrity for data at rest. In conjunction with enhanced error correction, the v4 features a standard error rate of 1 per 10^15. The v4's MTBF is 1.4 million hours, and it has an AFR of 0.63 percent while handling nearline workloads of 550TB.
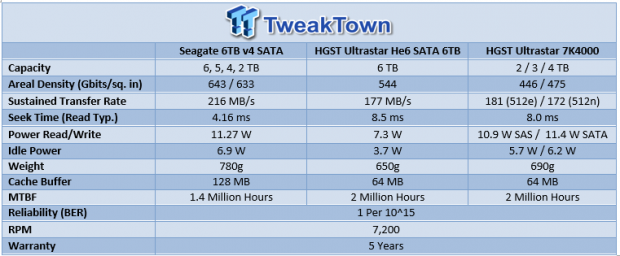
The HGST He6 drastically reduces power consumption by leveraging low-resistance helium to enable thinner, lighter platters. The Seagate v4 build is heftier at 780g due to the increased number of standard-sized platters. The primary difference between the Seagate and HGST offerings are performance and power consumption. Seagate's customer feedback has emphasized a priority for performance over power consumption. The Seagate v4 has higher power draw than its competitor, but it has made significant efficiency gains.
The typical operating power of the Seagate v4 is 11.27W, the same as their previous generation Constellation ES.3. This Seagate v4 exhibits a marked improvement of 1.87W-per-TB, compared to 2.81W-per-TB for the ES.3. The only slight increase over the ES.3 is idle power, which went from 6.73W to 6.9W. The HGST He6 is designed from the ground up for efficiency, even at the expense of performance. This leads to an admirable power consumption of 1.2W-per-TB (operating) and a low 3.7W idle power draw.
The maximum sustained transfer rate of the Seagate v4 is 216 MB/s, which is considerably faster than the He6's 177 MB/s. Another performance differentiator is the faster seek time of 4.16ms for the v4, and the Seagate v4 features a larger 128MB multi-segmented cache buffer.
The philosophies behind the two drives are drastically different even though they cater to the same market. The Seagate v4 looks to provide more storage within the existing power envelope and with increased performance. The HGST He6 unabashedly strives to lower ongoing power consumption to deliver enhanced TCO, even if performance remains on-par, or below, previous generation drives.
For months, we have relied upon both companies' word on the matter, so now let's dive in and see for ourselves.
PRICING: You can find the Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 (6TB) for sale below. The prices listed are valid at the time of writing but can change at any time. Click the link to see the very latest pricing for the best deal.
United States: The Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 (6TB) retails for $596.33 at Amazon.
Canada: The Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 (6TB) retails for CDN$801.39 at Amazon Canada.
Seagate Enterprise Capacity v4 Internals and Specifications
Seagate 6TB Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 Internals
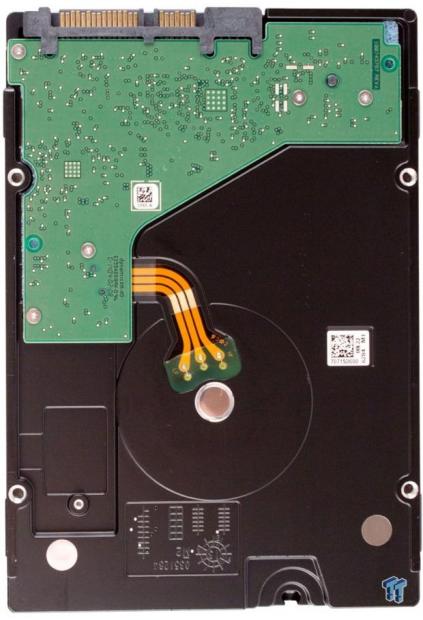


The Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 comes in the familiar 3.5-inch form factor. The breather hole to the upper left of the Seagate logo reminds us of the v4's standard drive architecture. The HGST He6 is a sealed drive and does not require the use of a breather hole, enabling use in immersed and high-humidity environments. The Seagate v4 has a humidity sensor that detects when the drive is above spec and alerts the user. The v4 features ramp load technology and a top-cover attached motor.
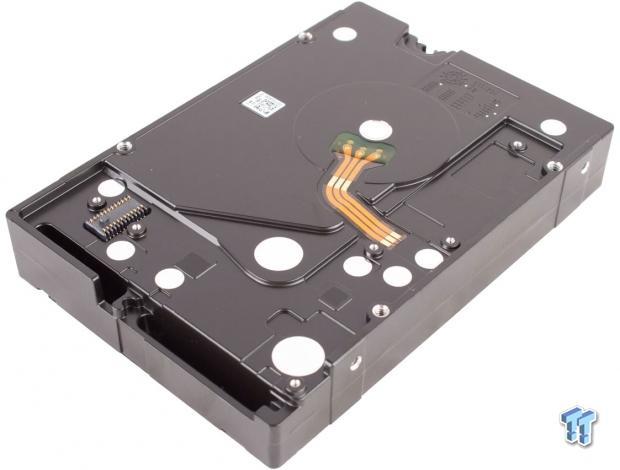

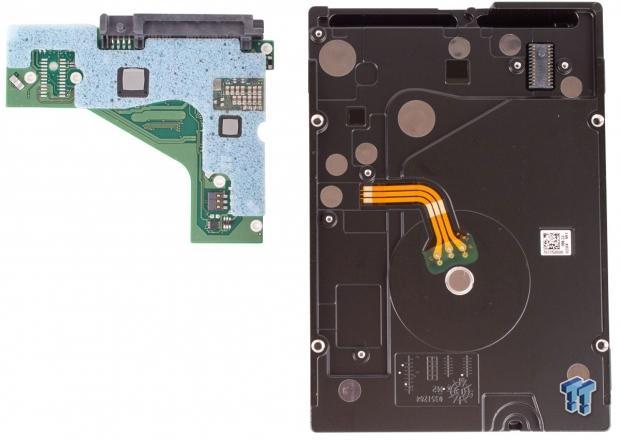
The v4 has a different hole-spacing layout than typical HDDs, lacking two of the typical middle screw emplacements on the side of the drive. The remaining fastener mounts line up with the same mounts on the He6. Both drives feature a modified position on the bottom rear fasteners. Users need to be aware and plan accordingly, but a slight modification of most side-mount trays will suffice.
The foam covering rests between the PCB and the drive to absorb vibration. Thermal pads cover the controller and motor controller to shed heat into the case of the drive. There is a sheer plastic cover over three rows of capacitors on the right edge of the PCB.
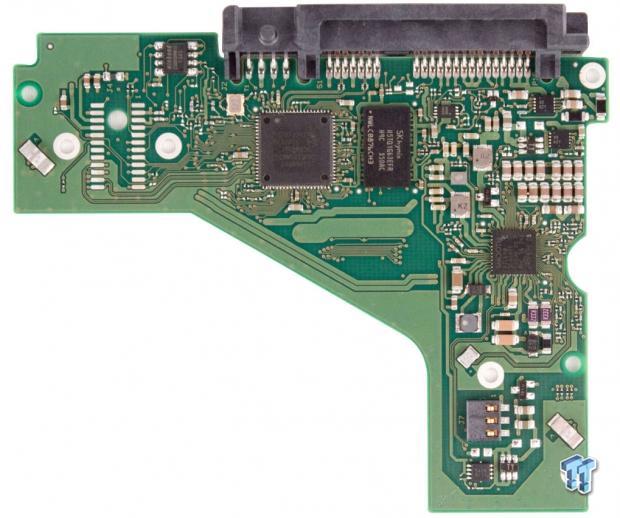

There are no discernible manufacturer markings to identify the drive controller. The SK Hynix memory chip offers 128MB of multi-segmented cache. The SMOOTH drive motor controller resides to the bottom right of the PCB. Two accelerometers occupy opposing corners of the PCB and help counteract drive movement and vibration. The Seagate v4 touts industry-leading rotational vibration tolerance.
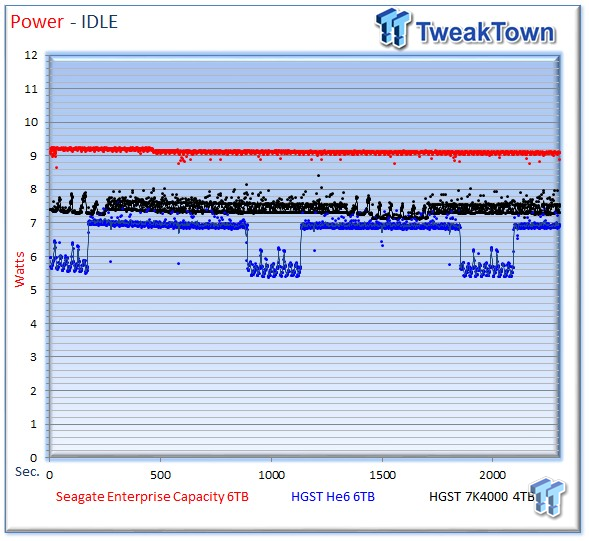
Idle power consumption is a pain point in the datacenter. The Seagate Enterprise Capacity v4 utilizes PowerChoice Technology. PowerChoice is Seagate's proprietary implementation of the T10/T13 Approved Standard. PowerChoice provides four enhanced idle modes that place the drive into deeper quasi-sleep cycles to conserve power. In a typical implementation, the feature is enabled with a SAS Mode Page or SATA Set Feature command. Once enabled, PowerChoice places the drive into successively deeper idle states triggered by the length of drive inactivity.
