Introduction

HGST, a Western Digital company, has a complete range of storage offerings for the datacenter. The looming merger completion with WD has not had much effect on business for HGST; they have continued to acquire companies with flash-based portfolios and IP. VeloBit, sTec, and Virident have all come under the HGST umbrella to bolster their SSD ranks, and many see this as the bellwether of HGST becoming WD's SSD wing upon merger completion.
A full family of platter-based products solidify the base of HGST's product stack. HGST still collaborates with Intel in a joint development program that leverages Intel's industry leadership in core controller and NAND technologies, and Intel leans on HGST's vast experience with the SAS interface. HGST's NAND supply is guaranteed through a Joint Development Agreement with Intel, though the specifics of that agreement are not public knowledge. However, guaranteed NAND supply of any variety is a big win for HGST, and it provides them a significant advantage during periodic flash shortages.
The mainstream use of MLC has led to stratification in the SSD product stack for the major manufacturers. The Tier-0 Ultrastar family consists of three members to address every performance segment: high endurance, mainstream endurance, and read intensive. The 12GB/s Ultrastar SSD800MH, codenamed Sunset Cove, sets atop of HGST's performance pyramid with class-leading speeds of 145,000/100,000 read/write IOPS. Sequential read speeds of 1,200 MB/s and 750 MB/s write speed leads the current crop of 12Gb/s SSDs.
The high-endurance Ultrastar SSD800MH comes in a 2.5-inch form factor with a 15mm z-height in 200GB, 400GB, and 800GB capacities. The drive can operate in two power envelopes, 9W or 11W, to satisfy requirements for performance hungry applications. Dual-port SAS provides full duplex operation, multipath, and failover High Availability features. The drives feature 512MB, 1024MB, or 2048MB of SDRAM depending upon capacity.
The SSD800MH features end-to-end data protection with T10 Data Integrity Field (DIF) compliance, extended ECC, and Exclusive-OR (XOR) parity for protection from die failure. Parity-checked internal data paths operate without an external write cache, and power loss management is provided by an electrolytic capacitor. These capacitors are more reliable and tolerate heat better than supercapacitor designs. This SSD provides the highest endurance with up to 25 DW/D (Drive Writes per Day) for the toughest workloads, such as HFT and OLTP environments. The 800GB model can tolerate 36.5PB of random writes in its five-year warranty period, or 20TB per day of random writes.
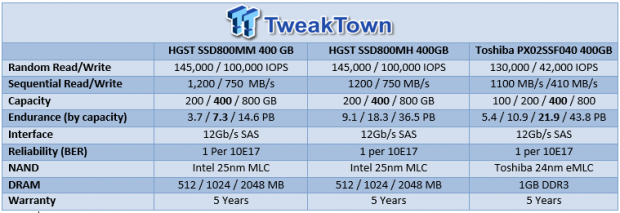
The mainstream endurance SSD800MM, evaluated here, features sequential speeds of 1,200/750 MB/s read/write and 145,000/100,000 read/write IOPS. This drive has an endurance rating of 10 DW/D (Drive Writes per Day).
The Read Intensive Ultrastar SSD1000MR brings up the low-end of the endurance pyramid, and it features sequential speeds of 1,200/700 MB/s read/write and 145,000/70,000 read/write IOPS, respectively. With an endurance rating of 2 DWPD, this SSD is clearly intended for the write-once, read-many class of applications, such as audio/video streaming, cloud computing, and other Internet applications. While the other models top out at a capacity of 800GB, the SSD1000MR offers a larger 1TB capacity point.
Today, we will test the SSD800MH against its mainstream brother, the SSD800MM, and the Toshiba PX02SSF040, the high endurance heavyweight contender from Toshiba.
HGST SSD800MH Internals and Specifications
HGST SSD800MH Internals
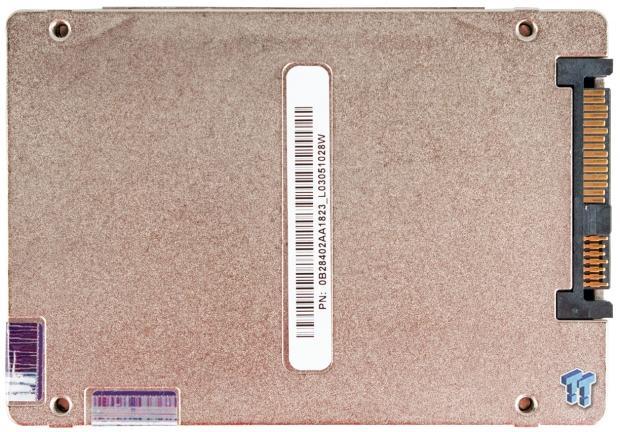


The HGST Ultrastar SSD800MH comes in a robust 2.5-inch metal casing with a 15mm z-height.
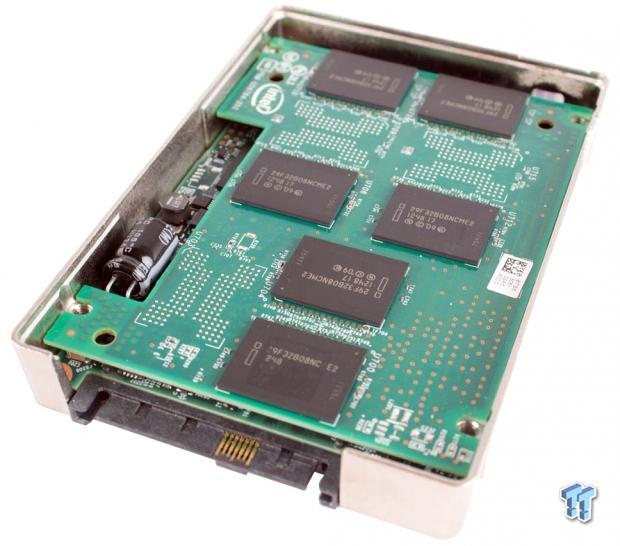

The dual-PCB architecture is fastened internally to the molded casing with four additional screws. Thick thermal pads are placed on each component to facilitate heat transfer.
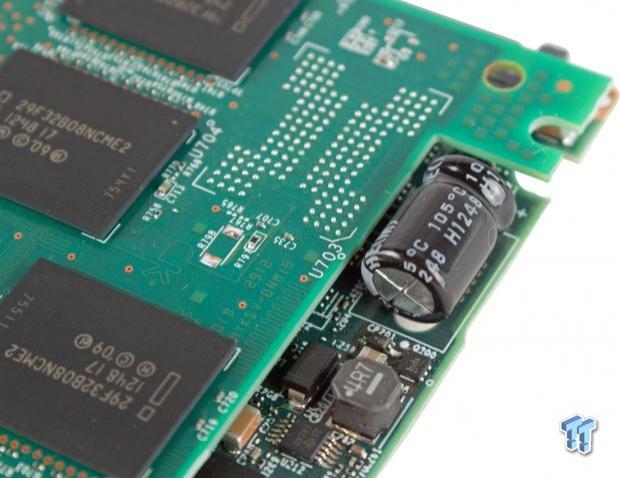


The daughterboard is slightly smaller than the main board, and it has a cutout for the inline electrolytic capacitor. HGST SSDs uses a single capacitor connected to the PCB to provide power hold-up in the event of power loss. This power-loss protection approach is similar to the method employed with the latest Intel SSDs. These capacitors handle high heat environments and have a longer average life than supercapacitors.
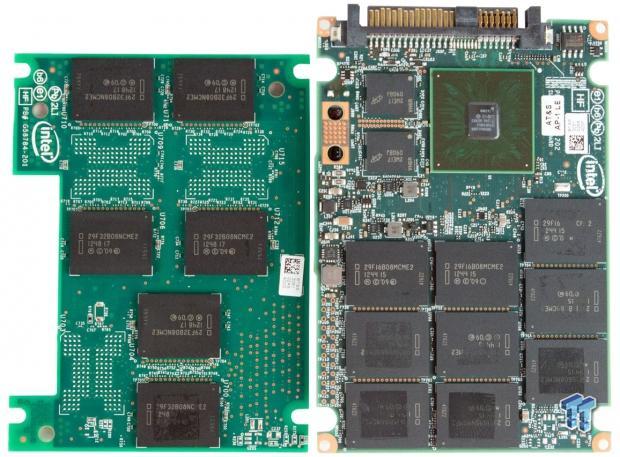
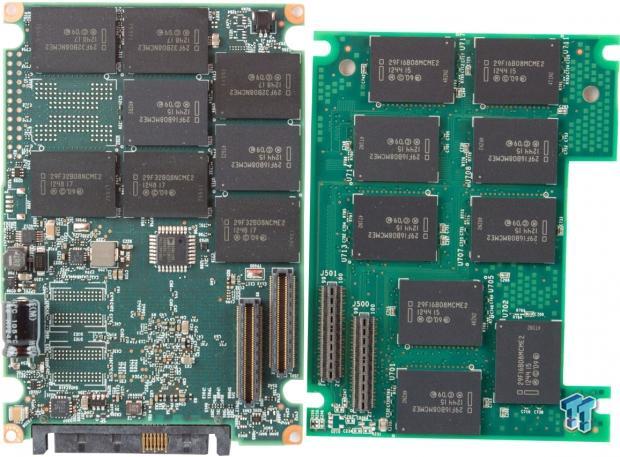


The HGST/Intel collaboration is apparent with the Intel logo emblazoned on the PCB, controller, and NAND. The two connectors on each PCB mate to provide communication between the main PCB and the daughterboard. The main PCB houses the controller, DRAM, and NAND. The daughterboard only hosts NAND packages. There is 1GB of SDRAM to the left of the controller.
