
The Bottom Line
Introduction and Quick Specs
It's been nearly three years since Micron introduced a new enterprise SSD. While others have been quick to jump on the NVMe train, Micron has been taking their time to do it right. Micron's new 9100 Series NVMe SSDs employ the NVMe software stack over a PCIe Gen3 x4 interface to bring nonvolatile memory as close as possible to the computer's processor. NVMe is architected from the ground-up to remove legacy layers of hard drive interfaces, taking full advantage of the speed and parallelism of solid state nonvolatile memory. NVMe lowers overall CPU overhead because NVMe has a simplified command set which minimizes the number of CPU clocks per I/O in comparison to AHCI. NVMe is designed to be future proof, with a protocol built for current and future non-volatile storage solutions. Previous AHCI interfaces supported only one SQ/CQ (Submission Queue/Command Queue), NVMe supports up to 64K separate SQ/CQs.

Micron's 9100 Series SSDs leverage Microsemi's (formerly PMC) ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) 16-core, 16-channel "Princeton" NVMe controller. Microsemi's ASIC NVMe controller is employed on many enterprise SSD designs, because of its highly customizable architecture. The customizable nature of the Microsemi controller allows Micron's engineering team to create solutions that are uniquely their own via proprietary firmware and software designs. Micron's 9100 Series NVMe SSDs are designed to meet the need for high-performance storage in today's datacenter. The 9100 SSD pairs Microsemi's NVMe controller with Microns own award-winning 16nm flash to deliver data fast and efficiently.
The 9100 family of SSDs are available in either read-centric (9100 PRO) or mixed-use (9100 MAX) classes. The 9100 has two endurance classes: the 9100 PRO for read-centric use at roughly one drive writes per day (DWPD); and the 9100 MAX for mixed-use workloads at about 3 DWPD. The PRO version comes in 800GB, 1.6TB and 3.2TB capacities; the MAX 1.2TB or 2.4TB. The difference in endurance as well as overall write performance between the two models, as far as we can tell, comes down to dedicated spare area. The read-centric 9100 Pro allocates a more conventional 20% of its total raw capacity as spare area dedicated for overprovisioning and redundant array of independent NAND (RAIN). The 9100 MAX allocates a whopping 40% of its total raw capacity as spare area dedicated for overprovisioning and RAIN.
Micron's 9100 Series SSD are a best fit for applications such as content delivery, database management, and high-performance computing. The device comes in two form factors: half-height/half-length (HHHL) add-in card (AIC) and 2.5-inch U.2 (small form factor 8639), both of which utilize a PCIe x4 Gen3 host interface. All capacities are available in both form factors.
Quick Specs

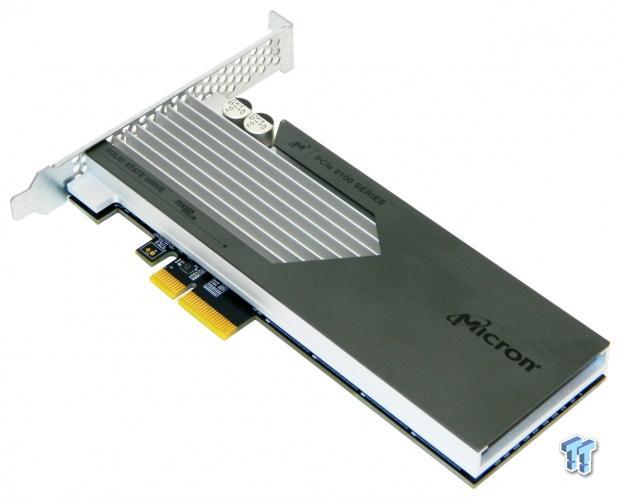
The Micron 9100 MAX 2.4 TB HHHL AIC we have on the bench today sports the following hardware and steady-state performance specifications: 4K Random Read/Write = 750K/300K. Sequential Read/Write = 3000/2000 MB/s. Power consumption = 27W Active/7W idle. Controller = Microsemi 16-Channel ASIC NVMe controller. NAND = Micron 16nm. Data DRAM Cache = 4GB. Onboard Power-loss Protection = Yes.
Micron warranties the 9100 MAX 2.4TB SSD for 9.6 Petabytes Written.
Micron 9100 MAX 2.4TB PCIe NVMe SSD-Photos and Specs
Photos

The drive ships in a clear plastic clamshell container. Micron includes both a half-height and full mounting bracket.