There is also the option for immediate host-initiated power transitions with SAS/SATA commands. Each consecutive sleep mode requires more time to resume. We test idle power consumption without PowerChoice activated, so there is an option for even lower idle power consumption. We tested idle power and measured the Seagate v4 at 9.1 watts, and the He6 measured in at 7 watts and 5.4-5.5 watts during deeper sleep intervals.
HGST Ultrastar He6 Specifications
The Seagate v4 offers SED models (AES-256) with ISE (Instant Secure Erase). ISE eases drive retirement and repurposing by eliminating the need for physical destruction. Seagate SED drives are typically the same price as standard drives. There is also an SED-FIPS 140-2 model available. The SED-FIPS version is only available at the 6TB capacity point. Seagate is the only drive manufacturer that offers SED-FIPS drives with tamper-evident coverings.
Test System and Methodology

Our approach to storage testing targets long-term performance with a high level of granularity. Many testing methods record peak and average measurements during the test period. These average values give a basic understanding of performance, but they fall short in providing the clearest view possible of I/O Quality of Service (QoS).
'Average' results do little to indicate performance variability experienced during actual deployment. The degree of variability is especially pertinent as many applications can hang or lag as they wait for I/O requests to complete. This testing methodology illustrates performance variability and includes average measurements during the measurement window.
While under load, all storage solutions deliver variable levels of performance. While this fluctuation is normal, the degree of variability is what separates enterprise storage solutions from typical client-side hardware. Providing ongoing measurements from our workloads with one-second reporting intervals illustrates product differentiation in relation to I/O QoS. Scatter charts give readers a basic understanding of I/O latency distribution without directly observing numerous graphs.
Consistent latency is the goal of every storage solution, and measurements such as Maximum Latency only illuminate the single longest I/O received during testing. This can be misleading as a single 'outlying I/O' can skew the view of an otherwise superb solution. Standard Deviation measurements consider latency distribution, but they do not always effectively illustrate I/O distribution with enough granularity to provide a clear picture of system performance. We utilize high-granularity I/O latency charts to illuminate performance during test runs.
We measure power consumption during precondition runs. This provides measurements in time-based fashion, with results every second, to illuminate power consumption behavior. We also present IOPS-to-Watts measurements to highlight efficiency.
Both test 6TB samples feature the SATA interface, and the HGST 7K4000 features a SAS interface. The 7K4000 is used as a representative of the fastest 4TB drive due to its previous-generation leading performance, power consumption, and efficiency. The first page of results will provide the 'key' to understanding and interpreting our test methodology.
Benchmarks - 4k Random Read/Write
4k Random Read/Write
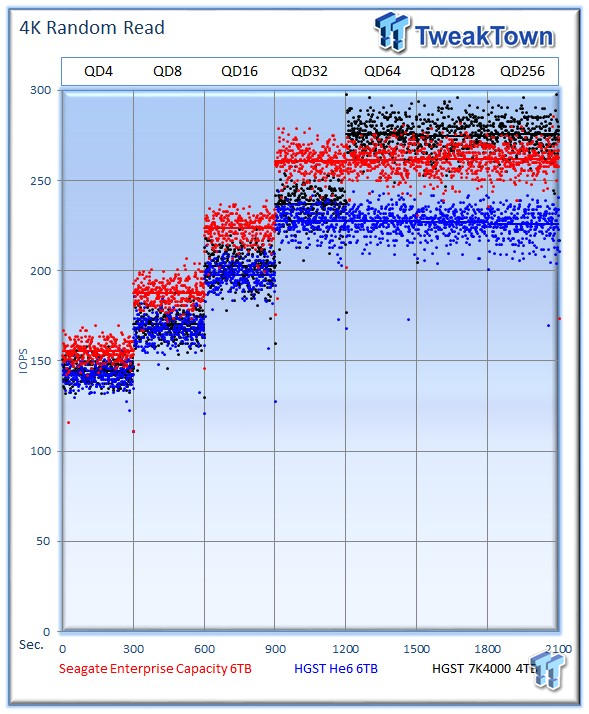
Each level tested includes 300 data points (five minutes of one second reports) to illustrate performance variability. The line for each queue depth represents the average speed reported during the five-minute interval. 4k random speed measurements are an important metric when comparing drive performance as the hardest type of file access for any storage solution to master is small-file random. One of the most sought-after performance specifications, 4k random performance is a heavily marketed figure.
The Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 averages 262 IOPS at QD256, the HGST Ultrastar He6 averages 234 IOPS at QD256, and the 7K4000 delivers an outstanding 275 IOPS. The Seagate v4 falls in this read-only test to the 7K4000 and its SAS connection, but it soundly bests the He6.
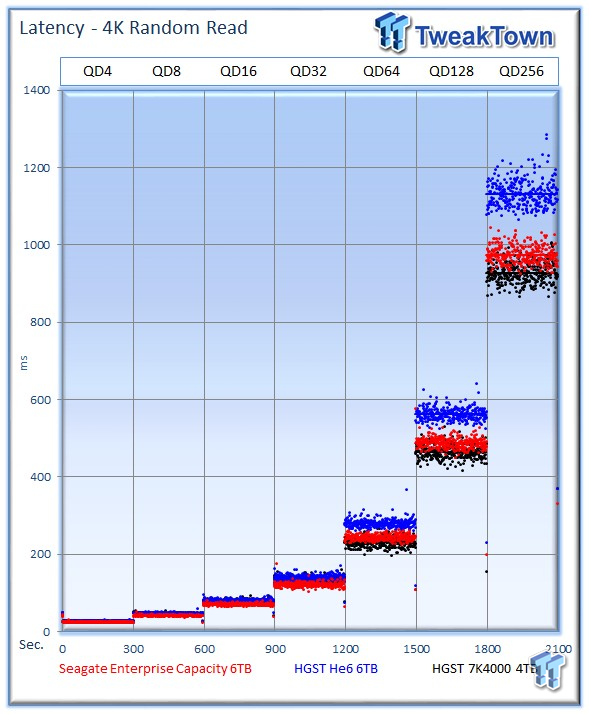
The 7K4000 delivers the lowest latency, and the Seagate v4 delivers a tighter performance profile than the HGST He6 at QD256.
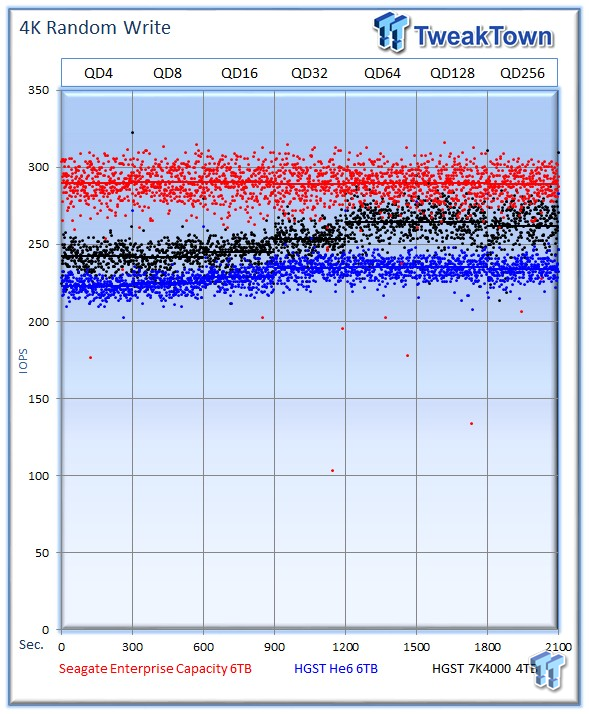
The write workload shines a different light on the Seagate v4, which runs away with the lead by delivering an average of 289 IOPS at QD256. The He6 averages 234 IOPS, and the 7K4000 averages 262 IOPS.