There are twenty 16GB and twelve 32GB 25nm MLC NAND packages, for a total of 704GB, of which 372GB is user-addressable. This heavy amount of overprovisioning provides incredible endurance and improves performance consistency.
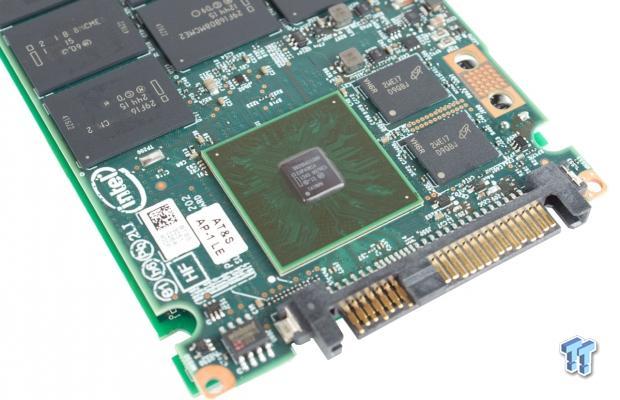

HGST and Intel jointly developed the surprisingly small 12-channel DB29AA11AB0 controller, and the associated firmware, that powers the drive.
HGST SSD800MH Specifications
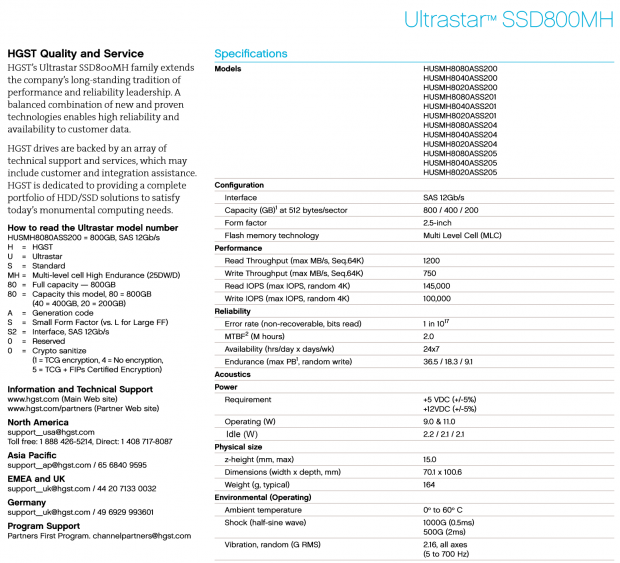
The SSD800MH features a read error rate of less than 1 LBA per 10^17 bits transferred, an MTBF of two million power-on hours, and a 0.44 percent AFR. The drives support variable sector sizes of 512B, 520B, 528B, 4096B, and 4224B. TCQ support is standard, and the drive features adaptive read-ahead algorithms.
TCG encryption, crypto sanitize, and TCG + FIPS-certified models are also available, and they retain the same performance specifications.
Test System and Methodology

Our approach to storage testing targets long-term performance with a high level of granularity. Many testing methods record peak and average measurements during the test period. These average values give a basic understanding of performance, but they fall short in providing the clearest view possible of I/O Quality of Service (QoS).
'Average' results do little to indicate performance variability experienced during actual deployment. The degree of variability is especially pertinent as many applications can hang or lag as they wait for I/O requests to complete. This testing methodology illustrates performance variability, and includes average measurements, during the measurement window.
While under load, all storage solutions deliver variable levels of performance. While this fluctuation is normal, the degree of variability is what separates enterprise storage solutions from typical client-side hardware. Providing ongoing measurements from our workloads with one-second reporting intervals illustrates product differentiation in relation to I/O QoS. Scatter charts give readers a basic understanding of I/O latency distribution without directly observing numerous graphs.
Consistent latency is the goal of every storage solution, and measurements such as Maximum Latency only illuminate the single longest I/O received during testing. This can be misleading as a single 'outlying I/O' can skew the view of an otherwise superb solution. Standard Deviation measurements consider latency distribution, but do not always effectively illustrate I/O distribution with enough granularity to provide a clear picture of system performance. We utilize high-granularity I/O latency charts to illuminate performance during our test runs.
Our testing regimen follows SNIA principles to ensure consistent, repeatable testing. We measure power consumption during precondition runs. This provides measurements in time-based fashion, with results every second, to illuminate the behavior of power consumption in steady state conditions. We also present IOPS-to-Watts measurements to highlight efficiency.
The HGST Ultrastar SSD800MH operates in both 9W and 11W power modes, with the 11-watt mode providing a boost primarily in sequential write speed. We test in 11-watt mode to highlight the best performance. Note that power consumption will be lower, and IOPS-per-Watt efficiency higher, with 9W mode. The first page of results will provide the 'key' to understanding and interpreting our test methodology.
Benchmarks - 4k Random Read/Write
4k Random Read/Write
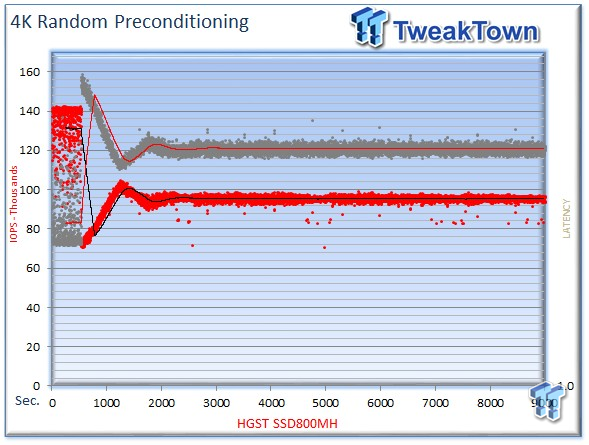
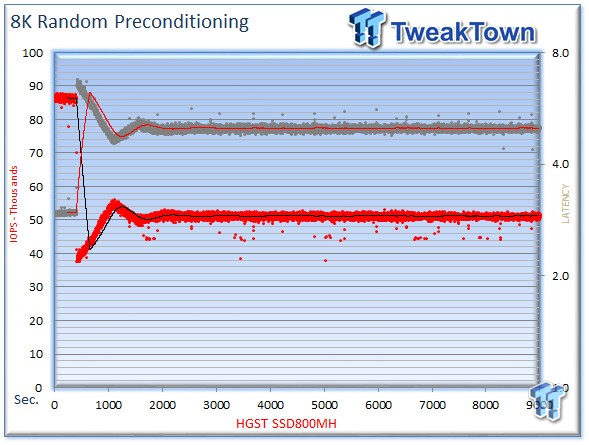
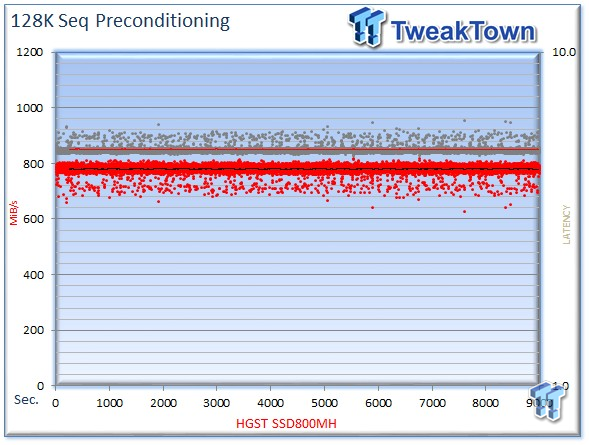
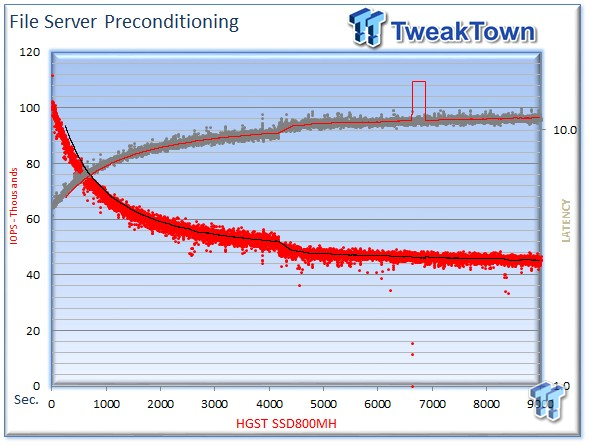
We precondition the HGST SSD800MH for 9,000 seconds, or two and a half hours, receiving performance reports every second. We plot this data to illustrate the drive's descent into steady state.
This dual-axis chart consists of 18,000 data points, with the IOPS on the left and the latency on the right. The red dots signify IOPS, and the grey dots are latency measurements during the test. We place latency data in a logarithmic scale to bring it into comparison range. The lines through the data scatter are the average during the test. This type of testing presents standard deviation and maximum/minimum I/O in a visual manner.