The top half of the drive's all black PCB is covered by a full-length aluminum heat sink. A grey shroud covers half of the heat sink to help direct and optimize airflow.

The bottom half of the PCB has no shielding; the components are exposed. This half of the PCB houses 16 of the drive's 32 Micron 16nm flash packages and five of the drive's nine Micron DRAM cache packages. Eight DRAM packages are dedicated for block placement and wear leveling data. The ninth DRAM package is dedicated for ECC further guaranteeing data integrity.

From this angle, we can see the opening at the back of shroud covered portion of the heat sink where a minimum of 300LF per minute of airflow is to be funneled, exiting through the drive's perforated mounting bracket. Two electrolytic capacitors provide enough power to flush data in transit to the NAND array in the event of a host power loss.

Removing the heat sink reveals that the drive's controller and major components are fitted with thermal pads to wick heat away. This side of the PCB houses the drive's controller, 16 of its 32 NAND flash packages, four 512MB DRAM cache packages, and dual electrolytic capacitors.

A detailed view of the drive's 16-channel, 16-core Microsemi (formerly PMC) 500MHz ASIC controller.

A detailed view of one of the drive's 128GB (32 in total) Micron 16nm BGA flash packages. Thirty two 128GB flash packages gives the 9100 MAX 2.4TB a raw total of 4096GB of flash. 2.4TB is available the end-user before formatting.

A detailed view of some of the drive's (9 in total) 512MB Micron 1600MHz DDR3 DRAM cache packages. Eight 512MB DRAM packages (4GB) serve as onboard data cache; the ninth 512MB cache package is dedicated for ECC.
Specifications and Features