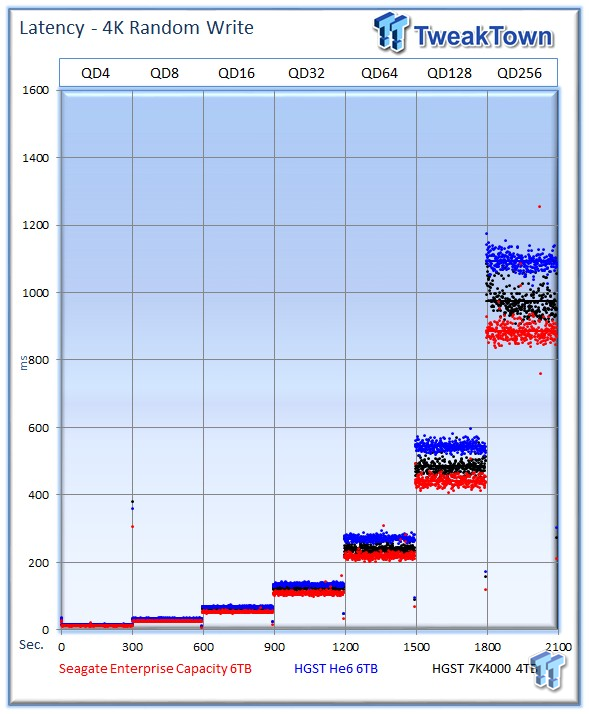
All three drives deliver optimum performance-to-latency ratios at lower queue depths.
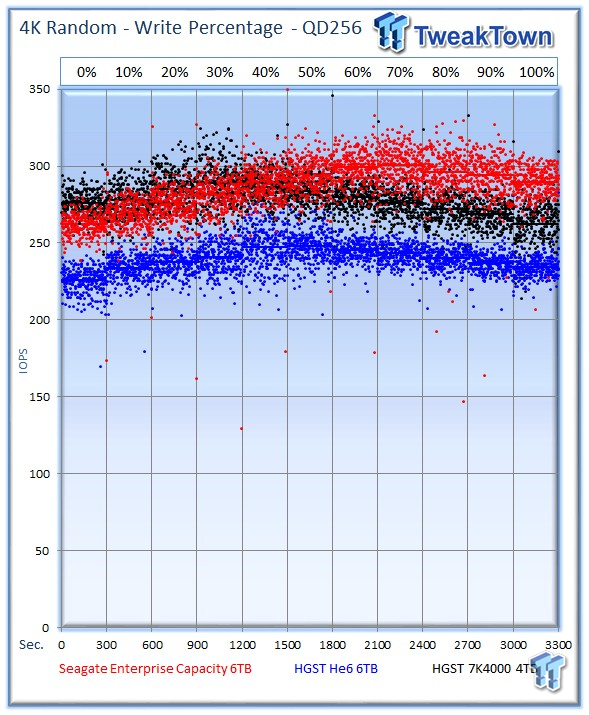
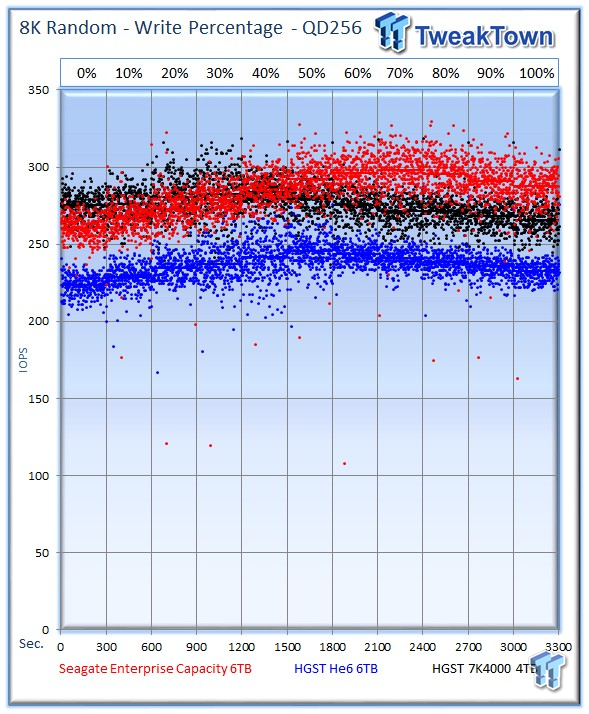
Our write percentage testing illustrates the varying performance of each solution with mixed workloads. The 100% column to the right is a pure write workload of the 4k file size, and 0% represents a pure 4k read workload.
The HGST 7K4000 leans on its impressive read speed to begin the test with a slight lead, but the Seagate v4 leads in seven of the 11 write mixtures.
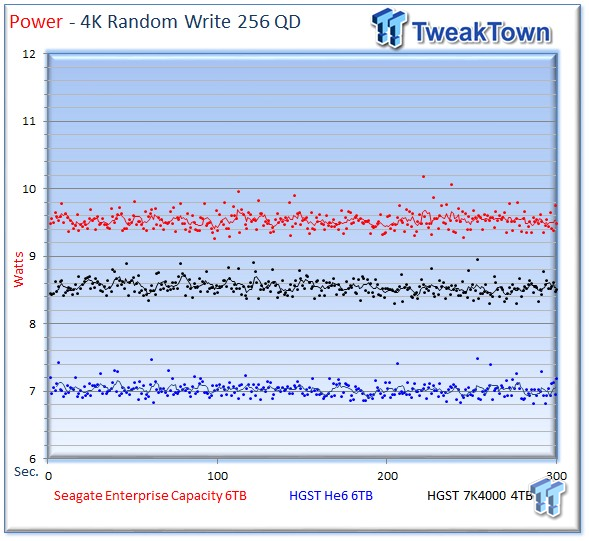
We record power consumption measurements during our test run at QD256. The Seagate v4 averages 9.53 watts, the He6 averages 7.03 watts, and the 7K4000 averages 8.55 watts during the measurement window.
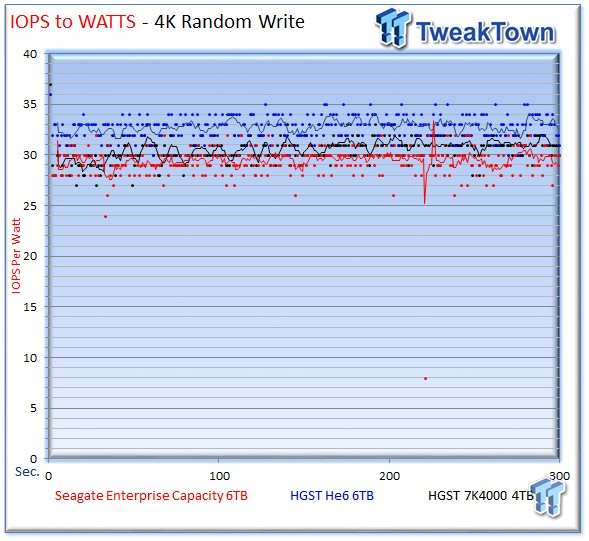
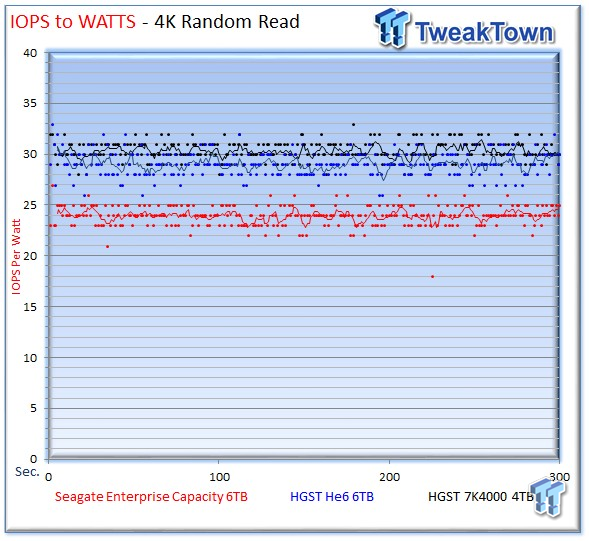
We generate IOPS-to-Watts measurements from data recorded during the test period. The spread for 4k random write activity is within four IOPS-per-Watt from highest to lowest, which is essentially a wash. For the 4k random read workload, the Seagate v4 averages 24 IOPS-per-Watt, the He6 provides 29 IOPS-per-Watt, and the 7K4000 measures 30 IOPS-per-Watt.
The Seagate v4 delivers a surprising level of efficiency in the write workload, and it only falls behind by 6 IOPS for the read workload. Higher performance helps offset the increased power consumption of the v4. The primary power advantage of the He6 is in Watts-per-TB measurements and idle power consumption.