Note that the IOPS and latency figures are nearly mirror images of each other. This illustrates that high-granularity testing can give our readers a good feel for latency distribution by viewing IOPS at one-second intervals. This should be in mind when viewing our test results below. This downward slope of performance only occurs during the first few hours of use, and we present precondition results only to confirm steady state convergence.
We usually do not comment on precondition results, but a beastly average of 98,000 IOPS deserves mention.
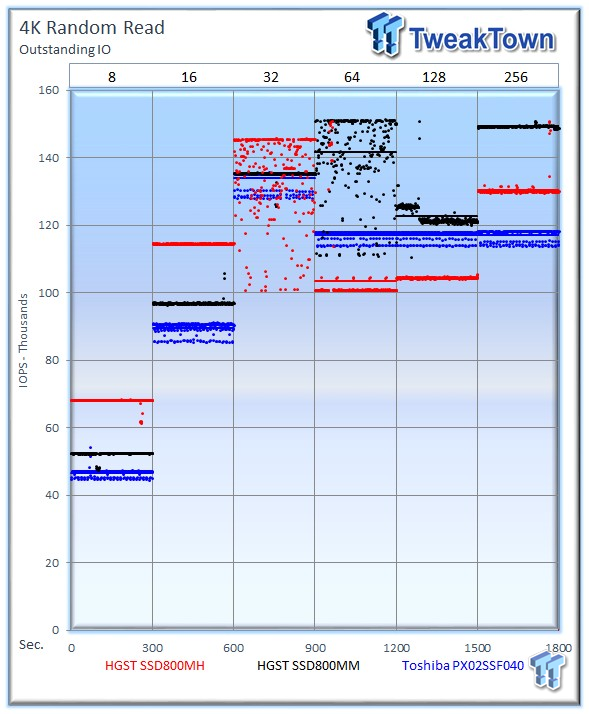
Each level tested includes 300 data points (five minutes of one second reports) to illustrate performance variability. The line for each OIO depth represents the average speed reported during the five-minute interval. 4k random speed measurements are an important metric when comparing drive performance as the hardest type of file access for any storage solution to master is small-file random. One of the most sought-after performance specifications, 4k random performance is a heavily marketed figure.
The SSD800MH averages 130,468 IOPS with a 4k random read workload at 256 OIO (Outstanding I/O), but its peak is at 32 OIO, where it delivers an exceptional 135,570 IOPS. The Toshiba PX02SS averages 117,289 IOPS with a 4k random read workload at 256 OIO (Outstanding I/O), but its peak is at 32 OIO, where it delivers an outstanding 133,871 IOPS. The HGST SSD800MM peaks at 256 OIO with 149,352 IOPS. Perhaps the only chink in the vaunted HGST SSD's armor comes with this 4k random read workload, where it experiences a drop in performance in 64 and 128 OIO workloads. It is important to note our samples are pre-production with A100 firmware.
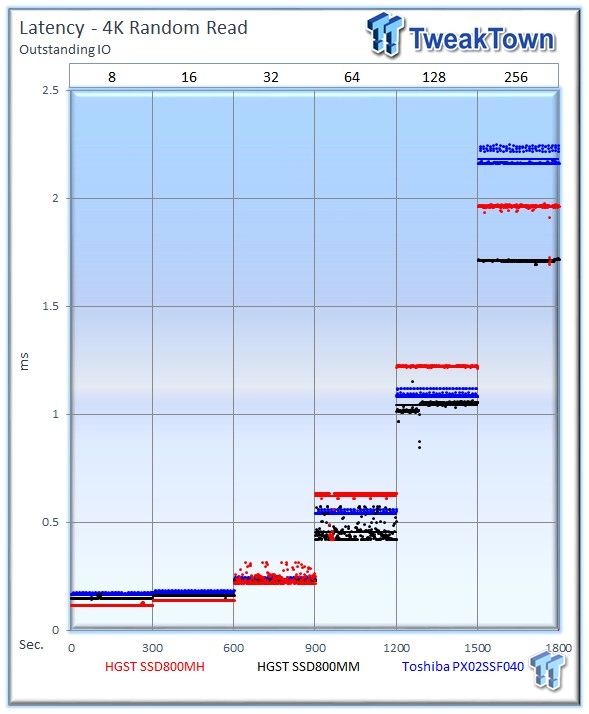
The PX02SS provides the best performance-v-latency at 32 OIO, while the SSD800MH thrives at the higher 256 OIO.
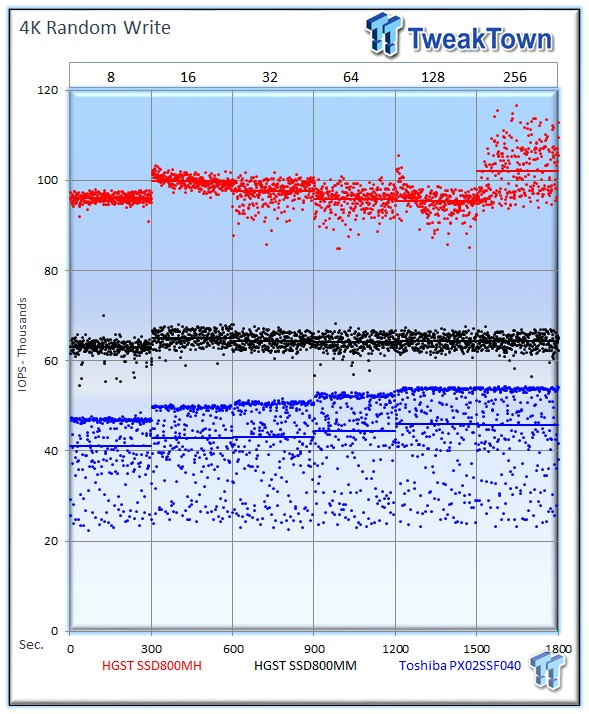
Garbage collection routines are more pronounced in heavy write workloads, leading to performance variability.
The HGST SSD800MH averages an incredible 102,085 IOPS, the SSD800MM averages 64,279 IOPS, and the PX02SS provides 45,786 IOPS at 256 OIO. This is the highest 4k write speed we have measured with a 2.5-inch SSD in steady state.
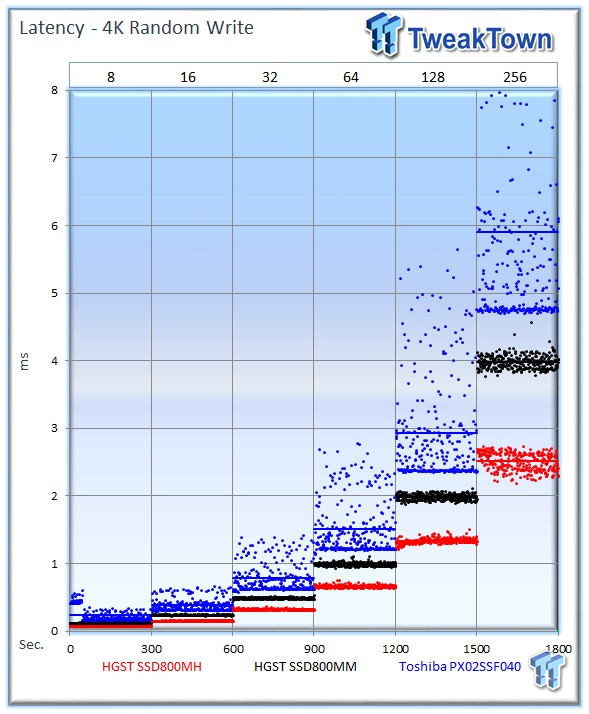
The SSD800MH adds remarkably consistent performance to the chart-topping 4k write performance.
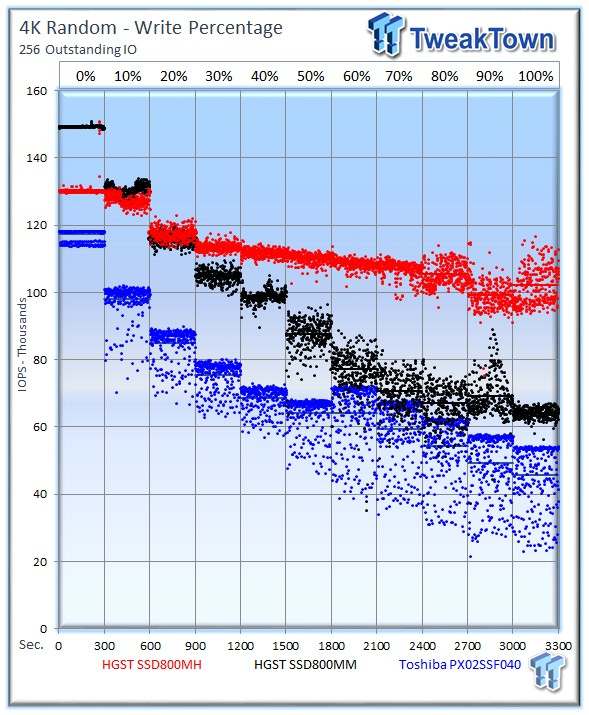
Our write percentage testing illustrates the varying performance of each solution with mixed workloads. The 100 percent column to the right is a pure write workload of the 4k file size, and 0 percent represents a pure 4k read workload.