We are going to go over the 2.4TB 9100 Max' specifications. For other capacities please refer to the above mfg. spec sheet. Micron's 9100 MAX 2.4TB Enterprise PCIe NVMe SSD comes in a half-height, half-length, low-profile Add-in Card (AIC) Form factor as well as a 2.5" U.2 (SFF-8639) variant. Factory specifications for both form factors are identical.
Features include a PCIe Gen 3.0 x4 interface, Microsemi NVMe controller, and Micron 16nm NAND Flash Memory. XPERT, eXtend Performance, End-to-End data protection featuring RAIN parity protection and advanced ECC bit correction on all internal and external memories in the data path for protection at every layer.
Micron 9100 MAX 2.4TB PCIe NVMe SSD steady-state factory specs:
- Sequential 128KB Read (up to): 3000 MB/s
- Sequential 128KB Write (up to): 2000 MB/s
- Random 4KB Read (up to): 750,000 IOPS
- Random 4KB Write (up to): 300,000 IOPS
- Read/Write latency: 120/30us at QD1 (typical)
Reliability: MTBF 2 million device hours, UBER: <1 sector per 10^17 bits read, End-to-end data protection, Temperature Protection, Enhanced power-loss data protection, SMART monitoring, Bad block management, Wear-leveling.
Endurance: PBW (Petabytes Written): 2.4TB = 9.6 PBW
Pricing: Micron's 9100 MAX is set to retail for approximately $1.35 per gigabyte.
Test System Setup and Testing Methodology
Jon's Enterprise SSD Review Test System Specifications
- Motherboard: ASRock Rack EPC612D8A-TB (Intel C612 chipset) - Buy from Amazon
- CPU: Intel Xeon E5-2699 V3 18 Core 36 Thread - Buy from Amazon
- Cooler: Supermicro Air Cooling
- Memory: Samsung 64GB DDR4 ECC 2133MHz - Buy from Amazon
- Video Card: Onboard Video
- Power Supply: Seasonic Platinum 1000 Watt - Buy from Amazon
- OS: Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 64 Bit - Buy from Amazon
- Drivers: Micron Proprietary NVMe driver
We would like to thank ASRock Rack, Crucial, Intel, Samsung, Seagate, and Seasonic for making our test system possible.
TweakTown's Enterprise SSD testing methodology replicates typical enterprise workload environments as closely as possible. Our test systems use strictly enterprise based hardware. Enterprise chipsets, Intel Xeon processors, ECC DRAM, and standard air-cooling. Storage drivers are Windows standard drivers, except as otherwise required for the test device to operate as designed.
TweakTown strictly adheres to industry-accepted Enterprise Solid State Storage testing procedures. Each test we perform repeats the same sequence of the following four steps:
- Secure Erase SSD
- Write entire capacity of SSD a minimum of 2x with 128KB sequential write data, seamlessly transition to next step
- Precondition SSD at maximum QD measured (QD32 for SATA, QD256 for PCIe) with the test specific workload for a sufficient amount of time to reach a constant steady-state, seamlessly transition to next step
- Run test specific workload for 5-minutes at each measured Queue Depth, record results
We chart workload preconditioning IOPS or MB/s and latency for each specific test. We plot workload preconditioning using scatter charts with each recorded 1-second data point represented on the chart, allowing us to see some of the performance variability exhibited by our test subjects. We chart workloads using line charts plotting average workload IOPS or MB/s and latency at each measured QD. Utilizing line charts provides a good visual perspective of the test subject's performance curve.
To summarize, we test with Enterprise hardware, Windows Server Operating System, and we strictly adhere to industry-accepted Enterprise SSD testing procedures. Our goal is to provide results that are consistent, reliable, and repeatable.
Benchmarks - 4K Random Write/Read
4K Random Write/Read

We precondition the drive for 16,000 seconds, or 4.44 hours, receiving performance data every second. We plot this data to observe the test subject's descent into steady-state. We plot both IOPS and Latency. We plot IOPS (represented by blue scatter) in thousands and Latency (represented by orange scatter) in milliseconds. We observe steady-state is achieved at 4,000 seconds of preconditioning. Average steady-state write performance at QD256 is approximately 310K IOPS.


With our configuration, we are able to exceed Micron's 4K random write factory specification of 300,000 IOPS at QD16-256. This is unprecedented pure 4K random write steady-state performance; double that of the next closest contender in our test pool. The XC100E5C delivers 4k random write performance that exactly matches that of Samsung's XS1715. The results of this test clearly display the malleable nature of Microsemi ASIC controlled SSDs through proprietary firmware, software optimizations and flash array configuration. The XS1715, XC100E5C, and 9100 MAX employ essentially the same controller.


The 9100 MAX trails the field slightly at QD8-32. Samsung's XS1715 leads the field from QD8-64. Intel's dual controller DC P3608 running in RAID 0 outperforms the competing drives in our test pool at QD128-256. It is worth noting that the DC P3608 occupies eight PCIe lanes. The 9100 MAX picks up steam at QD128, surpassing the XC100E5C; at QD256 the 9100 MAX surpasses the XS1715. At its peak performance (QD256), the DC P3700 trails the 9100 MAX by approximately 280K IOPS.
Conclusion (TL;DR): The 9100 MAX wows with its incredible pure 4K random write performance; crushing the competing drives in our test pool.
Benchmarks - 8K Random Write/Read
8K Random Write/Read

We precondition the drive for 16,000 seconds, or 4.44 hours, receiving performance data every second. We plot this data to observe the test subject's descent into steady-state. We plot both IOPS and Latency. We plot IOPS (represented by blue scatter) in thousands and Latency (represented by orange scatter) in milliseconds. We observe steady-state is achieved at 5,000 seconds of preconditioning. Average steady-state write performance at QD256 is approximately 156K IOPS.