Benchmarks - 8k Random Read/Write
8k Random Read/Write
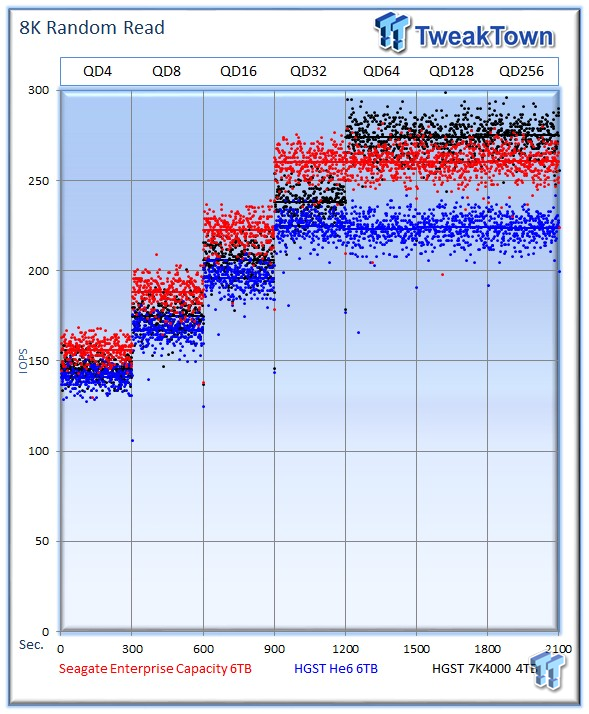
Server workloads rely heavily upon 8k performance, and we include this as a standard with each evaluation. Many of our server tests also measure 8k performance with various mixed read/write workloads.
The average 8k random read speed of the Seagate Enterprise Capacity v4 averages 260 IOPS at QD256, but it reaches its pinnacle faster than the 7K400, which tops out at 275 IOPS. The HGST Ultrastar He6 averages the lowest at 223 IOPS.
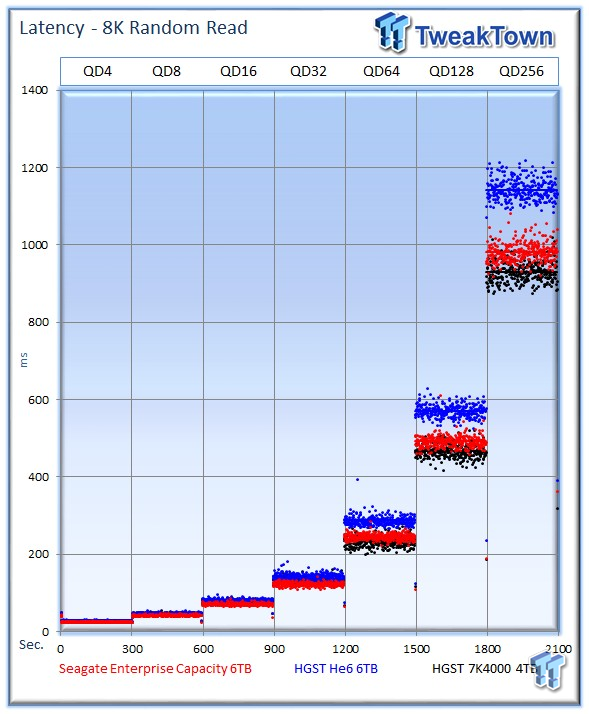
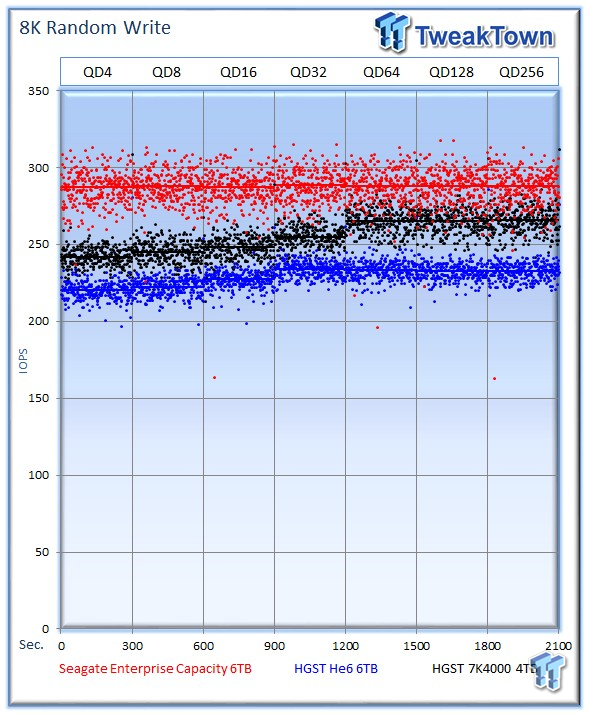
The Seagate v4 leads easily with an average of 289 IOPS at QD256, whereas the He6 offers up 232 IOPS, and the 7K4000 averages a middle-of-the-pack 265 IOPS.
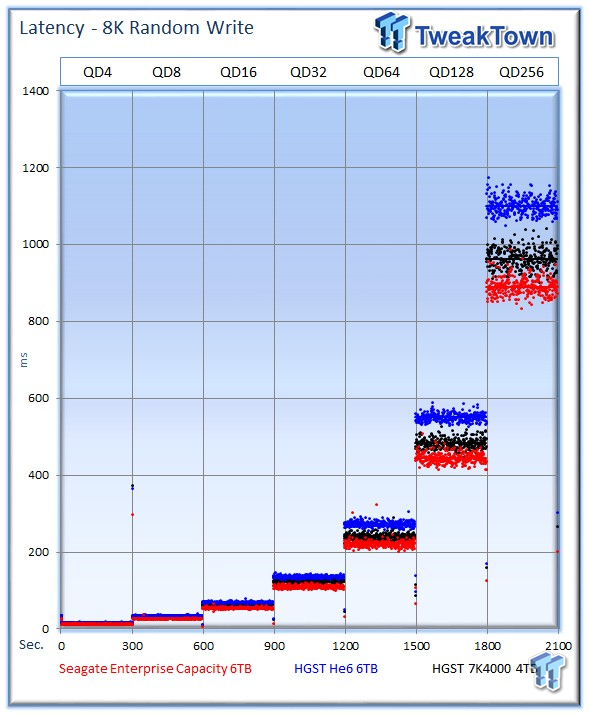
The Seagate v4 once again takes the lead as we mix in more write activity.
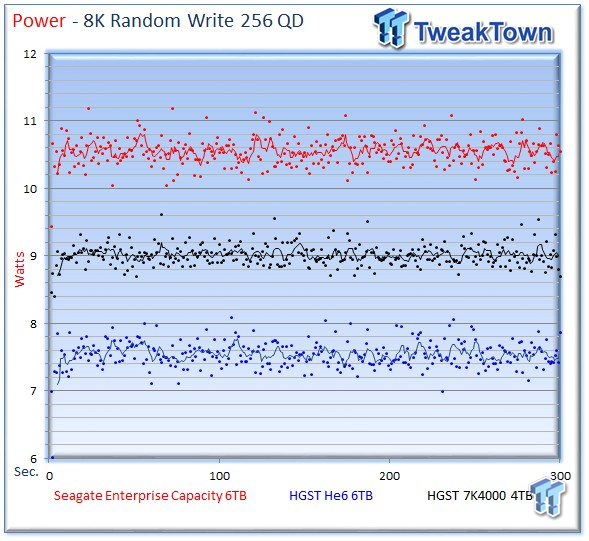
Power consumption for the Seagate v4 averages 10.5 watts, and the He6 averages a miserly 7.54 watts, which is considerably lower than the 7K4000's 9-watt average.
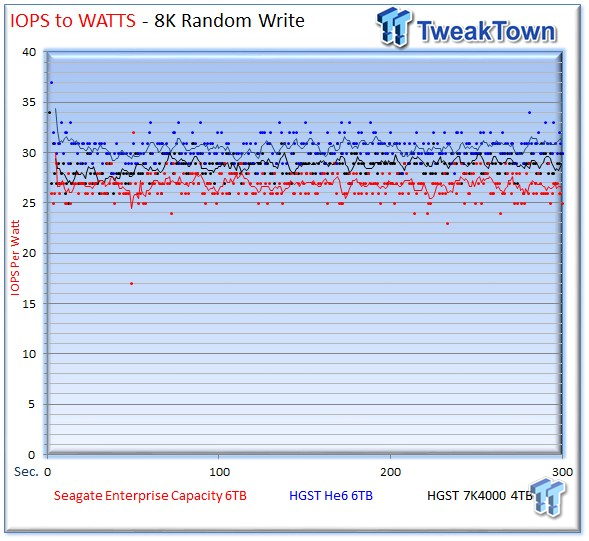
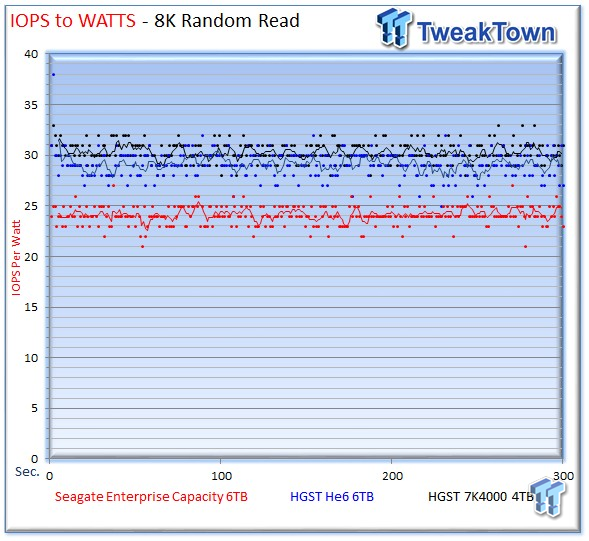
All three drives fall into similar efficiency profiles for write activity, and only three IOPS-per-Watt separate the highest from the lowest. Once again, the Seagate v4 lags behind in read efficiency by roughly five IOPS-per-Watt, surprisingly close considering its higher power consumption under operation.