The SSD800MH tears through this test with ease, easily outpacing its sibling and the Toshiba PX02SS. The consistent performance envelope is impressive.
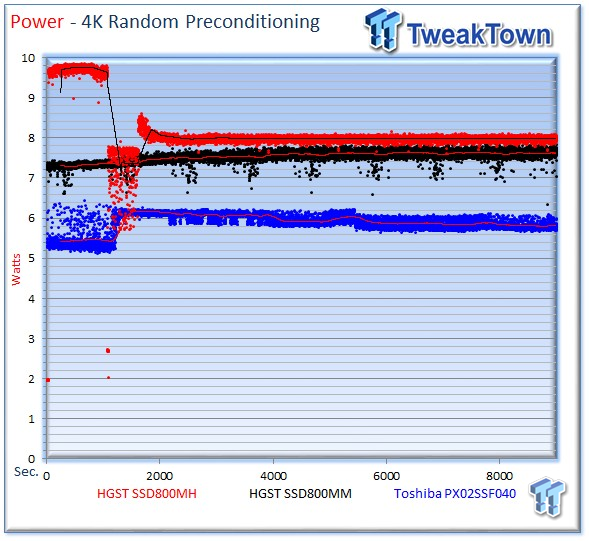
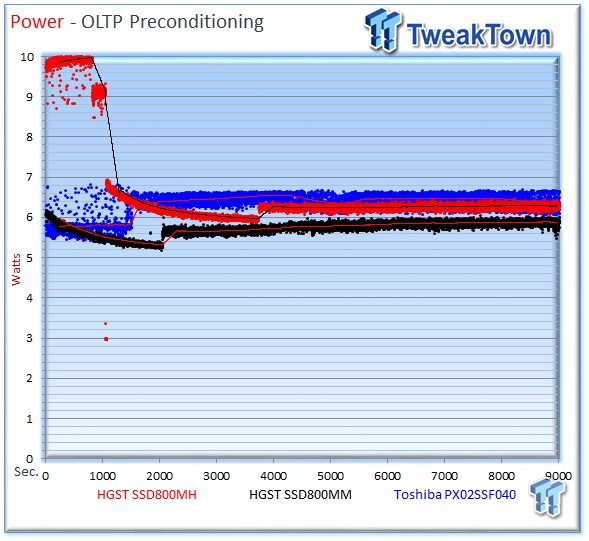
We record the power consumption measurements during our precondition run. We calculate the stated average results during the last five minutes of the test, after the device has settled into steady state.
The SSD800MH averages 7.98 watts, the SSD800MM averages 7.56 watts, and the PX02SS averages 5.85 watts during the measurement window.
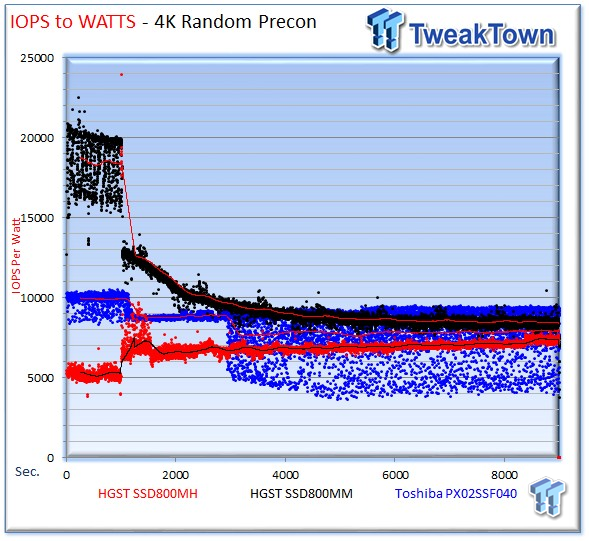
IOPS-to-Watts measurements are generated from data recorded during our precondition run, and the stated average is from the last five minutes of the test.
The SSD800MH averages 9,017 IOPS-per-Watt, the Toshiba PX02SS averages 7,869 IOPS-per-Watt, and the SSD800MM averages 8,977 IOPS-per-Watt. It is important to note the IOPS-per-Watt set forth in the specifications of all drives is with read activity. We measure IOPS-per-Watt with write activity.
Benchmarks - 8k Random Read/Write
8k Random Read/Write

Server workloads rely heavily upon 8k performance, and we include this as a standard with each evaluation. Many of our server emulations also test 8k performance with various mixed read/write workloads.
The average 8k random read speed of the HGST Ultrastar SSD800MH is 91,661 IOPS at 256 OIO; the Toshiba PX02SS measures an outstanding 100,277 IOPS at 256 OIO to take the lead, while the SSD800MM offers up 91,622 IOPS.
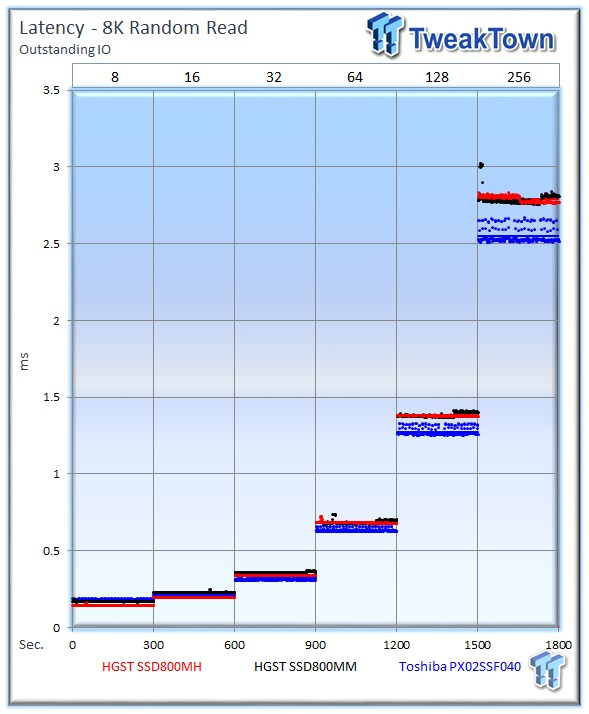
All three SSDs exhibit a tight latency range during the 8k random read test, but the Toshiba PX02SS provides the lowest latency.
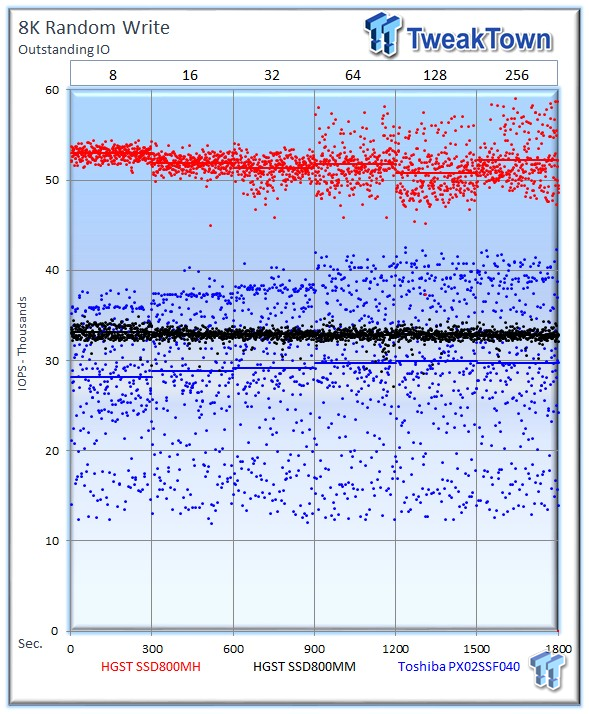
The SSD800MH easily leads with an average of 52,180 IOPS; the PX02SS experiences significant variability while managing an average of 29,714 IOPS; and the SSD800MM sports a consistent average of 32,878 IOPS at 256 OIO.
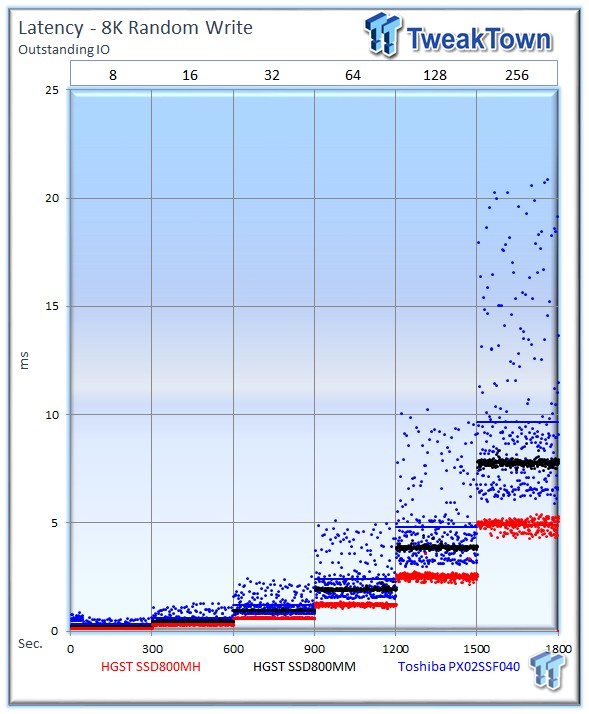
The Toshiba SSD experiences significant latency variability.