8K random is a more demanding workload than 4K. No surprise here, the 9100 Max eviscerates the competing drives in our test pool, cutting through this demanding test with ease. Of the drives in our test pool, Intel's DC P3700 is the 9100 MAX's closest competition with 94% less performance than the 9100 MAX at QD256. The XC100E5C and XS1715 don't follow the same performance curve this time. The XC100E5C leads the XS1715 from QD16-QD256. The XC100E5C sports the same Microsemi controller as the 9100 MAX, but it is outperformed by the 9100 MAX by a massive 167%.


The 9100 Max trails the field at QD8-16. At QD32 -256 the 9100 Max begins to separate itself from Intel's DC P3700. At QD256, the 9100 Max extends its lead over the DC P3700 to 116K IOPS. Samsung's XS1715 leads the field up to QD32. At QD64 and beyond, the dual controlled DC P3608 flexes some muscle; leading all three Microsemi powered SSDs by roughly 104K IOPS.
Conclusion (TL;DR): The 9100 MAX again wows with incredible pure 8K random write performance.
Benchmarks - 128K Sequential Write/Read
128K Sequential Write/Read

We precondition the drive for 6,500 seconds, or 1.8 hours, receiving performance data every second. A sequential steady-state is achievable in a much shorter span of time than a random steady-state. We plot both MB/s and Latency. We plot MB/s using blue scatter and Latency using orange scatter. We observe that steady-state is achieved at 0 seconds of preconditioning, indicating that the previous 2x LBA fill phase achieved a sequential steady-state.
The 9100 MAX is performing well above its factory sequential steady state write specification of 2000 MB/s. We observe a small number of tightly bound outliers. However, even the outliers are all above factory sequential write specification. Average steady-state write performance at QD256 is approximately 2300 MB/s.


Micron's 9100 MAX shows off some more of its write prowess, again dominating the field from QD8-256. Overall write performance at this level is unprecedented as far as we know. Our combined write results to this point indicate that if even a small dose of write is mixed into a workload, the 9100 MAX will deliver best-in-class performance. The 9100 MAX easily outperforms its closest competitors; the DC P3608 and DC P3700. The XC100E5C shares a similar hardware configuration with the 9100 MAX however, the 9100 MAX outperforms XC100E5C by 750 MB/s.


Intel's dual controlled DC P3608 in RAID 0 mode easily wins this test. The 9100 MAX and the XC100E5C battle it out for second place at QD64-256. Overall though, the XC100E5C outperforms Micron's 9100 MAX with a pure 128K sequential read workload.
Conclusion (TL;DR): The similarly configured Techman XC100E5C slightly outperforms the 9100 MAX with pure sequential read workloads. The 9100 MAX takes the competition to the woodshed with a pure sequential write workload.
Mixed Workload Benchmarks – Email Server
Email Server

We precondition the drive for 16,000 seconds, or 4.44 hours, receiving performance data every second. We plot this data to observe the test subject's descent into steady-state. We plot both IOPS and Latency. We plot IOPS (represented by blue scatter) in thousands and Latency (represented by orange scatter) in milliseconds. We observe steady-state is achieved at 7,000 seconds of preconditioning. Average steady-state workload performance at QD256 is approximately 208K IOPS.