Benchmarks - 128k Sequential Read/Write
128k Sequential Read/Write
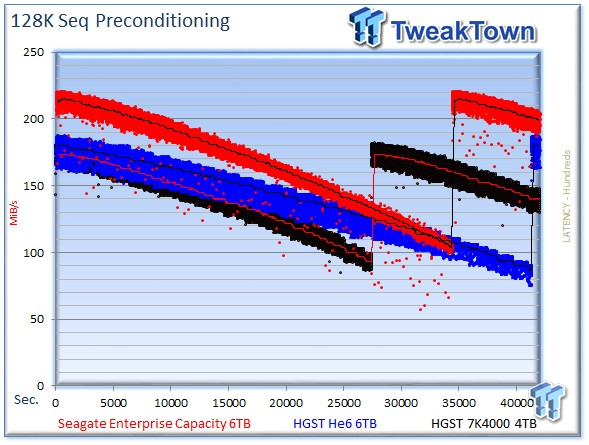
We write to every LBA on both drives to highlight performance degradation from the outer to inner tracks of the drives. The drives begin with much higher speed on the outer tracks: 215 MB/s for the Seagate Enterprise Capacity v4, 180 MB/s for the HGST Ultrastar He6, and 171 MB/s for the 7K4000. As we move to the inner tracks, the Seagate v4 averages 109 MB/s, the He6 falls to a low average of 86 MB/s, and the 7K4000 falls to 93 MB/s. Even at the innermost tracks, the v4 retains a commanding sequential write performance advantage over the competing drives.
The He6 requires 11.5 hours to write the entire 6TB of data, but the Seagate v4 is considerably faster, completing the task in 9.5 hours. The 7K4000 finishes its pass over its smaller 4TB capacity the fastest, taking just 7.5 hours.
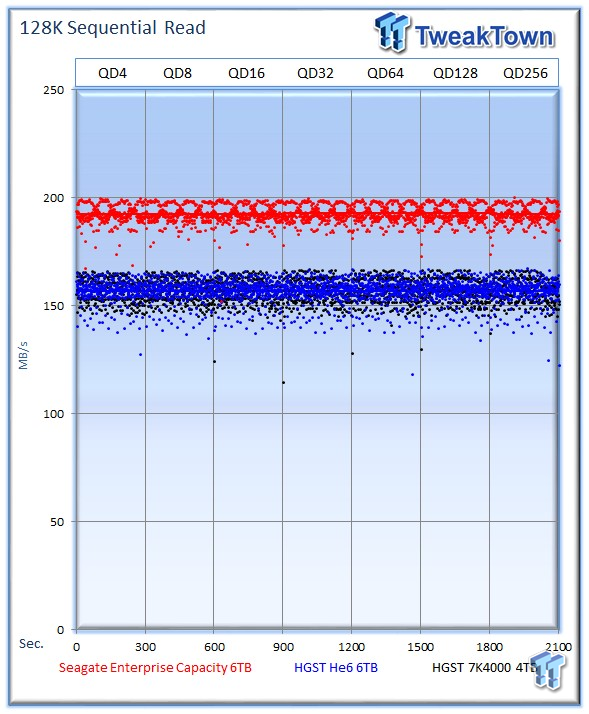
128k sequential speed reflects the maximum sequential throughput of the HDD. The Seagate v4 wins easily with an average of 192 MB/s and exhibits a tight performance profile. The He6 follows with an average of 156 MB/s, and the 7K4000 averages 157 MB/s.
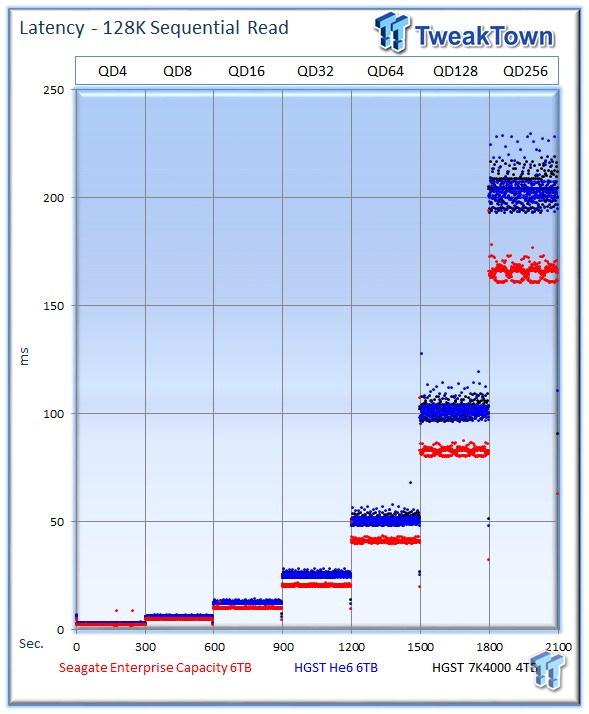
The Seagate v4 provides lower latency across the board with sequential read activity.
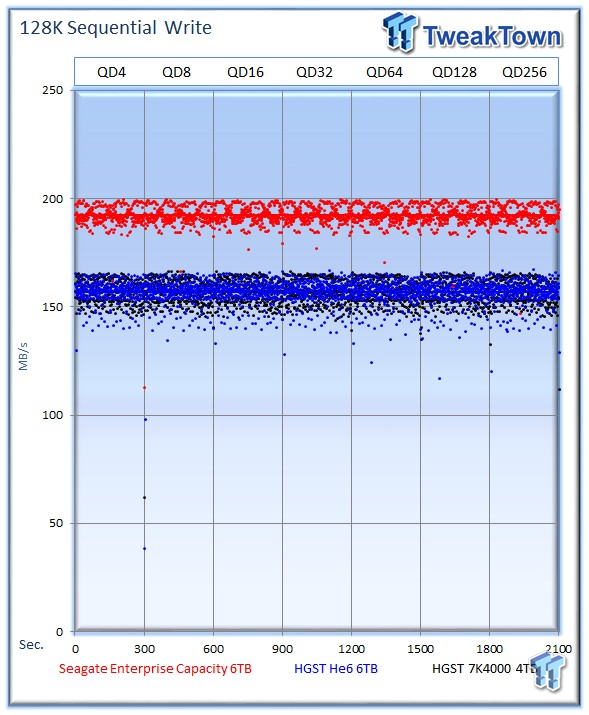
The Seagate v4 leads with an average of 192 MB/s, and the He6 averages 156 MB/s compared to 157 MB/s from the 7K4000.