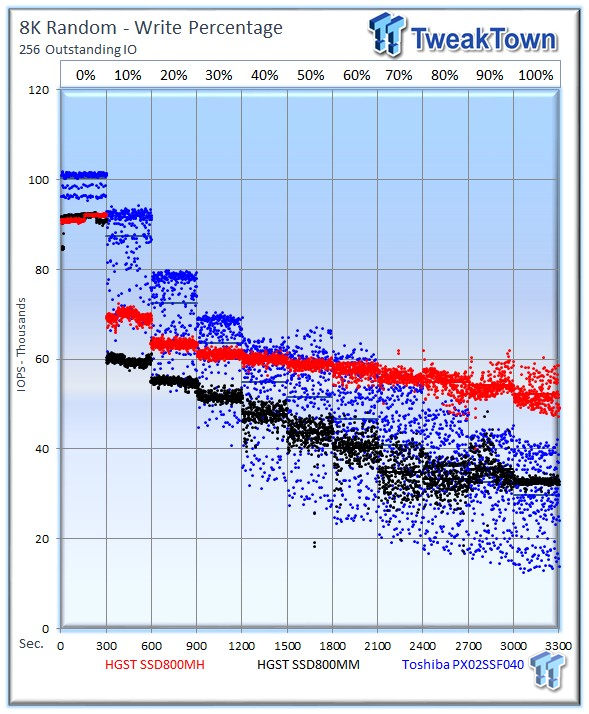
The PX02SS also has an affinity for 8k workloads, but the SSD800MH also excels at this workload. The PX02SS wins with lighter write workloads, from 0-30 percent, but falls to the incredible consistency of the SSD800MH from 40-100 percent as the write workload intensifies.
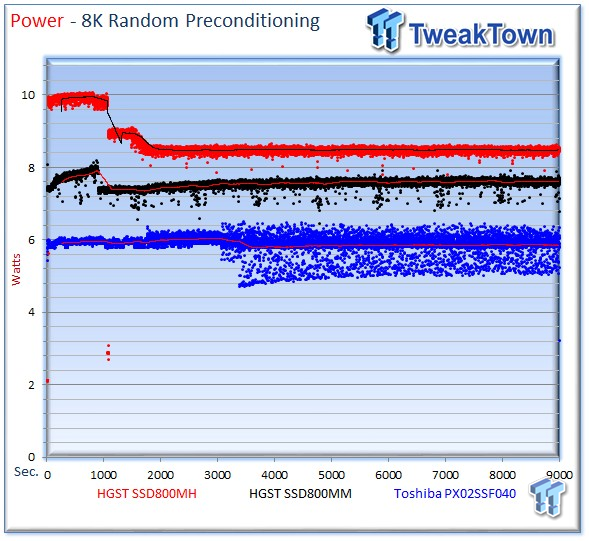
Power consumption for the SSD800MH averages 8.48 watts, the PX02SS averages 5.84 watts during the measurement window, and the SSD800MM requires 7.60 watts.
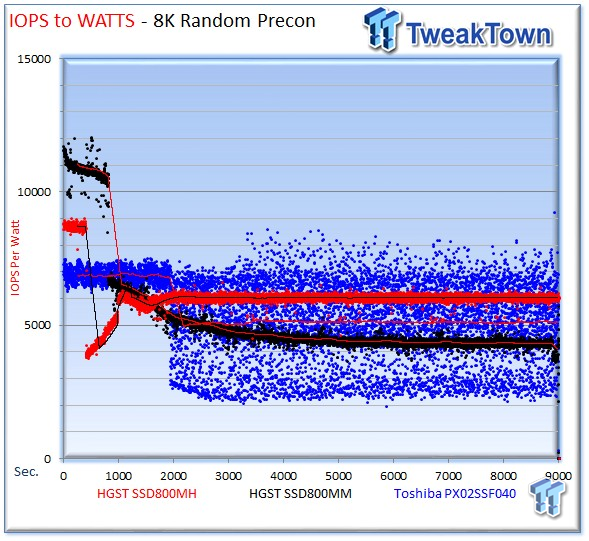
The SSD800MH leads this chart with 6,036 IOPS-per-Watt; the PX02SS's variability shows up in the efficiency results, but it still averages 5,103 IOPS-per-Watt, and the SSD800MM measures 4,159 IOPS-per-Watt.
Benchmarks - 128k Sequential Read/Write
128k Sequential Read/Write
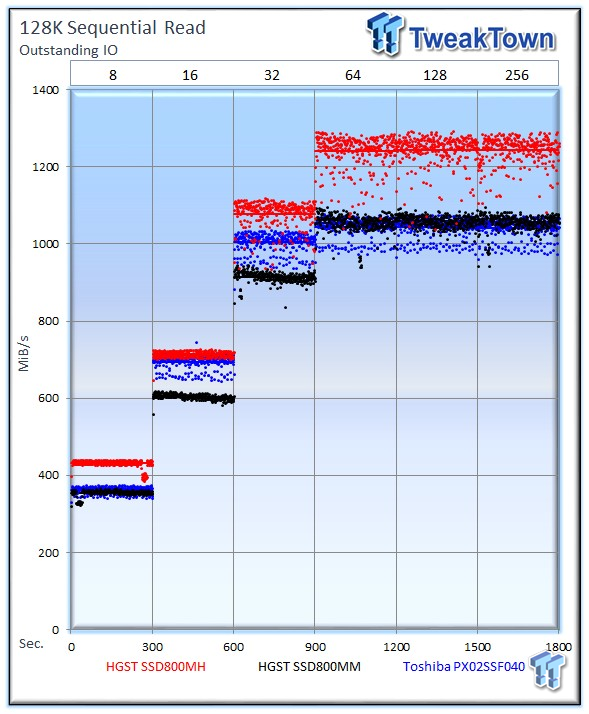
128k sequential speed reflects the maximum sequential throughput of the SSD. The HGST Ultrastar SSD800MH is in its own league with the highest sequential read speed we have recorded from a single 2.5-inch SSD. It came in at 1,243 MiB/s. The Toshiba PX02SS goes toe-to-toe with the HGST SSD800MM in sequential read speed, with both delivering an average of 1,040 MiB/s and 1,056 MiB/s, respectively.
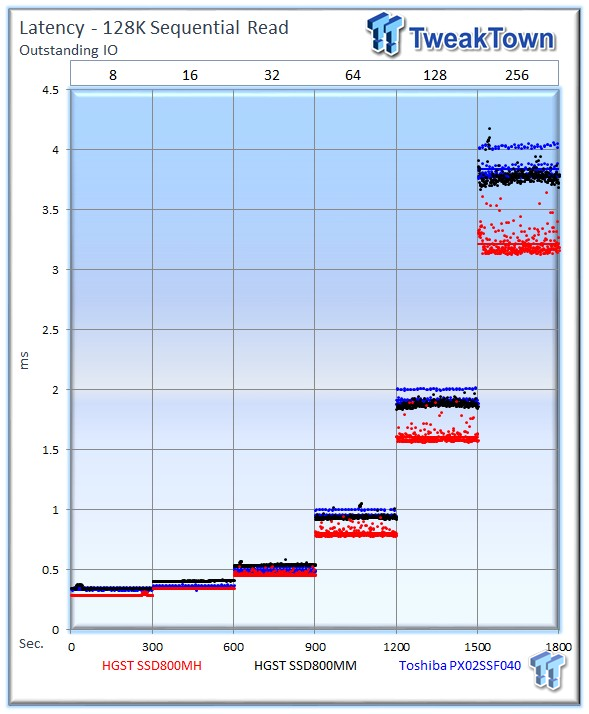
All three SSDs are very consistent, but the SSD800MH provides the lowest overall latency.
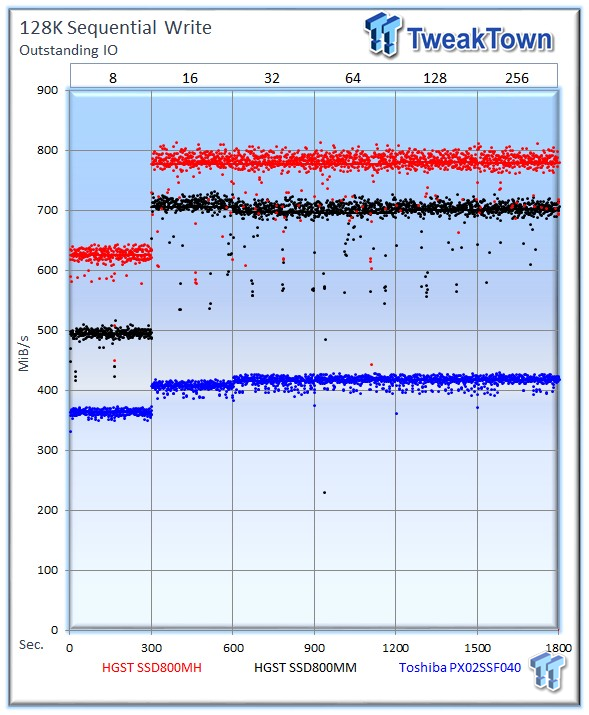
The SSD800MH sets another record with a sustained speed of 779 MiB/s, and the SSD800MM averages 702 MiB/s. The PX02SS scores slightly over its rated speed at 417 MiB/s. It is important to note that the PX02SS is not designed with sequential workloads in mind; its specification for sequential write is 410 MiB/s.