An Email Server workload is a demanding 8K test with a 50 percent R/W distribution. This application gives a good indication of how well a drive will perform in a write heavy workload environment.
The competing drives in our test pool provide no competition at all. As we speculated, when writes are added into the mix, the 9100 MAX delivers best-in-class performance. Compared with the similarly configured XS1715 and XC100E5C, the 9100 MAX is delivering 120% more performance at QD256. Intel's DC P3700 takes second place at QD8-64, the DC P3608 at QD128-256.
Conclusion (TL;DR): Micron's 9100 MAX delivers best-in-class mixed workload performance, in fact; it's a whole new level of performance.
Mixed Workload Benchmarks - OLTP/Database
OLTP/Database

We precondition the drive for 16,000 seconds, or 4.44 hours, receiving performance data every second. We plot this data to observe the test subject's descent into steady-state. We plot both IOPS and Latency. We plot IOPS (represented by blue scatter) in thousands and Latency (represented by orange scatter) in milliseconds. We observe steady-state is achieved at 7,000 seconds of preconditioning. Average steady-state workload performance at QD256 is approximately 246K IOPS. We observe an extremely tight consistent pattern from the 9100 MAX.


An On-Line Transaction Processing (OLTP) / Database workload is a demanding 8K test with a 66/33 percent R/W distribution. OLPT is online processing of financial transactions such as credit cards and high-frequency trading in the financial sector. Database workloads are challenging for any storage solution.
In terms of pecking order, this test follows exactly what we saw from our email workload testing. Micron's 9100 MAX again eviscerates the competing drives in our test pool. The DC P3700 delivers the second best performance from QD8-64, the DC P3608 from QD128-256. Samsung's XS1715 edges out the XC100E5C at QD8-16. At QD32-128, the XC100E5C takes the lead over Samsung's XS1715; both drives deliver identical performance at QD256.
Conclusion (TL;DR): The 9100 MAX delivers best-in-class mixed workload performance.
Mixed Workload Benchmarks - Web Server
Web Server

We precondition the drive for 16,000 seconds, or 4.44 hours, receiving performance data every second. We plot this data to observe the test subject's descent into steady-state. We plot both IOPS and Latency. We plot IOPS (represented by blue scatter) in thousands and Latency (represented by orange scatter) in milliseconds. We precondition the test subject with an inverse 100% random write workload. We observe steady-state is achieved at 5,000 seconds of preconditioning.

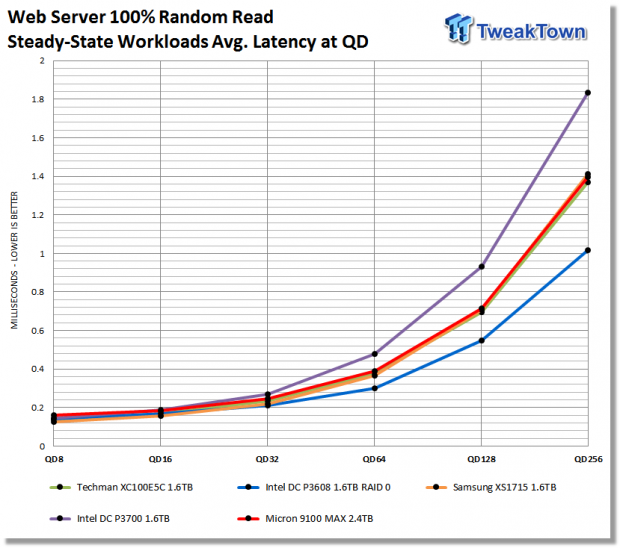
The Web Server workload is a pure random read test with a wide range of file sizes. Our test consists of the following file sizes and corresponding percentage of the overall 100 percent workload file size: 512B = 22 percent, 1KB = 15 percent, 2KB = 8 percent, 4KB = 23 percent, 8KB = 15 percent, 16KB = 2 percent, 32KB = 6 percent, 64KB = 7 percent, 128KB = 1 percent, and 512KB = 1 percent.
With a 100% random read workload, Intel's dual controller DC P3608 configured as a RAID 0 volume handily outperforms the competing drives in our test pool. The 9100 MAX outperforms Intel's DC P3700, but that's it; showing that a pure read workload does not land in the 9100 MAX' wheelhouse. Samsung's XS1715 delivers, overall, the second best performance and even leads the DC P3608 at QD8-16. At QD256, second place goes to the XC100E5C, the 9100 Max slips into third place, and the XS1715 into fourth.
Conclusion (TL;DR): The only time any SSD in our test pool can outperform Micron's 9100 MAX is with a 100% read workload.
Final Thoughts