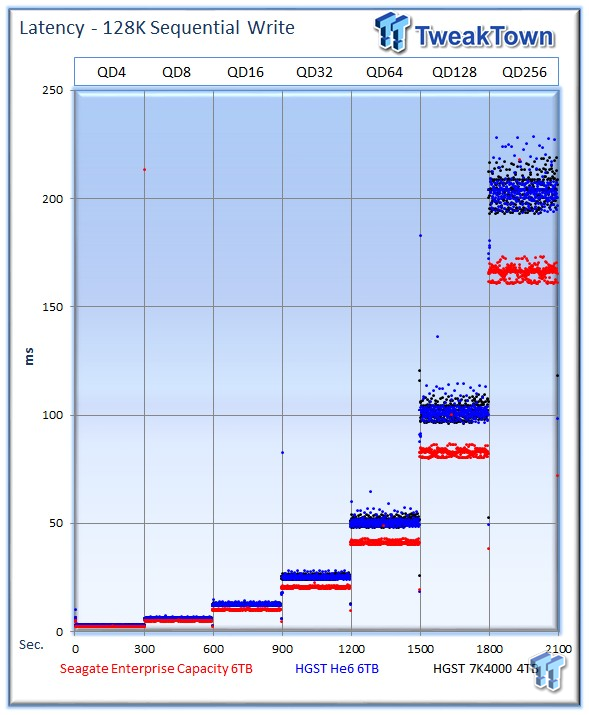
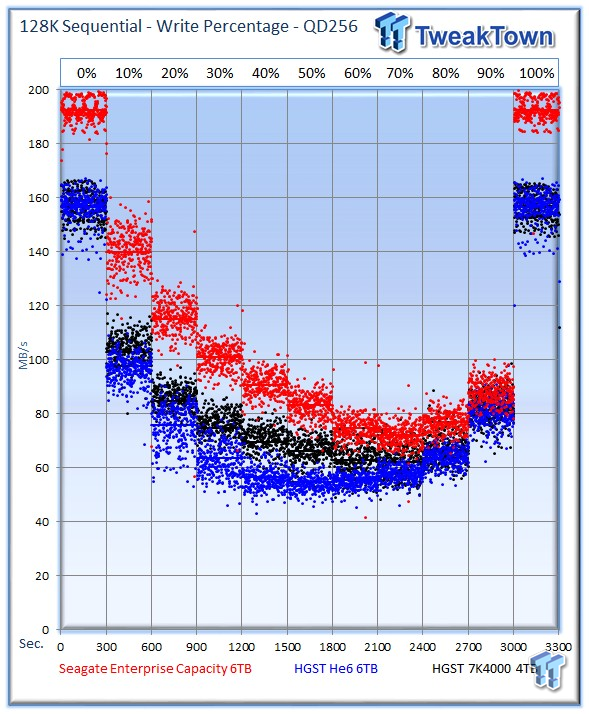
The Seagate v4 dominates the mixed sequential testing, easily running away with the win in every category.
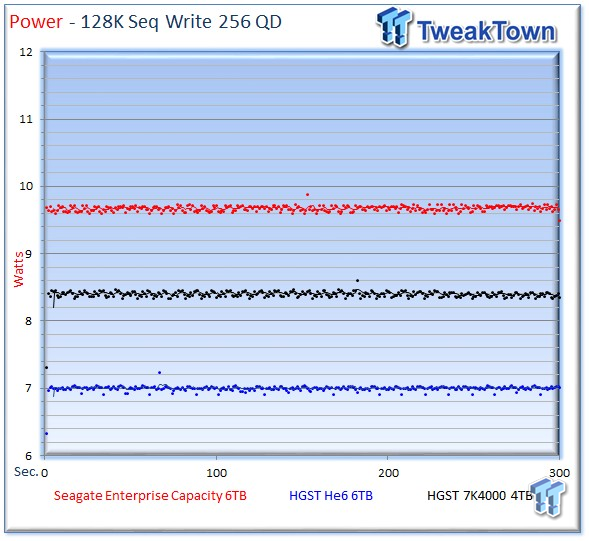
The Seagate v4 averages 9.67 watts, the He6 averages a flat 7 watts, and the 7K4000 averages 8.4 watts.
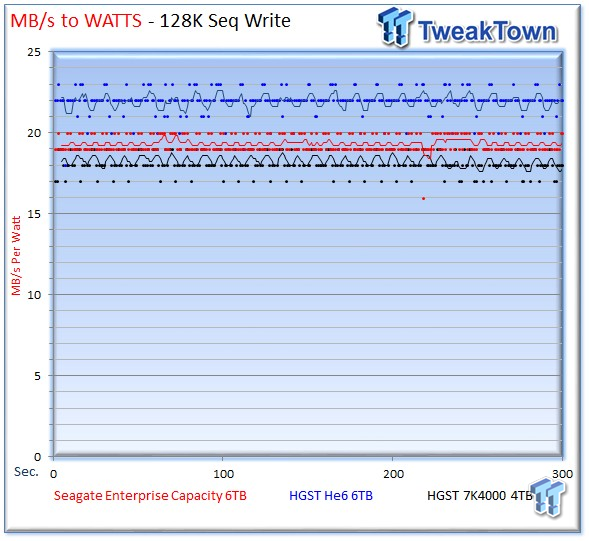
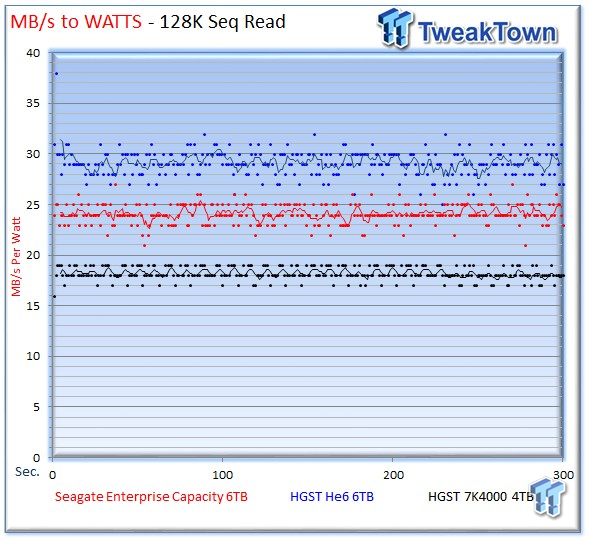
The Seagate v4 benefits from its much higher sequential performance to squeeze past the 7K4000 in write efficiency, and it widens the gap in read efficiency.
Benchmarks - Database/OLTP and File Server
Database/OLTP
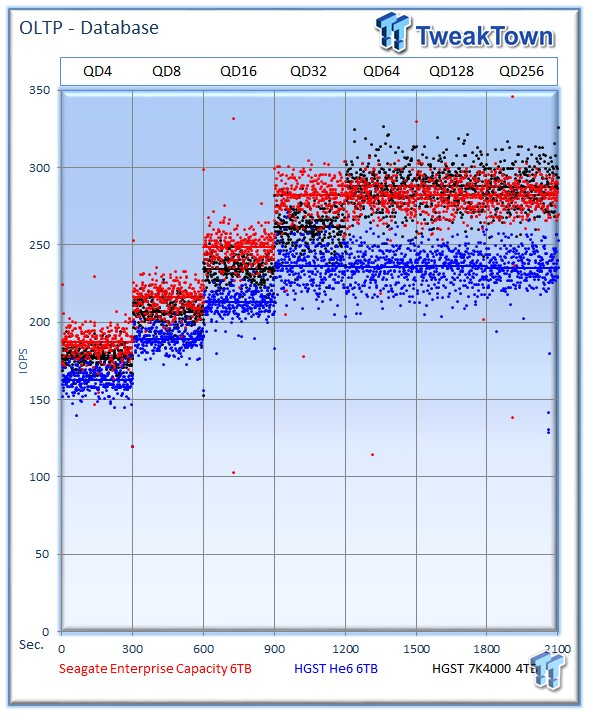
This test emulates Database and On-Line Transaction Processing (OLTP) workloads. OLTP is the processing of transactions such as credit cards and high frequency trading in the financial sector. Databases are the bread and butter of many enterprise deployments. These demanding 8k random workloads with a 66 percent read and 33 percent write distribution bring even the best solutions down to earth.
The Seagate v4 averages 282 IOPS, the He6 235 IOPS, and the 7K4000 averages 280 IOPS at QD256.
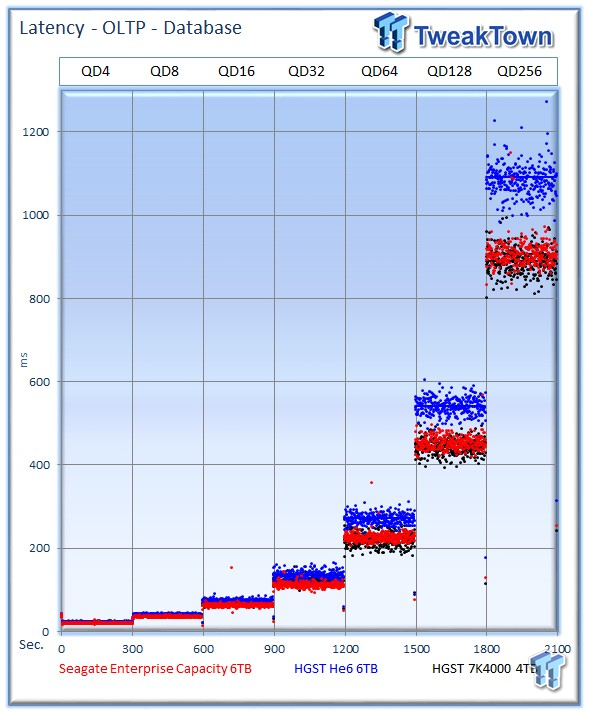
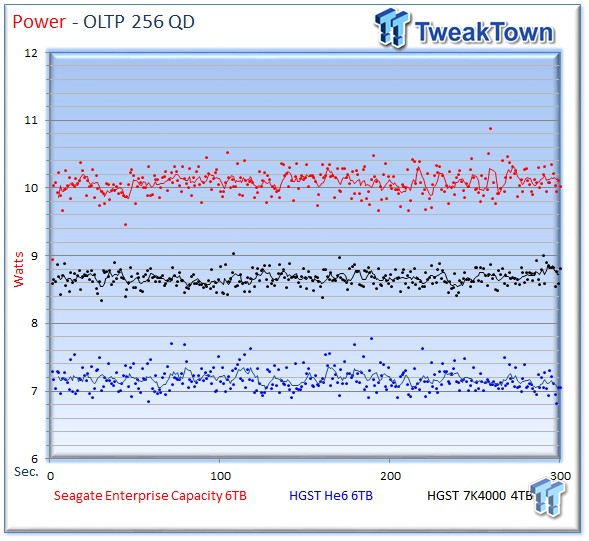
The Seagate v4 averages 10.08 watts, the He6 averages 7.17 watts, and the 7K4000 requires 8.67 watts.