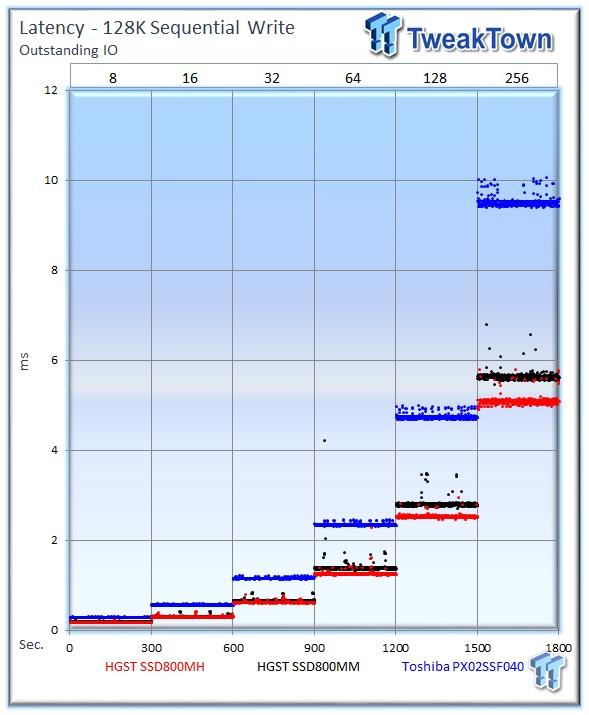
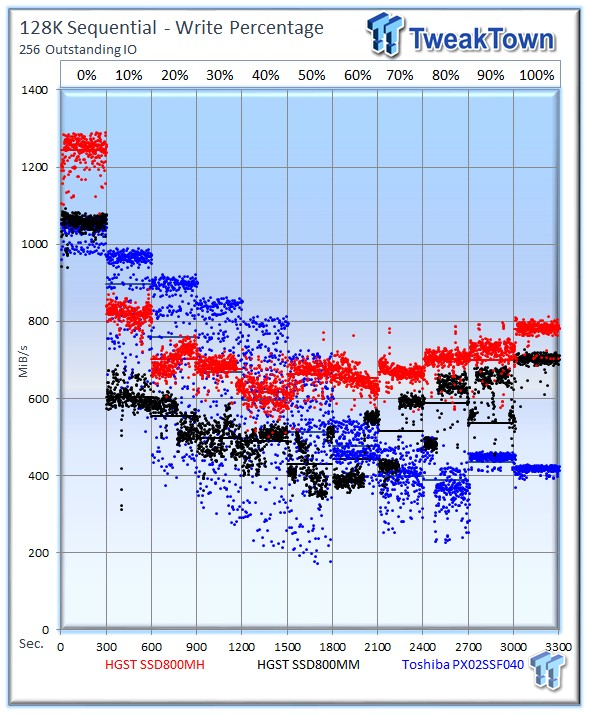
The SSD800MH takes the lead in the 128k mixed workload test.
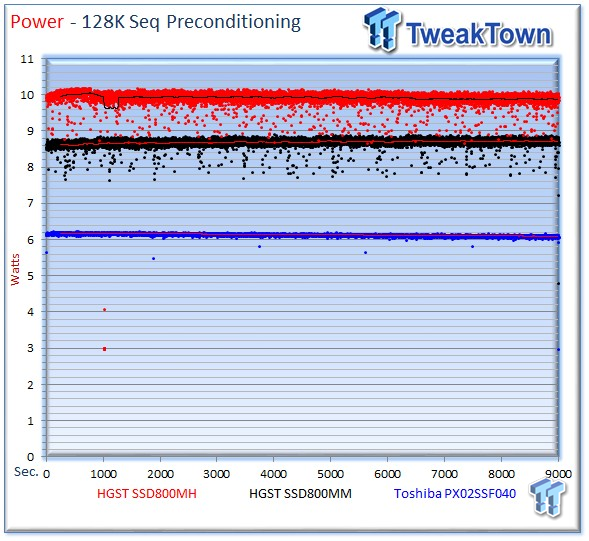
The SSD800MH averages 9.87 watts, the PX02SS averages 6.08 watts and the SSD800MM requires 8.68 watts for the sequential write workload.
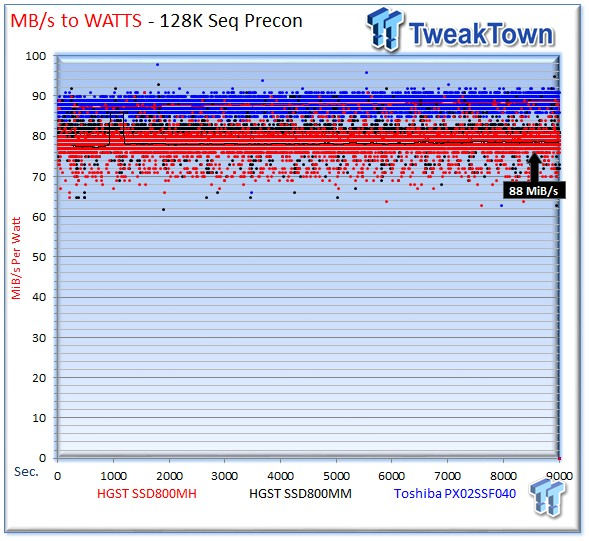
The SSD800MH averages 78.4 MiB/s-per-Watt, the PX02SS averages 88 MiB/s-per-Watt, and the SSD800MM provides 80 MiB/s-per-Watt.
Benchmarks - Database/OLTP and File Server
Database/OLTP
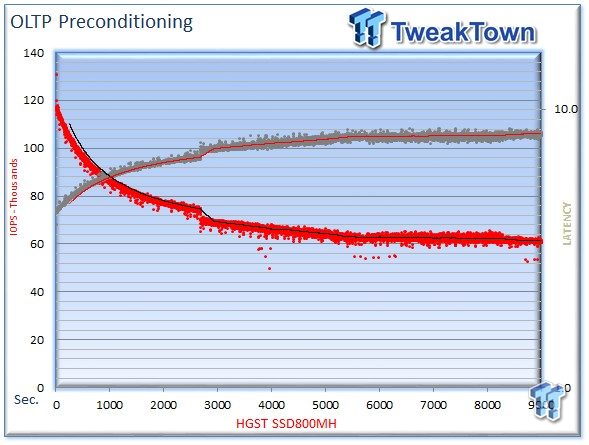
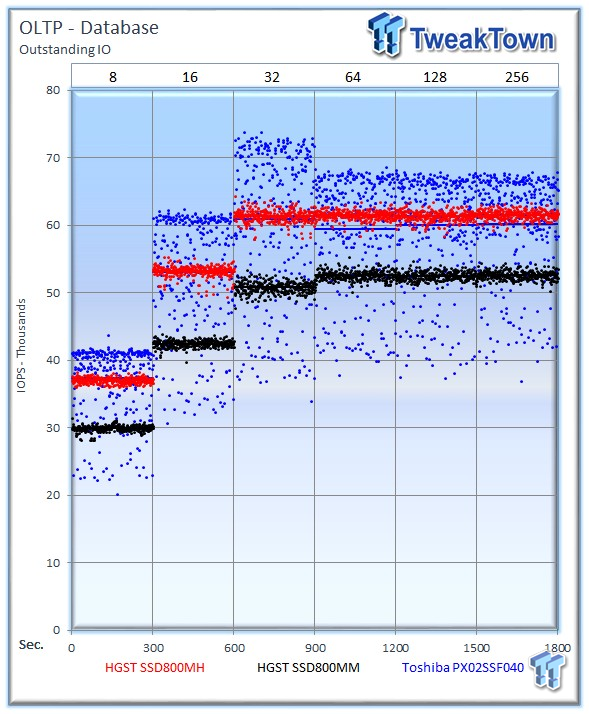
This test emulates Database and On-Line Transaction Processing (OLTP) workloads. OLTP is the processing of transactions such as credit cards and high frequency trading in the financial sector. Databases are the bread and butter of many enterprise deployments. These demanding 8k random workloads with a 66 percent read and 33 percent write distribution bring even the best solutions down to earth.
The HGST Ultrastar SSD800MH averages an extremely consistent 61,599 IOPS, the Toshiba PX02SS averages 60,240 IOPS at 256 OIO, and the SSD800MM averages 52,630 IOPS. The superb consistency of the HGST SSDs is convincing in this workload.