Micron has been a bit late to throw their hat into the NVMe ring. We can't help but wonder if they were just biding their time, waiting for the right moment to drop a bomb on the competition. Whether or not this is the case we do not know, but our testing clearly shows that the 9100 MAX is overall the best performing Enterprise SSD to ever grace our test bench. Micron's 9100 MAX, as far as we are able to discern, owes its overwhelming performance advantage to an unprecedented amount of overprovisioning. Does overprovisioning make that big of a difference? You bet it does. This is a clear case of Micron tossing a bunch of flash into the battle and coming away with a decided victory. You can do this when you own the NAND fab.
We did not find a warranty period listed in the documentation we were given, so we inquired and were informed that the 9100 series carries a three-year warranty, but Micron bases their warranty more on TBW because the 9100 series is focused more on the hyperscale market where they have on average a 3-year refresh cycle. This is of course a consideration that should be factored into any purchase, but consider the following: Looking at our mixed workload results, we see that the 9100 MAX delivers about double the IOPS of similarly configured competing solutions at QD256. This means that in a 3-year time span, the 9100 MAX will deliver more total IOPS in a typical mixed workload environment than similarly configured competing solutions will in 5 years. Additionally, the 9100 MAX is priced significantly lower per gigabyte than any similarly configured/performing Enterprise SSD we are aware of.
Micron's 9100 MAX now wears the Enterprise SSD performance crown. A bit late to the game, but doing it better than anyone else earns the Micron 9100 MAX 2.4TB Enterprise SSD a well-deserved TweakTown Editor's Choice Award.
Pros:
- Available as HHHL AIC and U.2 versions
- Sequential Write
- Random Write
- Data Protection Scheme
Cons:
- None

| Performance | 99% |
| Performance Consistency | 98% |
| General Features | 98% |
| Value for Money | 99% |
| Quality, Design, Build and Warranty | 98% |
| Overall | 98% |
The Bottom Line: Micron's 9100 MAX 2.4TB is overall the best performing enterprise SSD we've tested to date. Priced at just $1.35 per GB, it is also the best value we've seen to date.
PRICING: You can find products similar to this one for sale below.
 United
States: Find other tech and computer products like this
over at Amazon.com
United
States: Find other tech and computer products like this
over at Amazon.com
 United
Kingdom: Find other tech and computer products like this
over at Amazon.co.uk
United
Kingdom: Find other tech and computer products like this
over at Amazon.co.uk
 Australia:
Find other tech and computer products like this over at Amazon.com.au
Australia:
Find other tech and computer products like this over at Amazon.com.au
 Canada:
Find other tech and computer products like this over at Amazon.ca
Canada:
Find other tech and computer products like this over at Amazon.ca
 Deutschland:
Finde andere Technik- und Computerprodukte wie dieses auf Amazon.de
Deutschland:
Finde andere Technik- und Computerprodukte wie dieses auf Amazon.de
What's in Jon's PC?
- CPU: AMD Ryzen 7800X 3D
- MOTHERBOARD: GIGABYTE AORUS Master X670E
- RAM: Kingston Fury Renegade 7200MHz 32GB
- GPU: ZOTAC AMP Extreme GeForce RTX 4090
- SSD: Crucial T700 2TB Gen5
- OS: Windows 11 Pro
- COOLER: Lian Li Galahad 360 AIO
- CASE: Lian Li Lancool III
- KEYBOARD: Corsair K65 RGB Mini
- MOUSE: SteelSeries AEROX 5 Wireless
- MONITOR: ASUS ROG Strix PG27AQN 360Hz 1440p ULMB2
Related Tags