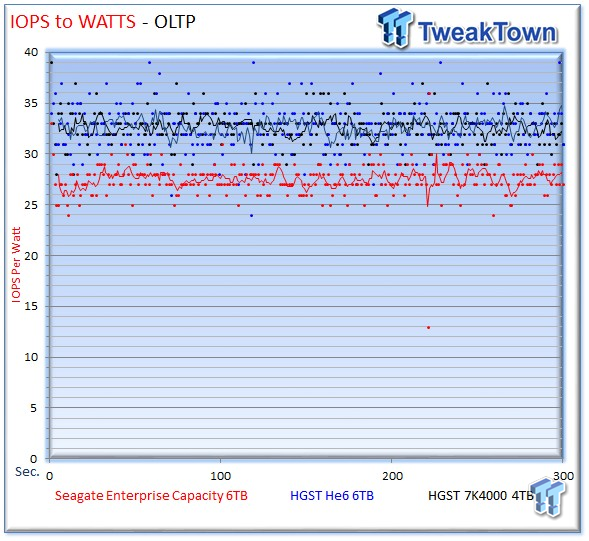
The Seagate v4 averages 28 IOPS-per-Watt, and the He6 averages of 32 IOPS-per-Watt, which is matched by the 32 IOPS-per-Watt from the 7K4000. The Seagate v4 closes the gap in mixed workloads, with only a scant four IOPS-per-Watt difference during the workload.
File Server
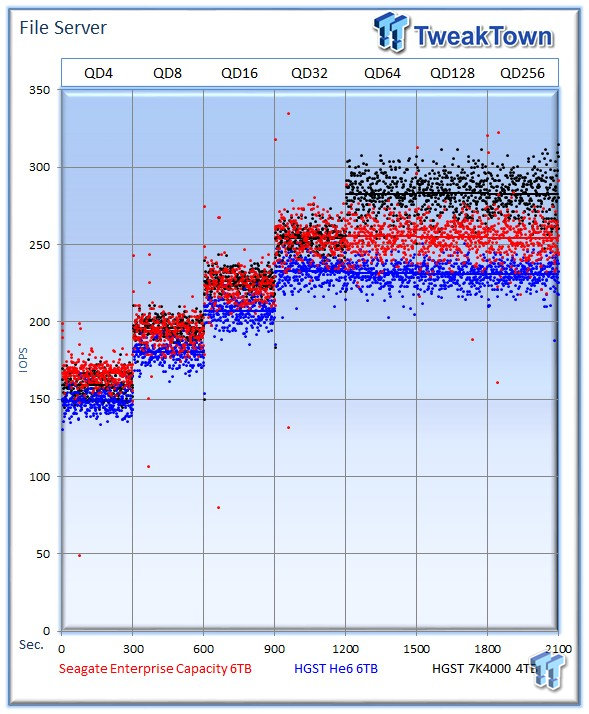
The file server profile represents typical file server workloads. This profile tests a wide variety of different file sizes simultaneously with an 80% read and 20% write distribution.
The Seagate v4 averages 254 IOPS at QD256, the He6 delivers an average of 230 IOPS, and the 7K4000 averages a leading 282 IOPS.
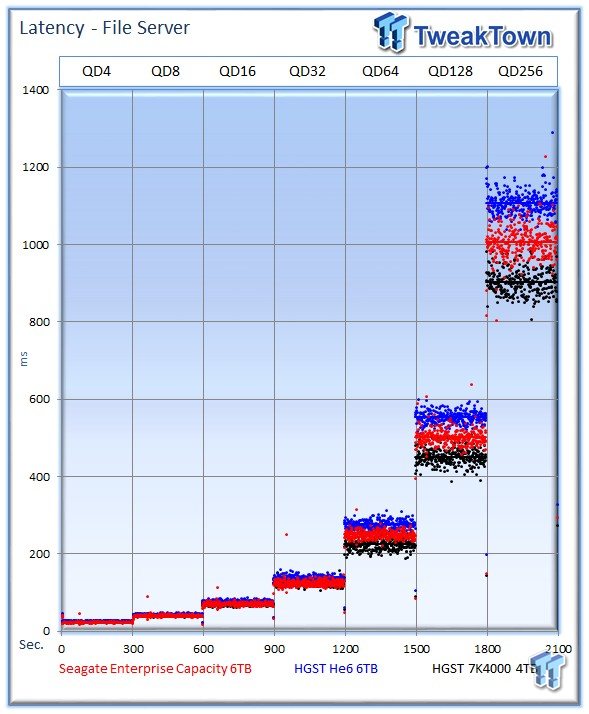
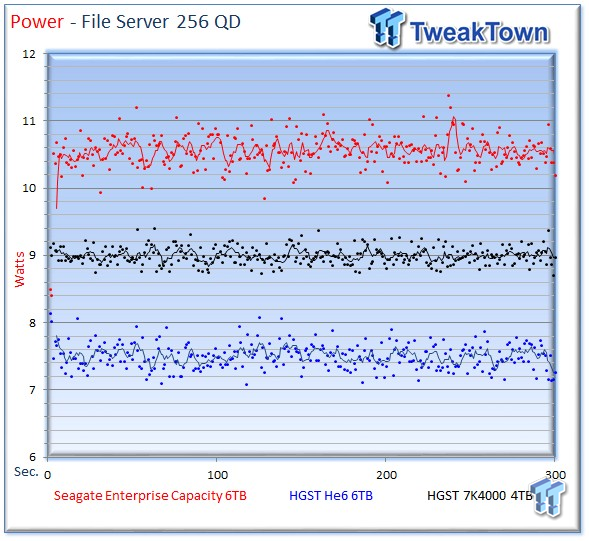
The Seagate v4 averages 10.5 watts, the He6 averages of 7.5 watts, and the 7K4000 averages 9 watts.
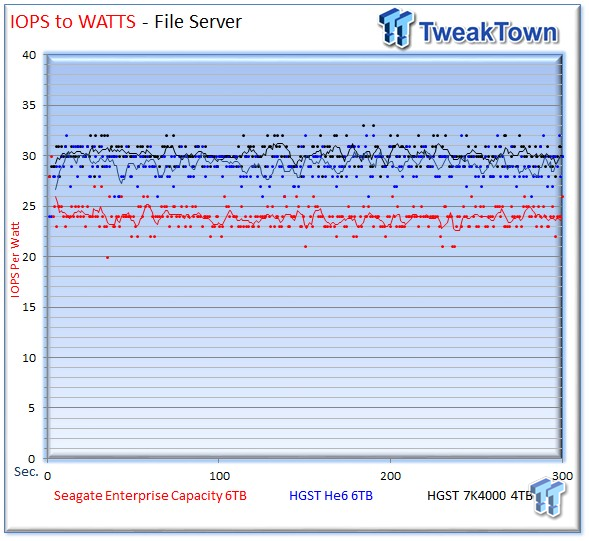
Once again, the Seagate v4 comes within striking distance during a mixed workload.
Benchmarks - Email Server
Email Server
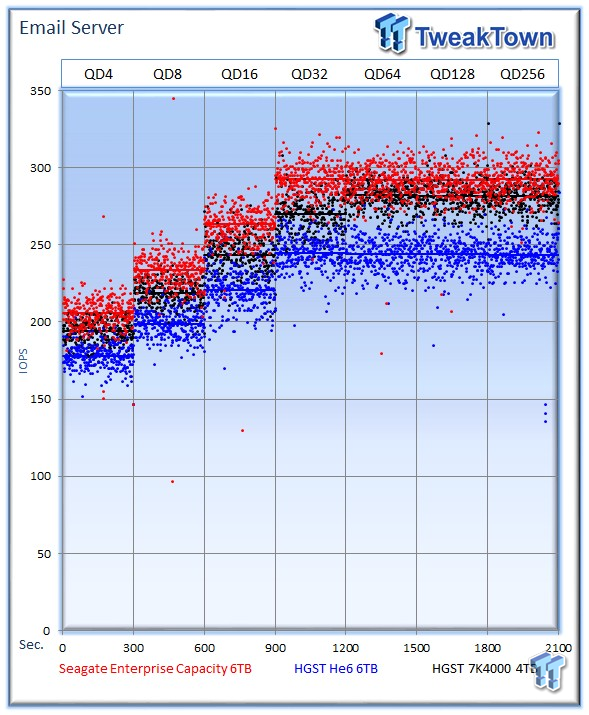
The email server workload is a demanding 8k test with a 50% read and 50% write distribution. This application is indicative of the performance in heavy write workloads.