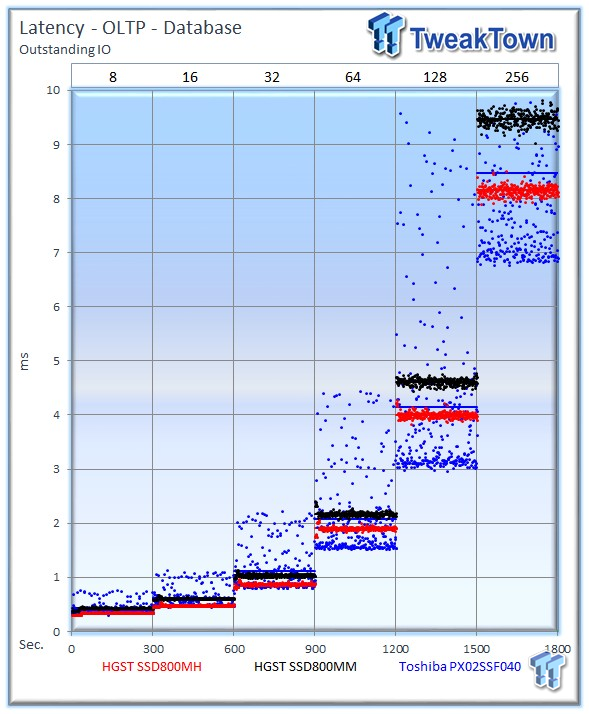
The SSD800MH averages 6.28 watts, the Toshiba averages 6.44 watts, and the SSD800MM requires 5.87 watts.
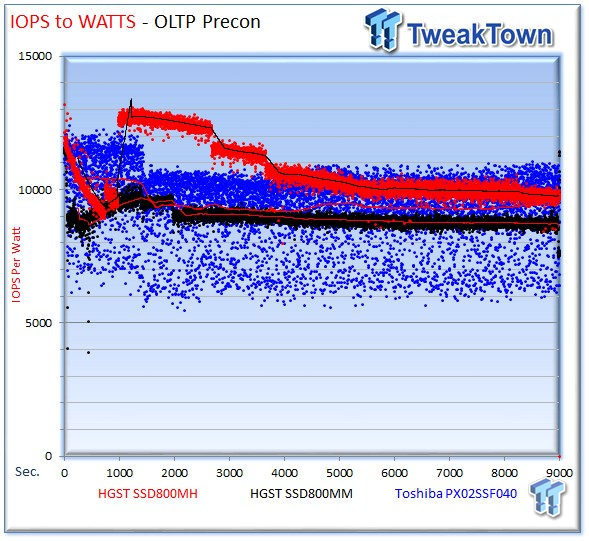
The SSD800MH averages 9,753 IOPS-per-Watt, the PX02SS averages 9,075 IOPS-per-Watt, and the SSD800MM averages 8,670 IOPS-per-Watt.
File Server
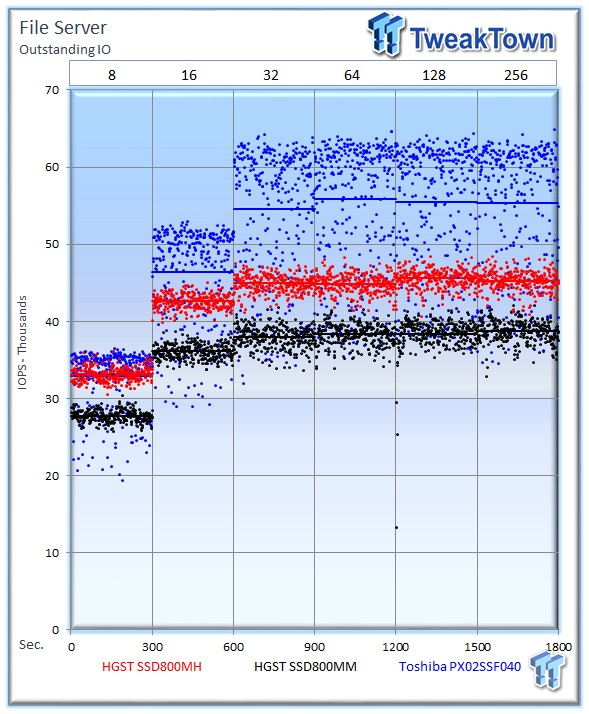
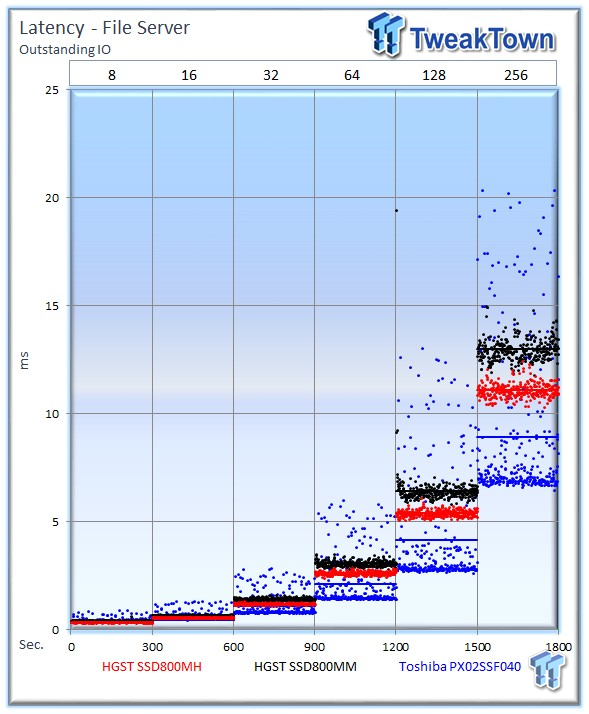
The file server profile represents typical file server workloads. This profile tests a wide variety of different file sizes simultaneously, with an 80 percent read and 20 percent write distribution.
The HGST Ultrastar SSD800MH averages 45,289 IOPS, falling to the PX02SS' average of 55,288 IOPS. The SSD800MM averages 38,737 at 256 OIO.
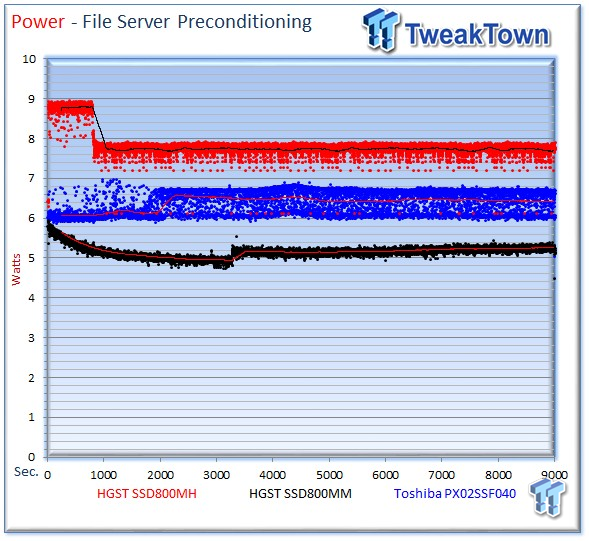
The SSD800MH averages 7.69 watts, the PX02SS requires 6.40 watts during the fileserver workload, and the SSD800MM pulls 5.26 watts.
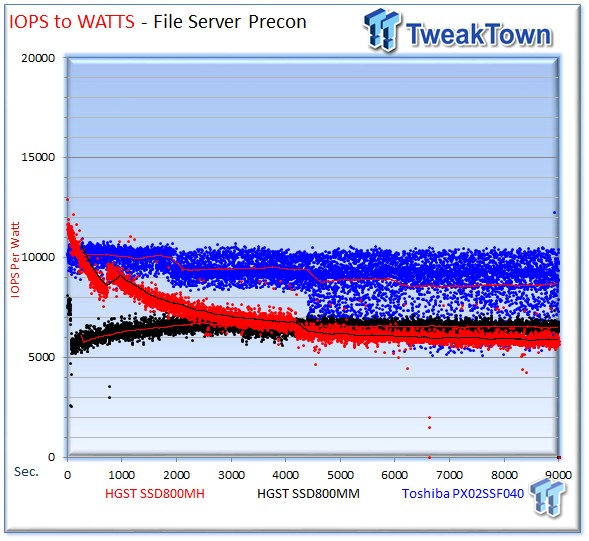
The Toshiba PX02SS leads this test easily with an impressive 8,693 IOPS-per-Watt, compared to 5,874 for the SSD800MH and 6,502 for the HGST SSD800MM.
Benchmarks - Email Server
Email Server
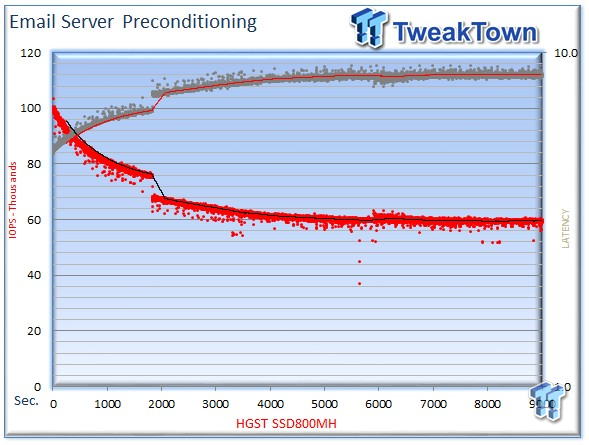
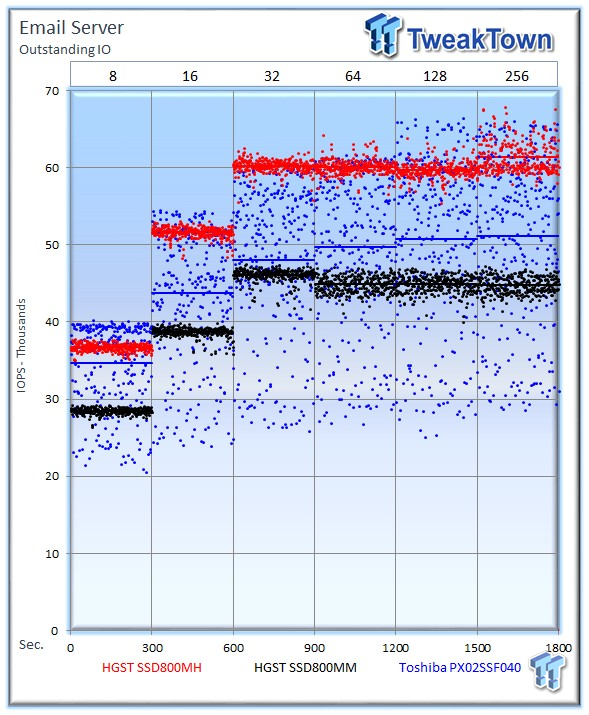
The email server profile is a demanding 8k test with a 50 percent read and 50 percent write distribution. This application is indicative of the performance in heavy write workloads.
The HGST Ultrastar SSD800MH averages 61,366 IOPS, the PX02SS averages 51,119 IOPS at 256 OIO, with the SSD800MM close behind at 44,804 IOPS.
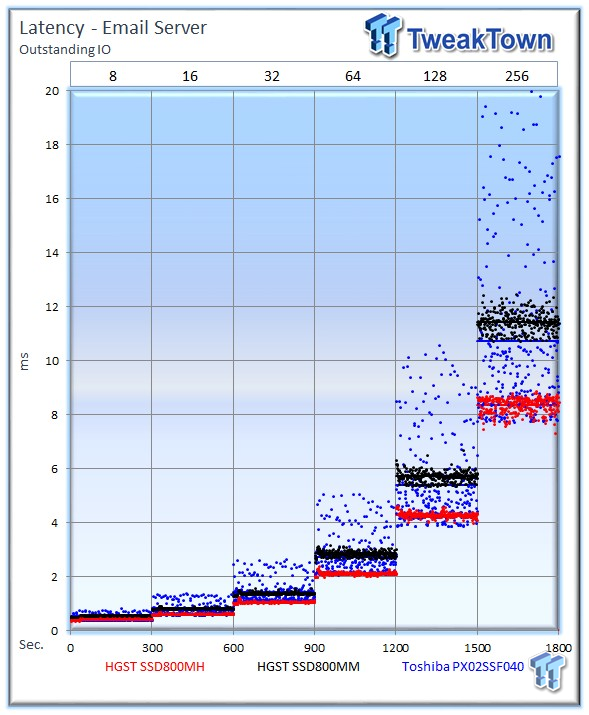
One area the HGST continues to shine is the consistent latency performance in this very demanding test.
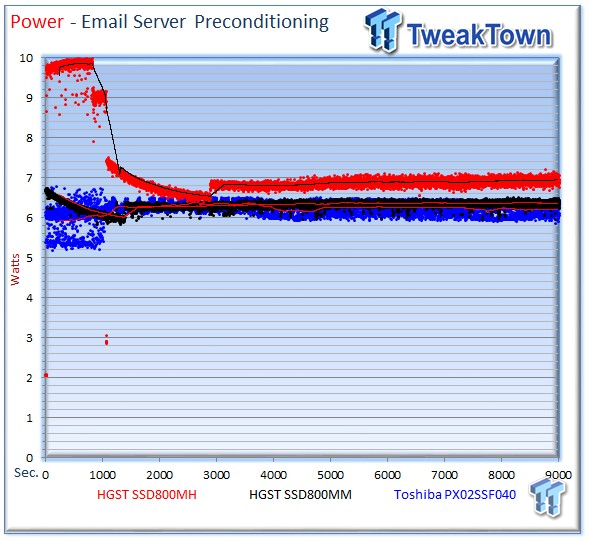
The SSD800MH averages 6.94 watts, the PX02SS averages 6.21 watts, and the SSD800MM averages 6.36 watts.
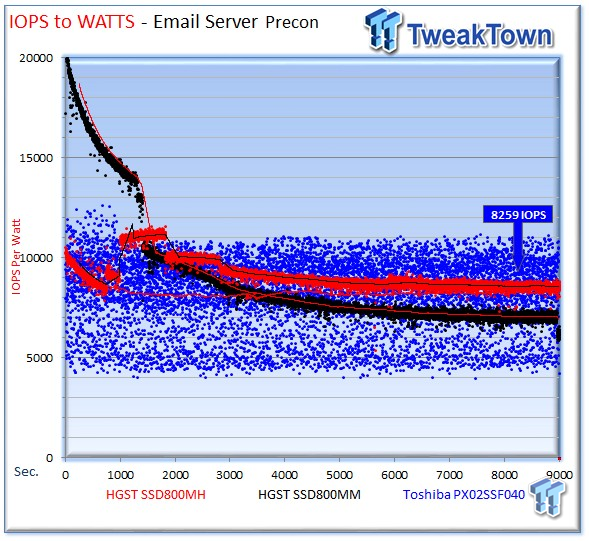
The SSD800MH averages 8,566 IOPS-per-Watt, the PX02SS scores 8,259 IOPS-per-Watt, ahead of the 8,259 IOPS-per-Watt from the SSD800MM.
Final Thoughts

The datacenter has an insatiable appetite for speed. Each generational increase in storage performance unlocks more CPU power, allowing more work with less power. Products like the HGST Ultrastar SSD800MH appease the need for performance density in multi-node and micro server applications. This increased performance density equates to lower power consumption and better system efficiency. Full system utilization can increase ROI per system, alleviating licensing burdens in HFT, OLTP, OLAP, and cloud computing architectures.
For OEMs and system integrators, guaranteed NAND supply is important. HGST enjoys many fruits from their cooperation with Intel, and arguably, a guaranteed NAND supply is chief amongst them. Integrating a storage solution into OEM units requires confidence supply will not dry up during periodic NAND shortages. The details of the agreement are not public, but HGST benefits from a lot more than just Intel's microprocessor and NAND technology.
Delivering PCIe-like performance in a 2.5-inch form factor can be better suited to applications where PCIe SSDs may not address High Availability requirements. Addressing performance challenges with multiple PCIe SSDs can be cost-prohibitive, and there are limitations on useable PCIe slots in dense architectures. The pristine performance consistency from the SSD800MH lends itself well to RAID usage and provides a scalable solution for space-constrained systems.
SAS SSDs have higher power consumption due to their Active-Active dual port functionality. We measured power in 11W mode during testing, placing it at a bit of disadvantage since the performance gains are primarily in sequential write. This lowered its efficiency measurements, but the HGST SSD800MH still offered up the best performance-to-Watts ratio of the Dual-Port SAS SSDs in our tests.
The only hiccup was at 64 and 128 OIO during 4k random reads. The SSD800MH still managed to lead the pack with a heavy workload, and peaked at 135,570 IOPS. The 4k write performance was amazing at an unheard-of 102,085 IOPS in steady state, easily the highest we have measured in this form factor. Perhaps most impressive was its excellent consistency characteristics.
The SSD800MH fell to the Toshiba PX02SS in the 8k random read workload, but came roaring back with a convincing win in 8k random write. This robust write performance also provided a huge advantage in the 8k mixed workload testing, and it continued to exhibit the consistent performance characteristics.
The HGST SSD also dominated our sequential testing in easy fashion, posting the highest sequential read/write performance we have recorded in a 2.5-inch form factor SSD. This high performance carried over to server workloads. It led in all tests except fileserver, where the Toshiba PX02SS took the lead. The Toshiba PX02SS also features a higher overall endurance rating, but the high endurance thresholds of both drives will leave very few wanting.
NVMe devices will begin making their debut this year, and many are questioning the future of SAS with the low-weight software stack from NVMe offering significant performance advantages. We do not foresee a complete sea change immediately, but competition will likely become heated in a few product generations as NVMe gains acceptance.
SAS has a long history and is termed the 'Ethernet of storage' for many reasons. Its entrenched infrastructure in the datacenter and its ability to fend off other architectures has allowed it to stand the test of time. The timely update cadence of SAS has also spurred its evolution into a specification that offers enhanced choices as a storage fabric. SAS will continue to be widely deployed, with competition becoming brisk when High-Availability concerns are addressed with NVMe.
The HGST Ultrastar SSD800MH dominates across the board in performance and efficiency, and has tremendous endurance that should satisfy even the most intense workloads, easily winning the TweakTown Editor's Choice Award.

 United
States: Find other tech and computer products like this
over at
United
States: Find other tech and computer products like this
over at  United
Kingdom: Find other tech and computer products like this
over at
United
Kingdom: Find other tech and computer products like this
over at  Australia:
Find other tech and computer products like this over at
Australia:
Find other tech and computer products like this over at  Canada:
Find other tech and computer products like this over at
Canada:
Find other tech and computer products like this over at  Deutschland:
Finde andere Technik- und Computerprodukte wie dieses auf
Deutschland:
Finde andere Technik- und Computerprodukte wie dieses auf