The Seagate Enterprise Capacity v4 averages a leading 292 IOPS, the HGST Ultrastar He6 averages 246 IOPS, and the 7K4000 averages 281 IOPS.
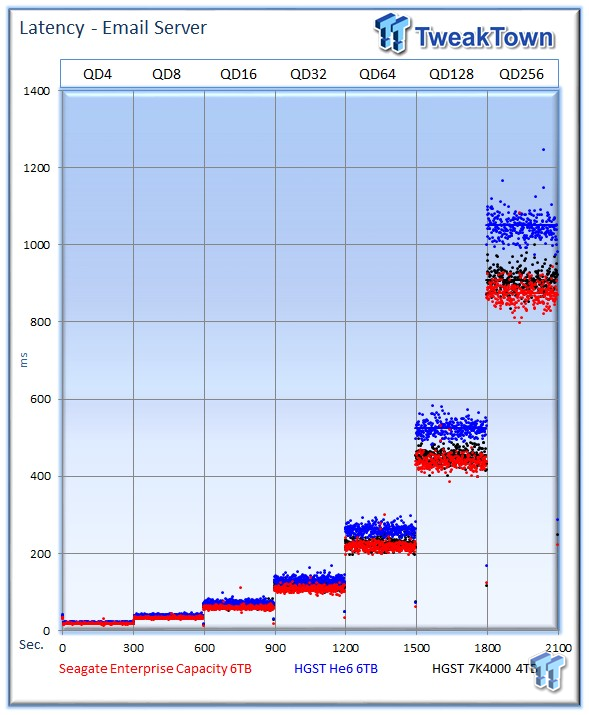
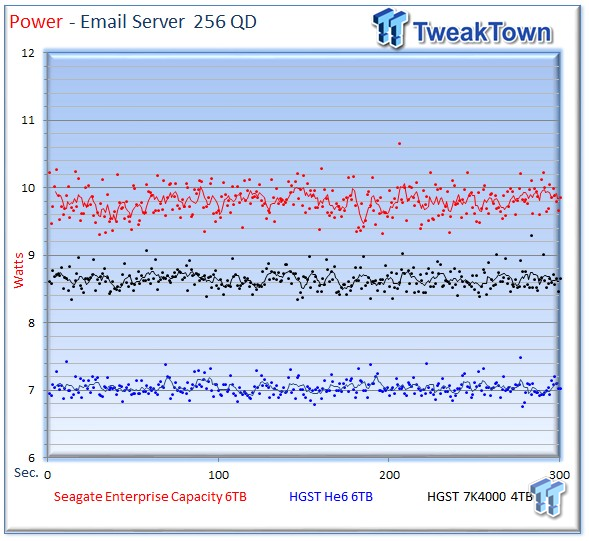
The Seagate v4 averages 9.8 watts, the He6 averages 7.04 watts, and the 7K4000 averages 8.6 watts.
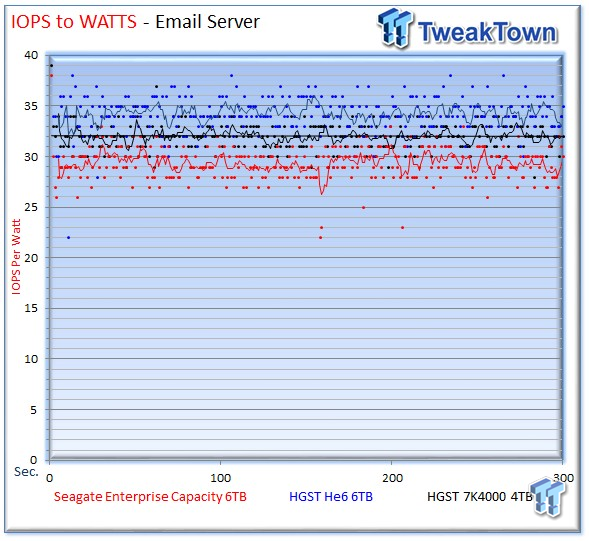
The Seagate v4 pulls within four IOPS-per-Watt in this workload.
Final Thoughts

The pace of areal density increases have slowed as we reach the end of PMR's scalability. However, ingenious innovations by Seagate deliver a big 50 percent capacity boost up to 6TB for their Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4. Recently, Seagate also announced plans to roll out 8 and 10TB drives in the near future. This could be the result of utilizing SMR in a similar design as the v4, or it could even be the arrival of long-awaited HAMR technology.
Seagate has brought a great entry to address the increasing capacity demands of the datacenter. The Seagate v4 addresses a few key challenges that present themselves when expanding capacity. The most common objections center around excessive RAID rebuild periods. Long RAID rebuild times with current 4TB HDDs has led to the use of performance-inhibiting architectures, such as object storage and advanced erasure coding, to circumvent the inevitable rebuilds. Seagate's RAID Rebuild technology, which will eliminate full rebuilds in many scenarios, is finally gaining traction. The increased speed of the v4 can also help keep full rebuilds within a reasonable timeframe. The significantly slower He6 could suffer in this category.
A huge pain point in the datacenter is power consumption, which brings about unavoidable comparisons between the Seagate v4 and the HGST He6. Both companies considered power heavily during the design process, but their divergent paths optimize for different objectives. HGST focused on a new design that could pave the way for future expansion. The He6 provides remarkable power consumption, but performance remained static, and in some cases decreased, from previous generation drives.
Seagate optimized for performance efficiency, and though the V4's power consumption doesn't dip as low as the He6, it brings a big boost in efficiency. Power requirements per TB are important, and the V4 consumes only 1.87W-per-TB, a decrease from 2.81W-per-TB for previous generation drives. Administrators can effectively add 50 percent more capacity within the same power budget. Enabling PowerChoice idle power modes also supplies an advantage that can reduce idle power by 32 percent per TB.
We didn't pull any punches in comparing power consumption and efficiency; the 7K4000 has been the most efficient 7,200 RPM drive for some time, and the He6 lowers the bar even further. In our testing, we found the Seagate v4 consumed more power than the He6 and 7K4000 across the board, but its higher overall performance kept it within 4-6 IOPS-per-Watt of the HGST competitors, particularly in mixed workloads. The v4's operating efficiency even unseated the 7K4000 in sequential workloads. Overall, we came away impressed with the efficiency of the Seagate v4.
Perhaps most importantly, the Seagate v4 doesn't sacrifice performance to increase power efficiency; it actually makes a big leap forward. Overall, the Seagate v4 is the fastest 7,200 RPM drive available today. In sequential tests, it led by a large margin over both drives, and it easily mastered our mixed sequential testing. The 7K4000 mustered a challenge in random read scenarios, while the v4 dominated in random write performance. The Seagate v4 led mixed random testing and scored very well in our workload testing, taking two of the three tests.
The Seagate v4 is clearly the fastest 6TB on the market. The performance of the He6 never encroached into the territory of the Seagate v4, which is not surprising considering its focus on efficiency. The differentiators between the Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 and the HGST He6 are almost night and day, and the needs of the operating environment will dictate purchasing decisions. The price of power consumption over several years can total as much as initial product acquisition costs, making the He6 enticing for those who value frugal power consumption above performance considerations. It also has an advantage in the some niche markets, such as immersion cooling designs.
The Seagate v4 will appeal to a wider audience. Its friendlier price point is attractive, and a boost in performance is always welcome in nearline environments. The v4 also brings improvements in power-per-TB efficiency that easily beats any 4TB offering. Seagate has provided an entire family of drives instead of a single capacity point. This brings the same advantages, such as untouchable sequential speed, to a wider range of drives.
The Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 delivers a big jump in density, impressive performance gains, and even increased power efficiency. With its five-year warranty, class-leading performance, and host of enterprise class features, it earns the TweakTown Editor's Choice Award.
PRICING: You can find the Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 (6TB) for sale below. The prices listed are valid at the time of writing but can change at any time. Click the link to see the very latest pricing for the best deal.
United States: The Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 (6TB) retails for $596.33 at Amazon.
Canada: The Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD v4 (6TB) retails for CDN$801.39 at Amazon Canada.